The value of beluga fish cannot be overestimated. Gourmets all over the world adore dishes made from its meat and caviar. They are considered delicacies of the highest category. This fish is one of the most expensive in the world. However, due to its large size and high value, its population is now in danger of extinction, and fishing has been banned to preserve this species of fish. Its description and characteristics are truly amazing, because the beluga can rightfully be called a descendant of prehistoric sea inhabitants.
What does a fish look like?
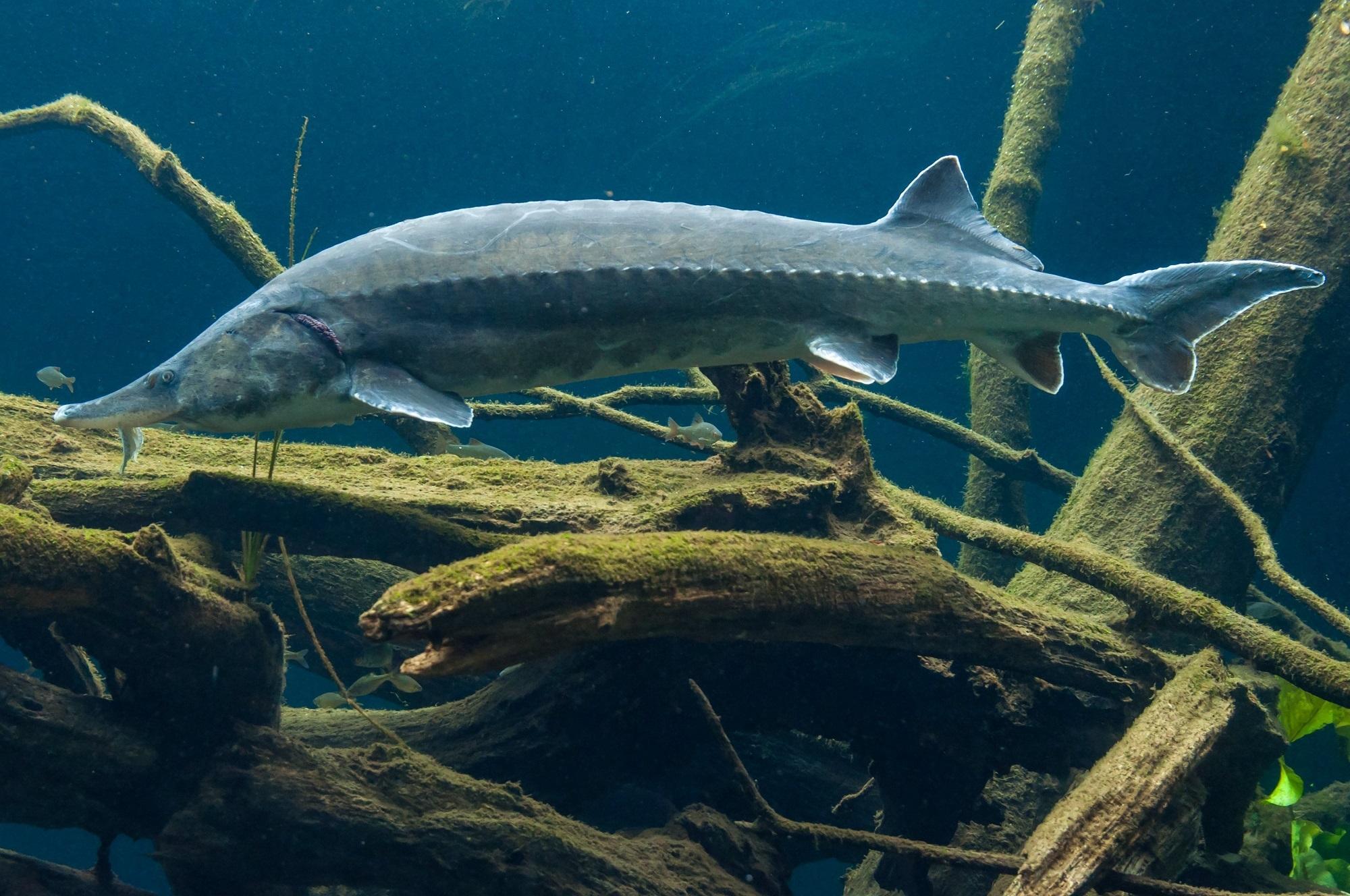
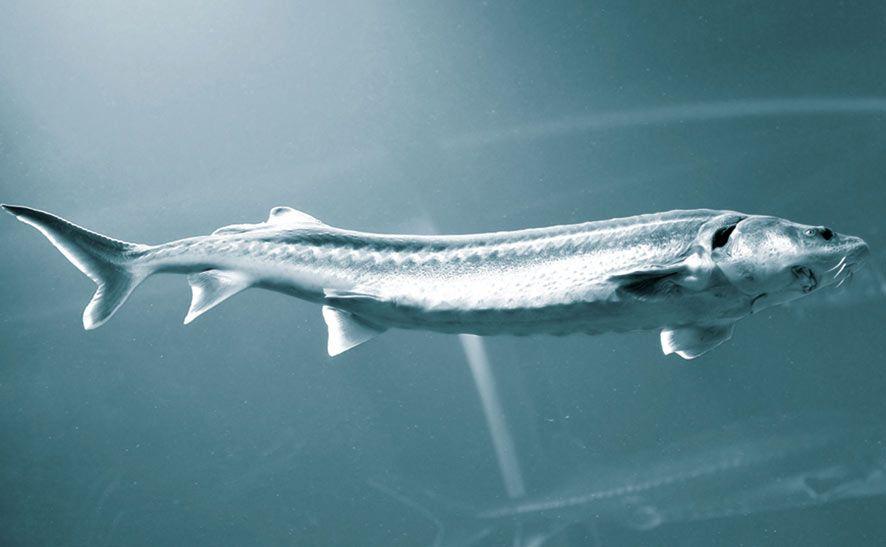
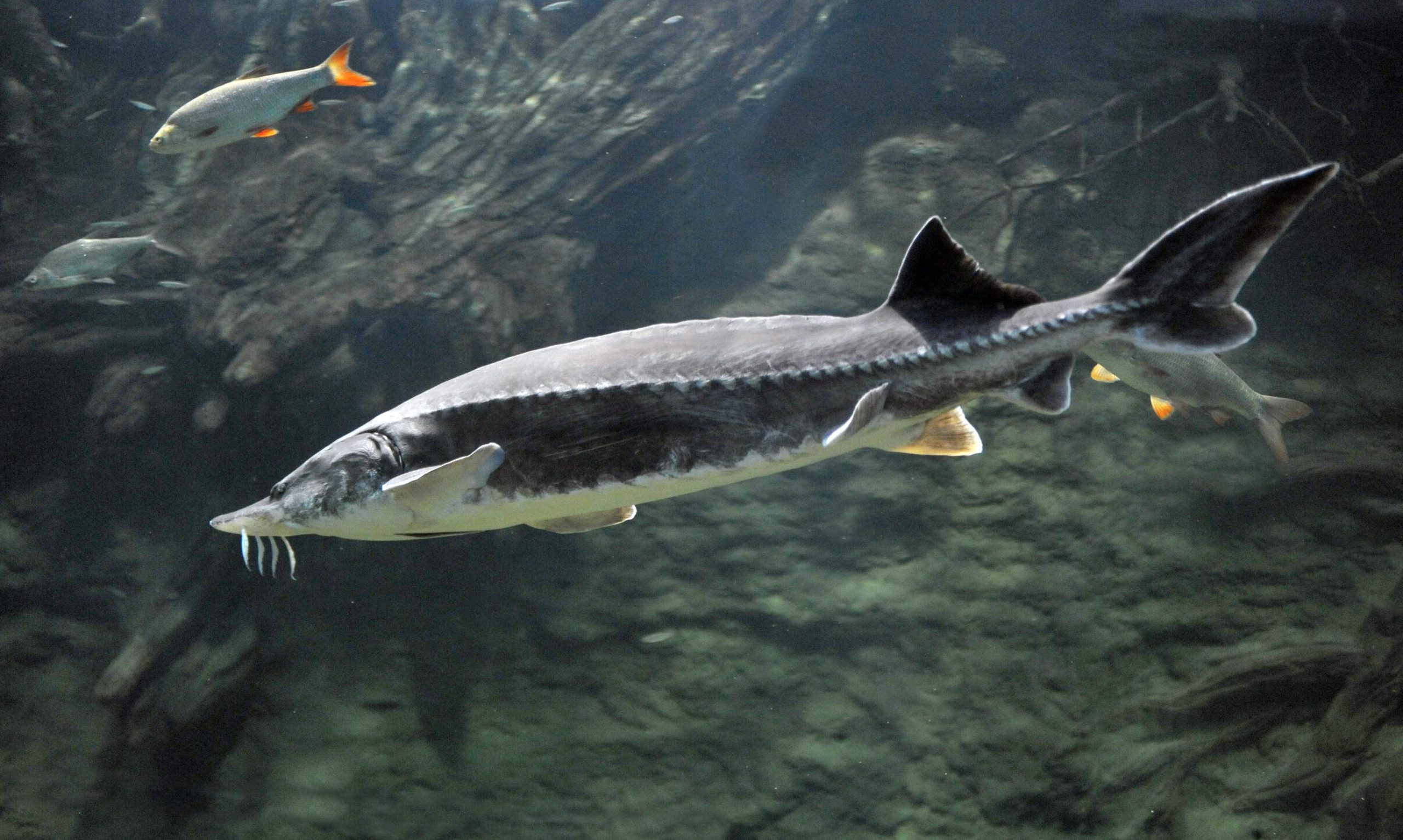
Beluga is the largest fish of the sturgeon family, living in the fresh waters of Eurasia and North America. This