Start – stopping milking for a certain period of time before calving. The period when a cow is about to start is called dry period; the animal’s body gains strength before giving birth. Every farmer should know how to properly start a cow before calving in a gradual or forced way, since the manipulations performed affect the health of the newborn calf and milk yield.
General rules for caring for animals
Milk production is stopped using a set of measures:
- changing your diet;
- reducing drinking portions;
- gradual cessation of milking;
- reducing the duration of grazing in spring and summer.
The recommended start time is the winter months. In winter, for natural reasons, the diet of cattle is poorer than in summer; animals consume less liquid, as a result, it is possible to start a cow faster and easier. During the dry period, livestock should be kept in a dry and warm room. If the launch falls on summer days, then the duration of grazing should be no more than 4 hours a day.
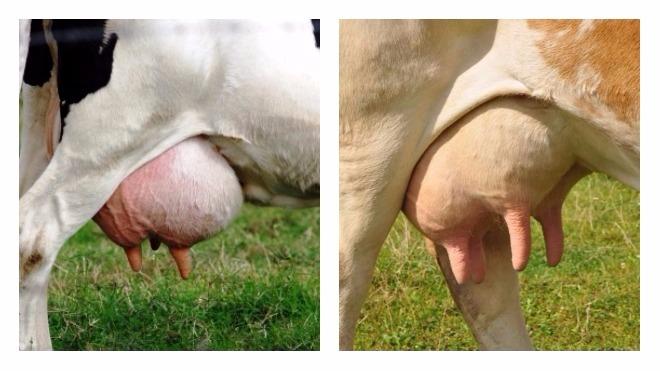
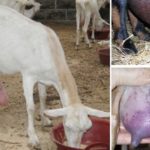
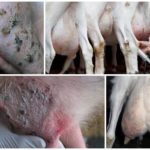
It is extremely important to monitor the health of the cow's udder during the dry period. It must be regularly inspected, palpated, washed, and massaged before milking to prevent stagnation of milk. Such manipulations reduce the likelihood of developing mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland due to congestion.
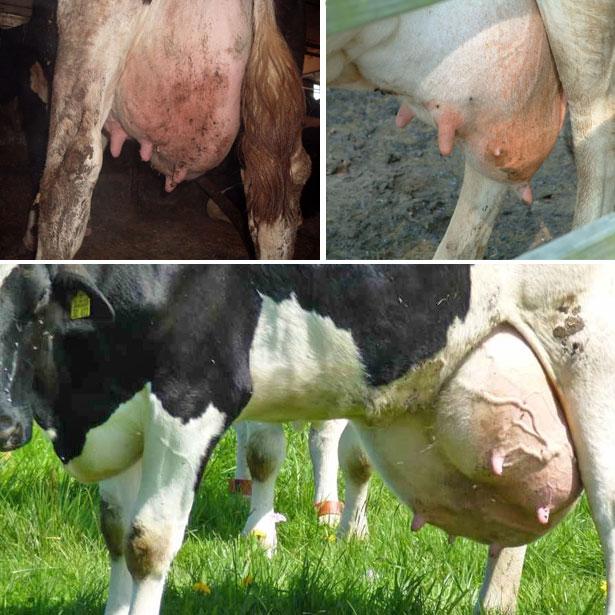
Mastitis during the dry period is a common occurrence. Symptoms are swelling, redness, hardening, soreness of the udder, curdled or flaky inclusions in the milk, purulent and bloody discharge from the nipples. The cow becomes lethargic, refuses food, and her body temperature rises. The farmer must call a veterinarian immediately.
Pre-launch factors
For each cow, the period when it needs to be started is determined individually. The following nuances are taken into account:
- the age and physical condition of the animal;
- estimated calving date;
- milk yield
It is recommended to start a cow pregnant for the first time 3 months before giving birth. A cow who has given birth before usually has 2 months to rest. In animals with average milk yield, milk production stops a week after the start. But for high-yielding individuals, half a month is often not enough. In this case, farmers have to forcefully medicate the cow.A dry cow's udder will shrink, this is normal. Just before birth, it will swell again and fill with milk.
Diet
Cattle's milk yield is determined by diet; milk production is stimulated by a high percentage of wet feed. To start livestock, reduce the formation of milk in the mammary glands:
- significantly reduce the portion of succulent and concentrated food;
- instead of reduced feed, they give more hay;
- reduce the amount of drink.
Pregnant cows are given warm water, heated to a comfortable temperature, 3 times a day. You should not give animals cold or hot water, as this can cause miscarriage. The diet of a dry cow should contain 30-50% succulent and concentrated feed, no more than 50 g of salt.
Milking mode
They stop milking the cow when milk synthesis stops and the udder shrinks. In animals that produce up to 5 liters of milk per day, such changes are noted on the 5th day. But milking is completed on the 7th.
