Old cattle breeds, which were bred in past centuries, have not yet lost their relevance and can compete with new varieties on equal terms. The animals are distinguished by their large size, productivity, and rapid weight gain, that is, those characteristics that are valued in farm livestock. Let's consider the description and characteristics of Charolais cows, how to feed and care for animals, and how to treat diseases.
Main characteristics and description of Charolais cows
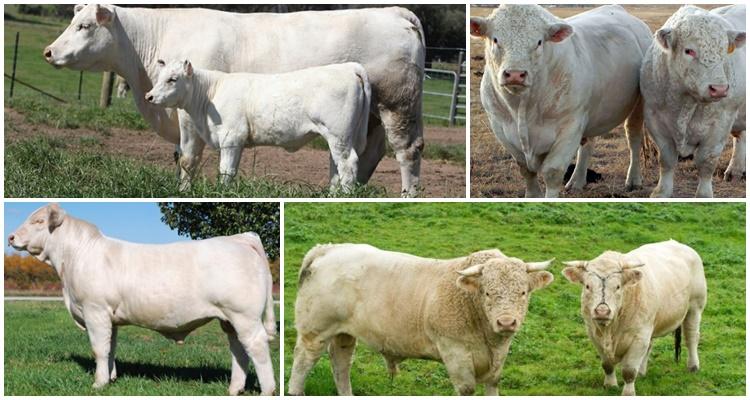
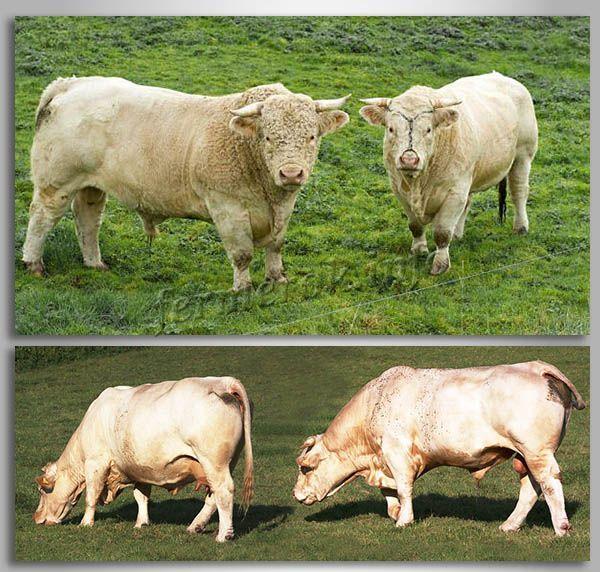
The physique of bulls and cows is massive, with highly developed muscles, the bones are rough, the back is smooth and straight.The animals' heads are medium-sized, with medium-sized horns. The neck is short and massive. The udder of cows is not voluminous. The color of the Charolais individuals is whitish, with a cream tint, and the coat is thin.
The main direction of breeding of the breed is meat, so individuals grow large. The height of Charolais bulls is up to 1.65 m, cows are 1.3-1.55 m. Body length is 2.2 m, chest girth is 1.9 m, width is up to 0.8 m. Calves are born weighing 40 -45 kg, grow quickly, adding 1-2 kg per day. Adult animals gain weight: bulls - 1-1.6 tons (maximum 2 tons), cows, on average, 600-750 kg (maximum 800 kg).
The meat yield of the Charolais breed reaches 65%. The meat is lean, tasty, with good texture. Milk yield is up to 2.5 thousand liters per year. Milk fat content is 4.1%.
How did you appear?
Work on developing the Charolais breed began in the 18th century in France. Animals were selected using the best of the best method from the offspring of local cows and Simmental and Shorthorn bulls. The selection continued until the middle of the next century. Nowadays cattle breeding is carried out on its own; some animals are used to work with other breeds. Animals are hardy and differ in the duration of use. Bulls can be used up to 15 years, females are slightly smaller - up to 13-14 years.
Pros and cons of the breed
Breeding bulls and cows are selected, there is a breeding plan, so finding a purebred animal for raising is not difficult.
However, despite this, the obvious advantages of the breed outweigh the disadvantages.
Maintenance and care
The rules for keeping Charolais cows are not much different from the rules for keeping other breeds of cattle. Bulls and cows need spacious, dry, clean, warm stalls with clean, fresh bedding at all times. It needs to be changed as often as possible, ideally every day. It is especially important that animals are kept warm in winter so that there are no drafts in the barn, which can make the animals sick. The barn needs to be disinfected 2 times a year, treating the walls, floors, and all equipment.
The importance of exercise can hardly be overestimated; without walking, cows are more likely to get colds, grow worse, and productivity decreases. In winter, it is necessary to maintain a sufficient level of lighting; you need to turn on the lights in the barn in the mornings and evenings, so that the total duration of daylight is at least 12 hours. Artificial lighting improves the well-being of animals, increases productivity, and increases the success of insemination.
What to feed
Without proper, complete feeding, you cannot get a good cow. Only if the animal receives plenty of food will it be able to gain weight, which is characteristic of the breed. The diet for Charolais cattle in summer and winter will be different.
During the summer
In late spring and summer, Charolais cows can graze on fresh grass and eat branches of bushes and trees.Bulls, pregnant and lactating cows should be fed with concentrates and root vegetables, and given 1-2 kg of feed per day.
In winter
In winter, the basis of the diet is dry hay. Additionally, you need to provide grain, concentrates, vegetables and root crops, silage, and mixed feed. Both in winter and in summer, it is necessary to give Charolais cows mineral supplements in the form of salt, chalk, and premixes.
Water
Animals should receive water 2-3 times a day, morning and evening. The water should be fresh and clean, the remains should be poured out of the drinking bowls so that the liquid does not stagnate. In winter, you need to heat the water so that the cows drink warm; in the summer, on the contrary, you need to give it cool.
Childbirth and calf
It is noted that Charolais cows can have difficult births, since the calf is born large. Therefore, you need to be present at the birth and, if necessary, help the animal. It is necessary to ensure that the calf drinks colostrum after birth, as this is the key to its future health. Cows accept calves without problems and begin caring for them immediately after birth.
It is recommended that calves be born in late winter or spring, then the babies will be strong, grow, and will not get sick. Calves are left with their mothers for 8-9 months during the grazing season.
For breeding, you need to choose purebred animals, bulls and cows, in order to maintain the purity of the breed. In this case, inbreeding must be avoided, so for mating it is necessary to select males and females belonging to different lines. The sire is used intensively for 2-3 years. When crossing Charolais bulls and female cattle breeds, crosses are obtained that are characterized by accelerated growth, size, weight, and productivity.
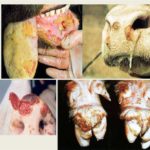
Frequent illnesses
Charolais cows are less likely to suffer from mastitis, since the calves live next to them and drink milk. If the animals are cared for correctly, they are provided with food and kept warm. If they stand in a dry and bright room, go for walks, the animals do not get sick, as they have a strong immune system. Infections appear when Charolais cows are forced to stand in a dirty, damp, cold room and are poorly fed.
Treatment of diseases, as in other cattle breeds, is standard. But in order to prevent the development of diseases, animals are vaccinated and the rules of keeping and feeding are followed.
The Charolais breed of cattle has been bred for 2 centuries. During this period, the variety did not lose the valuable consumer qualities for which it was bred. Livestock breeders are well aware of the virtues of cows. They are massive, large, early ripening. They gain weight, pay for their feed, and provide rich milk. Charolais individuals can be kept in households or on small farms for meat and milk. The duration of keeping and using individuals is 15 years, which is considered a long period for cattle.