Horse breeders know that the keys to horse health are proper care and a nutritious diet. But in most cases, it is not possible to completely avoid injuries and illnesses. Shared housing, infections, errors in nutrition, and body characteristics lead to the fact that horses sometimes get sick. Let's look at what diseases horses suffer from and what treatment is required.
- Common signs of illness in horses
- Classification of diseases
- Infectious diseases of horses
- Glanders
- Wash
- Horse flu
- Rhinopneumonia
- Infectious anemia
- Infectious encephalomyelitis
- anthrax
- Rabies
- Tuberculosis
- Pasteurellosis
- Leptospirosis
- Listeriosis
- Smallpox
- Salmonellosis
- Non-communicable diseases of horses
- Respiratory diseases
- Digestive pathologies
- Colic
- Invasive diseases
- Incidental disease
- Piroplasmosis
- Worms
- Scabies
- Diseases of the joints and hooves
- Tendon sprain
- Corolla serif
- Capelet
- Zakovka
- Hoof crack
- Laminitis
Common signs of illness in horses
A healthy horse is distinguished by an excellent appetite, liveliness, good mood, and joy from communicating with people. Diseases have different symptoms; only an experienced veterinarian can identify the pathology. There are a number of signs that may indicate that something is wrong with the animal:
- change in behavior - the appearance of anxiety or indifference and lethargy;
- dulling of fur, mane, excessive hair loss;
- rise in temperature;
- discoloration of mucous membranes, dull eyes;
- loss of appetite, refusal of favorite food.
You can guess about problems with legs and hooves by lameness and reluctance to run. With pathologies of the digestive tract, diarrhea may begin. A number of diseases are accompanied by breathing problems, shortness of breath, and rapid heartbeat. Grooms who constantly interact with animals usually quickly notice that their pet is having problems.
Classification of diseases
All equine diseases are divided into several groups according to the methods of development and damage:
- infectious – caused by bacteria, viruses;
- invasive – infection by parasites;
- non-infectious – gastrointestinal diseases, colds;
- skin;
- diseases of the limbs - hooves, joints.
For horse breeders, an essential feature is contagiousness, that is, the infectious nature of the disease. In this case, the horse must be urgently isolated to prevent the spread of the disease throughout the livestock.
Infectious diseases of horses
Contagious diseases must be identified quickly so that all horses on the farm are not affected.A number of diseases can be transmitted to humans.
Glanders
The causative agent is the bacterium Pseudomonas mallei. The bacterium multiplies in the lymph nodes, then spreads through the blood to the organs, causing multiple glanders and ulcers. The lungs, skin, and nasal mucous membranes are affected. Symptoms include rapid breathing, muscle tremors, weight loss, fever. There are no effective drugs, the horse dies.
Wash
The disease is caused by streptococcus (streptococcus). Characteristic signs of the disease are inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes, nasal and oral mucous membranes with suppuration and abscesses. Foals and young animals under 5 years of age are most often affected. The horse has difficulty swallowing due to inflammation of the pharynx, coughing, and swelling of the submandibular area. Treatment is a course of antibiotics, opening of abscesses.
Horse flu
Influenza is associated with horses catarrhal symptoms - coughing, mucus, sneezing, as well as fever. In severe cases, pneumonia develops. The disease is widespread, affecting horses of any age. Treatment is based on symptoms. Vaccination helps reduce risks.
Important: in case of infections, strict isolation of the sick horse, treatment of the stable with disinfectants, and regular inspection of the entire livestock are required.
Rhinopneumonia
The causative agent is equine herpesvirus. Young animals under one year of age are most often affected. Symptoms: conjunctivitis, respiratory tract catarrh, fever. The abortive form of rhinopneumonia leads to spontaneous abortions in mares or death of foals on the first day. Treatment is based on symptoms, medications to improve cardiac activity. Vaccinations provide short-term immunity.
Infectious anemia
The viral disease affects the hematopoietic system and is accompanied by fever, anemia, cardiac dysfunction and respiratory disorders in horses. Hemorrhage develops on internal and external organs.
Infectious encephalomyelitis
The causative agent is a virus that leads to damage to the central nervous system, atonic disorders of the digestive tract, and jaundice. Animals experience paresis, paralysis, and motor dysfunction. The disease has a seasonal course, most often occurring in autumn and spring. There is no specific treatment.
anthrax
The most dangerous and fast-acting of the infectious diseases of horses, which also affects humans. It is characterized by a severe form of septicemia, the formation of tissue edema, carbuncles, damage to the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. The incubation period is 1-3 days. Horses often develop a fulminant form with death within a few hours.
Rabies
The disease is caused by a special virus transmitted in saliva during the bite of a sick animal. Symptoms – the disease starts with an increase in temperature, continues with reflex excitability, reaction to light and noise. Riotousness and aggression alternate with apathy.
Animals die in 100% of cases from paralysis of the respiratory system (suffocation).
Tuberculosis
The disease is caused by mycobacterium. It occurs infrequently in horses; its course is latent and chronic. The animal loses weight, symptoms appear when a certain organ is damaged. A sick animal is slaughtered. For prevention, tuberculin tests are regularly done.
Pasteurellosis
Symptoms are fever, inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, arthritis, osteomyelitis. Young horses are more likely to suffer from the disease. Treat with polyvalent serum, antibiotics of a number of penicillins, sulfonamides.
Leptospirosis
U horses' temperature rises sharply, signs of jaundice, conjunctivitis, swelling of the eyelids, iridocyclitis, colic, swelling of the legs appear. For treatment, hyperimmune serum and Streptomycin are used.
Listeriosis
The bacterial infection comes in many forms, with symptoms ranging from photophobia and diarrhea to miscarriages in mares. The drugs are tetracycline antibiotics. Treatment is effective only in the early stages.