To start cattle, they milk according to the schedule indicated in the table.
| Day | Morning milking | Evening milking |
| 1 | + | + |
| 2 | + | + |
| 3 | + | – |
| 4 | + | – |
| 5 | – | + |
| 6 | – | + |
| 7 | + | – |
Startup process
To start cattle with low or medium milk yields, a natural gradual method is used. A high-yielding cow has to be started using forced medical methods when the natural method does not produce results. Do not be afraid of a decrease in profitability due to the dry period. Downtime will pay off, since a rested and strengthened cow after giving birth will significantly increase milk production.
Gradual
To successfully start a cow gradually, a meager diet based on hay and a small amount of liquid is introduced, and a lactation-reducing milking regimen is used, the diagram of which is given above.
These measures ensure the successful launch of both low-yielding and high-yielding cattle. To start highly productive individuals, the same principle of milking is used, only the change in regime is more extended. In the first few days, milk 2 times a day. When the amount of milk produced decreases, they switch to milking once a day; they milk according to this regimen for 4-7 days. Milking is completed after the cow's udder dries out, when the daily amount of milk released becomes less than 0.5 liters.
Forced
When an animal gives a lot of milk, by the end of the start, lactation decreases, but does not end. A cow that gave 10 liters of milk gives 3-5 liters, that is, her body does not rest until the next calving.
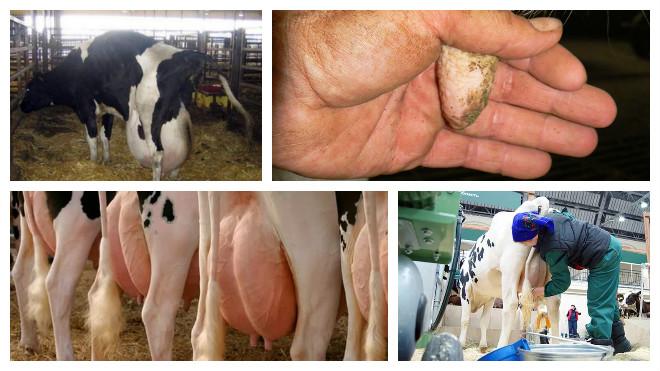
To start a cow and block the functioning of the mammary glands, the following veterinary drugs are used at home:
- "Mastometrin";
- "Orbenin EDC";
- "Nafpenzal DC";
- "Brovamast."
The listed drugs are intended for injection. They not only block lactation, but also reduce the likelihood of developing mastitis during the dry period. The forced method of starting a cow has several advantages:
- provides fast and 100% results;
- convenient for large livestock, where there are many pregnant individuals;
- reduces the likelihood of inflammatory processes in the udder;
- prevents the animal from untimely transition to the dairy-free phase;
- economical (monetary losses are 4 times less compared to a standard launch).
The medicinal method of starting does not mean that you can give up other activities. When using medications, cattle also need to be fed a dry diet and monitor the cleanliness and health of the udder.
Launching cows with high milk production
A cow with average productivity (from 5 liters per day) should be started 2 or 2.5 months before the expected birth. An animal with high milk production (from 10 liters) should be started 3 months before the calf is born.
Regardless of livestock productivity; The dry period should not last less than 40 days.
While cows that produce a little milk only need a week to enter the dry phase, it takes approximately 2 weeks for cattle with average milk production to start. And high-yielding individuals need a long 3-week start, but even this turns out to be ineffective if the milk yield reaches 15 liters per day. The reason is that in such animals milk synthesis decreases very slowly. Then medications are used to stop the functioning of the mammary glands.
The diet is changed immediately. But double milking at high productivity continues for 4-6 days from the start, sometimes even longer. When the daily milk yield is reduced to 3 liters, only then the cow is transferred to the standard transitional milking regime given in the table above. They stop milking highly productive cows, as well as ordinary ones, after the udder has been reduced and the amount of milk produced has been reduced to 0.5 liters.
Consequences of late launch
The sooner you manage to start a cow, the better for her body. But it is unacceptable to do this abruptly. The reduction in milking should be smooth. A late or abrupt start leads to:
- disruption of intrauterine development of the calf;
- reduced milk yield after calving.
The opposite situation also happens: spontaneous launch more than 3 weeks before the expected birth. The phenomenon is rare, associated with the individual characteristics of the animal’s body, usually harmless to the health of both the pregnant individual and the calf developing in the womb. In isolated cases, premature termination of the mammary glands signals illness.
The problem with premature launch is only in shortening the period of milk production, which is unprofitable for the farmer. The owner must identify individuals prone to premature launching after the first calving, and in subsequent pregnancies feed them plenty of succulent food and root vegetables. It is necessary to start a cow correctly and on time, regardless of the chosen method. The health of the calf and the amount of future milk yield depend on the correctness of the measures.