fish is known for its excellent meat and is prized as a delicacy.
It has a long and thin body with silvery scales and several pairs of small antennae with which it finds food. The head is quite massive, and it has sharp teeth with which it captures prey. The fish can live for several months without eating, which allows it to survive in low water temperatures.
Head
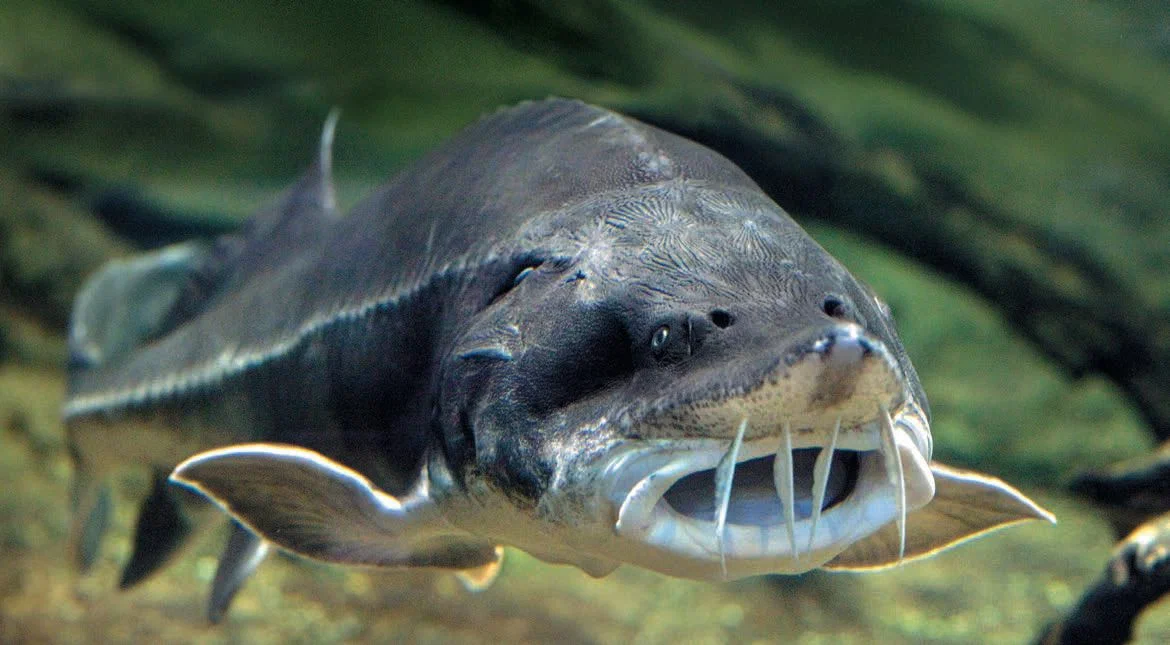