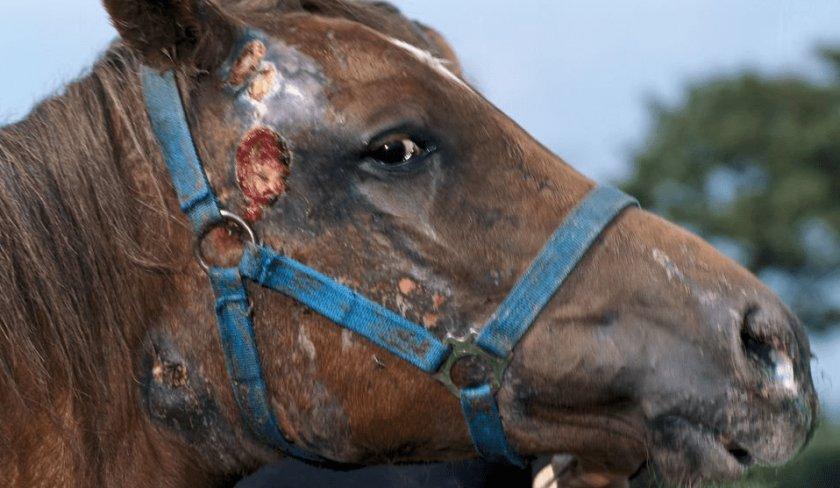
Smallpox
The cause is the smallpox virus. Symptoms include stomatitis, dermatitis with ulcers, lameness if the blisters are localized on the legs. Smallpox is treated with antibiotics, and gamma globulins are used to prevent inflammation. The ulcers are treated with emollient and cauterizing solutions. Immunity is lifelong.
Salmonellosis
With salmonellosis, there are signs of diarrhea, blood in the stool, fever, and lethargy. In the chronic course - cough, shortness of breath, swelling of the joints. Treatment is complex - sulfonamides, nitrofurans, and other antibiotics.
Non-communicable diseases of horses
Non-contagious diseases include a large group of diseases that do not require quarantine measures and strict isolation of the horse.
Respiratory diseases
Sneezing, coughing, and nasal discharge are signs of respiratory diseases. They may be of a cold or allergic nature. For treatment, herbal inhalations, expectorants, and bronchodilators are used.
Digestive pathologies
Digestive pathologies are associated with structural features of the gastrointestinal tract in horses and errors in feeding. These include colic, damage and blockage of the esophagus, stool disorders and much more. Treatment is symptomatic.
Colic
Sharp pain in the gastrointestinal tract is caused by food fermentation due to improper feeding, intense training, or due to certain diseases.
The horses' sides are kneaded, massages, enemas, and gastric lavage are given.It is important to normalize your diet.
Invasive diseases
Infection with parasites occurs through contact with a sick animal, through food and water, due to dirt in the stable and insect bites.
Incidental disease
The parasite (trypanosome) is transmitted during mating from a sick animal. Symptoms of infection are the formation of rounded formations, swelling of the genitals, changes in the shape of the croup, weight loss. Naganin, Novarsenol, Azidin-vet are used in treatment.
Piroplasmosis
The disease in horses is caused by the bites of ticks infected with piroplasms. Symptoms: high fever, shortness of breath, yellowing of mucous membranes, brown urine, painful urination. Azidine and Hemosporidine are used for treatment.
Worms
When infected with worms, a horse experiences weight loss, mucus in the stool, diarrhea and constipation. Deworming is carried out - Brovadazole, Brovalzen.
Scabies
When infected with scabies mites, the horse becomes restless, suffers from itching, and has scabs and scabs on the skin. Animals are treated with Wagenfeld ointment and Diazinon solution.
Diseases of the joints and hooves
Diseases of the extremities often develop as a result of injuries, then bacterial and inflammatory processes are added. Inappropriate care and conditions for horses may lead to loss of ability to move.
Tendon sprain
The tendon is damaged when the horse jumps and moves carelessly. No special treatment is required - the horse is given rest, a cold compress on the limb, and motor activity is limited. Use tight bandages on the leg when walking and working.
Corolla serif
The bruised wound is treated with antiseptic agents (iodine), the hair around it is first cut, and the horn of the hoof wall is trimmed.In case of suppuration, surgery is performed and treated symptomatically.
Important: in case of hoof diseases, horses need to be given rest, freed from stress for the entire duration of treatment, and provided with adequate food for recovery.
Capelet
Namins occur due to improper forging and size of the horseshoe, injury to the hooves. It is important to immediately remove the horseshoe, treat it with an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory agents, and ensure the limb remains at rest.
Zakovka
The problem arises when the horse is shoed incorrectly. The nails are removed from the hoof and the horseshoe is removed. For treatment, rinsing with antiseptic agents and a bandage are used.
Hoof crack
Hooves crack under high stress and trauma due to improper shoeing nail thickness. Blood is oozing from the hoof and the horse is limping. It is necessary to free the limb from the horseshoe, treat the wound with iodine, potassium permanganate if there is suppuration.
Laminitis
Inflammation of the lamina (fiscal cartilage) of the hoof leads to swelling of the limb and impaired blood supply. Rotation of the bone increases with movement. Anti-inflammatory drugs (Ainil) and drugs to improve blood circulation in the limbs are used for treatment. It is important to free the animal from stress.
A thoughtful diet, cleanliness in the stable, and careful care reduce the risk of developing diseases in horses. It is important to get vaccinations on time and monitor the condition of horses. Newly arrived animals are quarantined. At the first signs of illness or anxiety in the animal, a veterinarian is invited and treatment is started in order to maintain the health of the horses and prevent material damage on the farm.