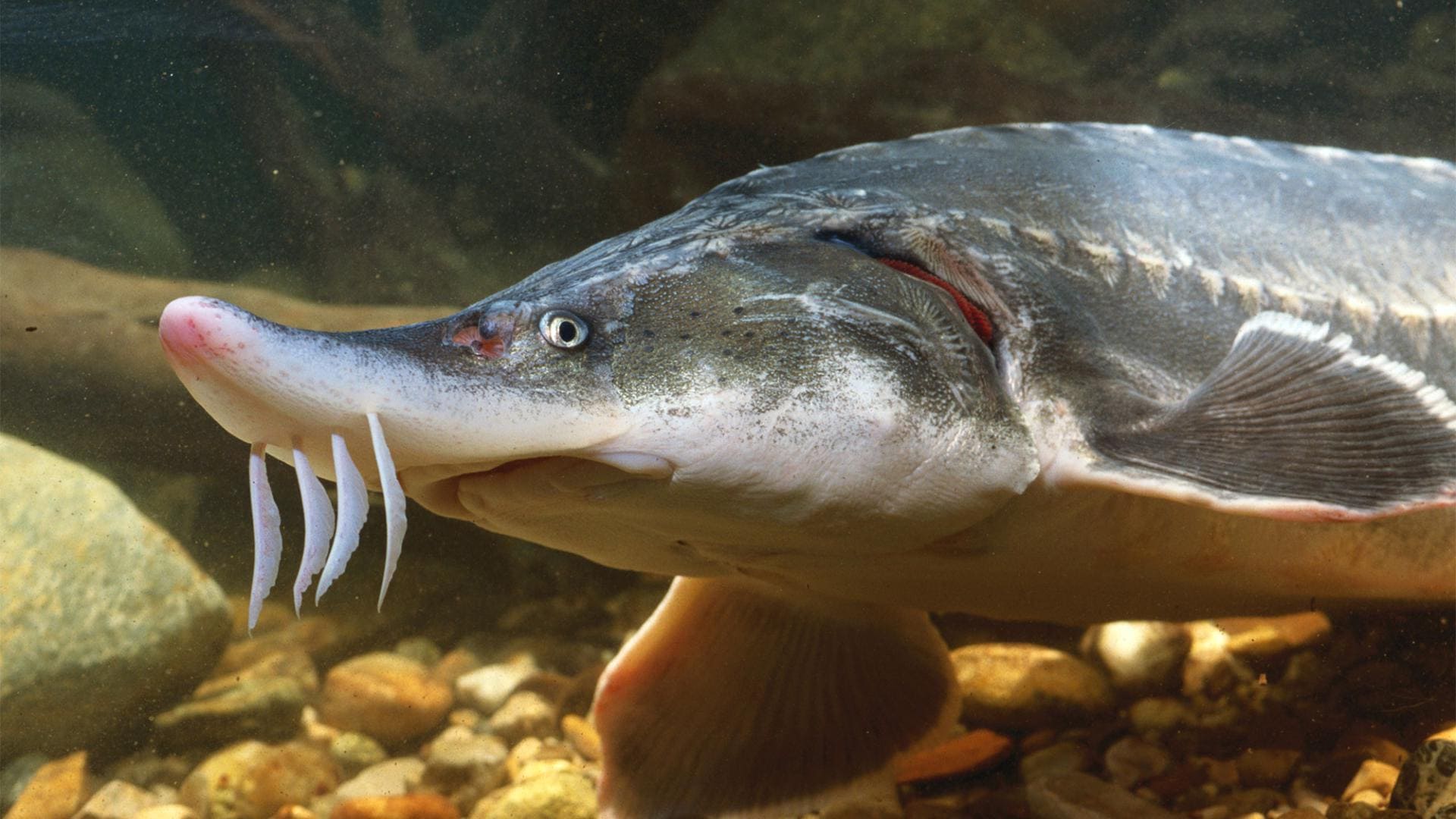
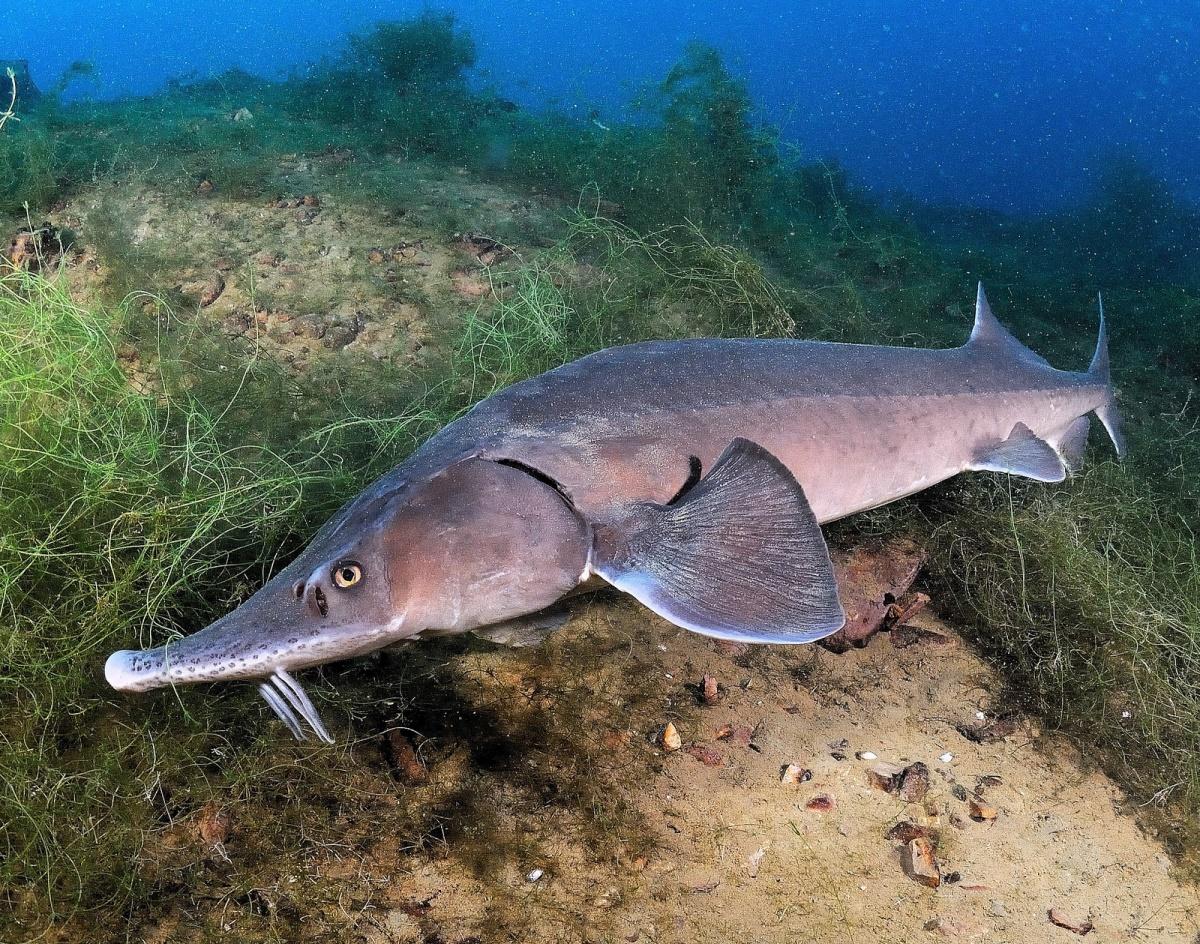
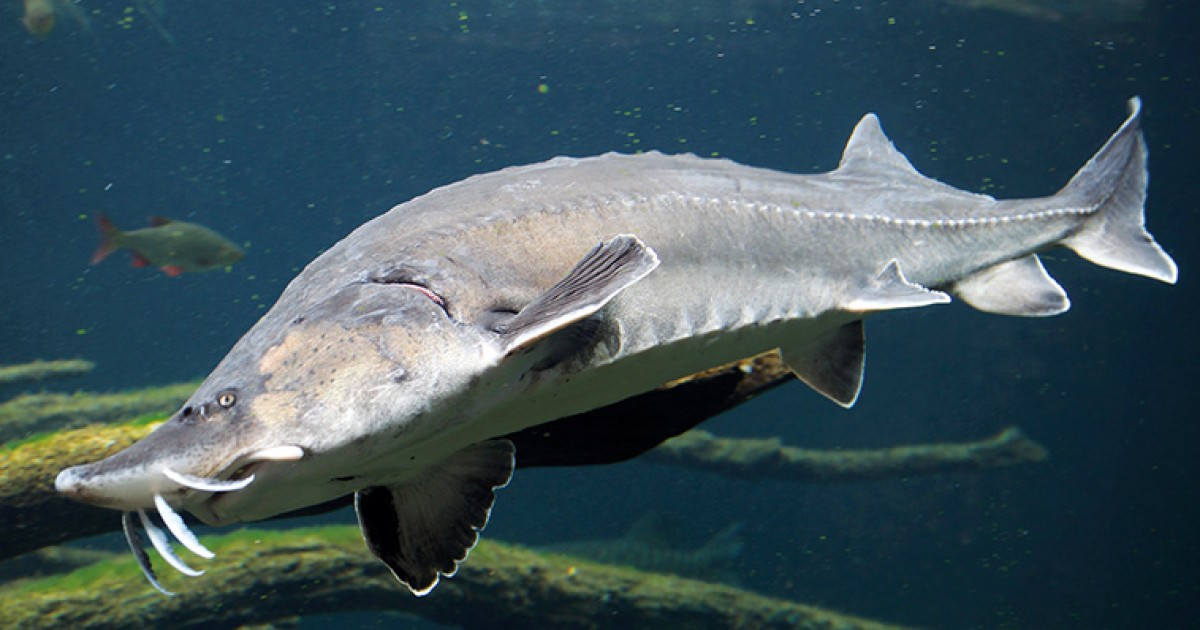
The characteristics of the beluga's head are unique and easily recognizable. Its size seems enormous in combination with its massiveness, and it is significantly wider than the body. At the top of the head is a short, pointed snout. The lateral and upper sides of the snout are soft, not covered with bony scutes. The mouth is located under the snout, and when closed resembles a sickle shape. However, when the mouth opens, it takes on a crescent shape and is framed by thick, fleshy lips. The lower lip is cut into two parts.
The beluga does not have the back of its upper jaw, so it cannot close its mouth completely. Instead, the fish uses the powerful muscles of the tongue and pharynx to capture and grind food.
Below the mouth are four flat antennae with leaf-like appendages. Beluga lacks teeth as adults, but they are present in young fish. The eyes are small and located on the top of the head. The vision of this fish is poorly developed, so its orientation mainly occurs with the help of an acute sense of smell and sensitive antennae near the mouth.
Despite the bulkiness and massiveness of the head, it is very suitable for life in cold waters.It carries a large layer of fat, which regulates body temperature, and the short snout and soft areas make it easy to maneuver in conditions of high hydrodynamic stress caused by strong currents and cold waters.
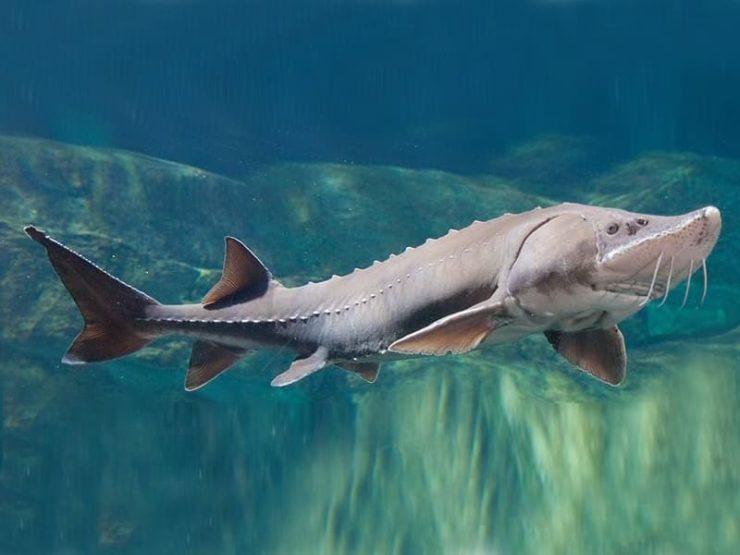
Body
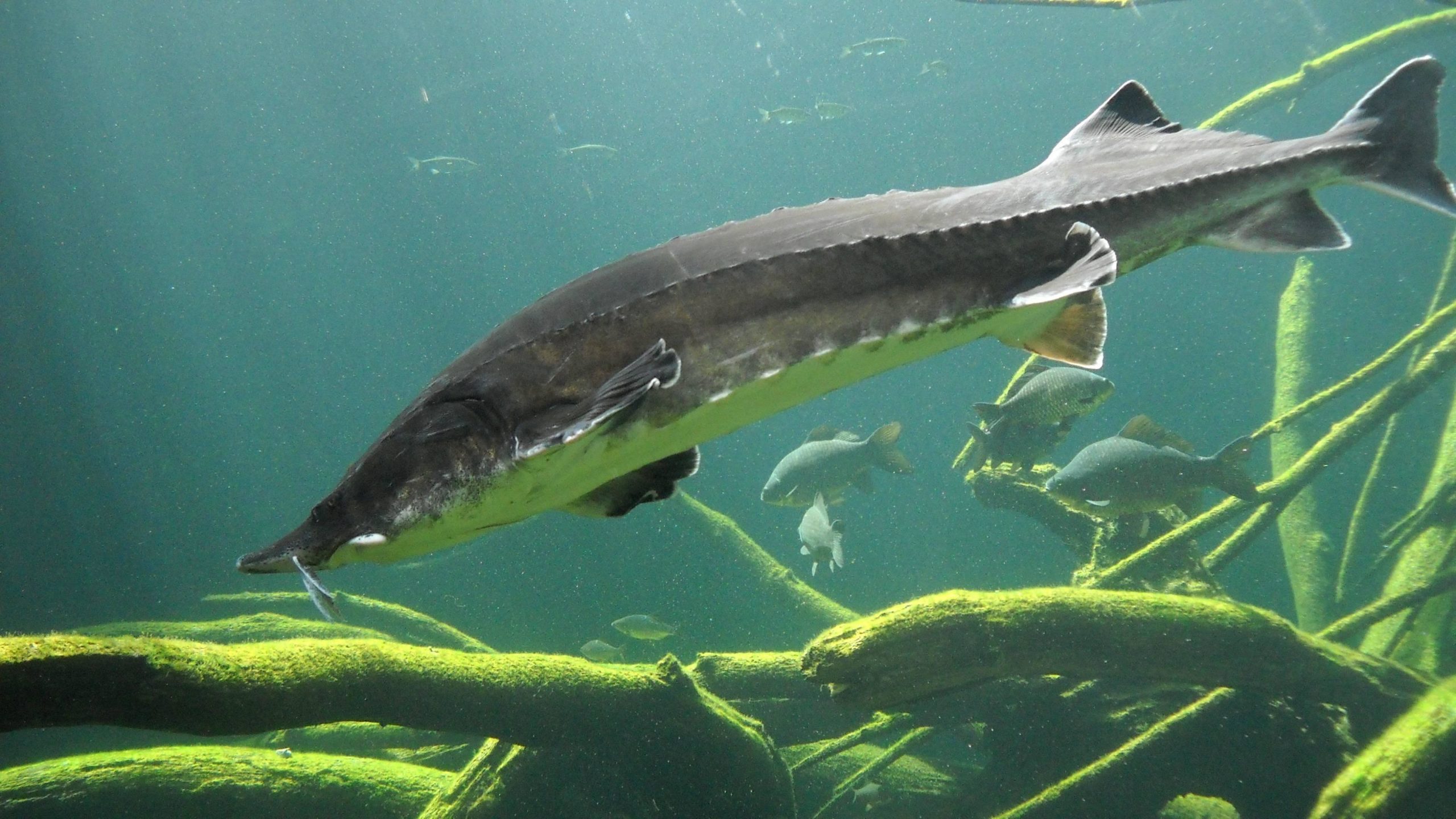
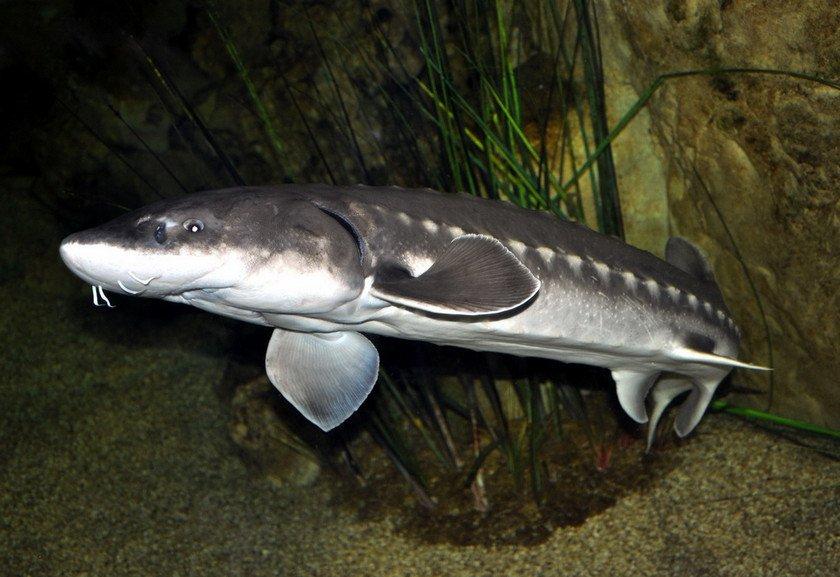
The body of the beluga is long, cylindrical, covered with smooth skin, without scales. It tapers towards the head and tail. The tail is narrow and cone-shaped, which helps the fish swim quickly and maneuverably. The lateral lines of the body, represented by rows of small holes, serve for sensitivity and orientation in water.
Body color can vary, but is usually silver-white or gray. There are often dark spots or stripes of various shapes and sizes on the sides and back. Color may vary depending on the age and habitat of the fish. For example, belugas, which live in cold waters, are dark in color. And those that live in warm waters look lighter.
Their body is covered with bony plates called bugs. There are from 11 to 14 of them in the dorsal row, from 41 to 52 in the lateral rows, and from 9 to 11 on the belly. There are bone grains between the bugs. These plates form a tough armor that protects the fish from predators and other dangers.
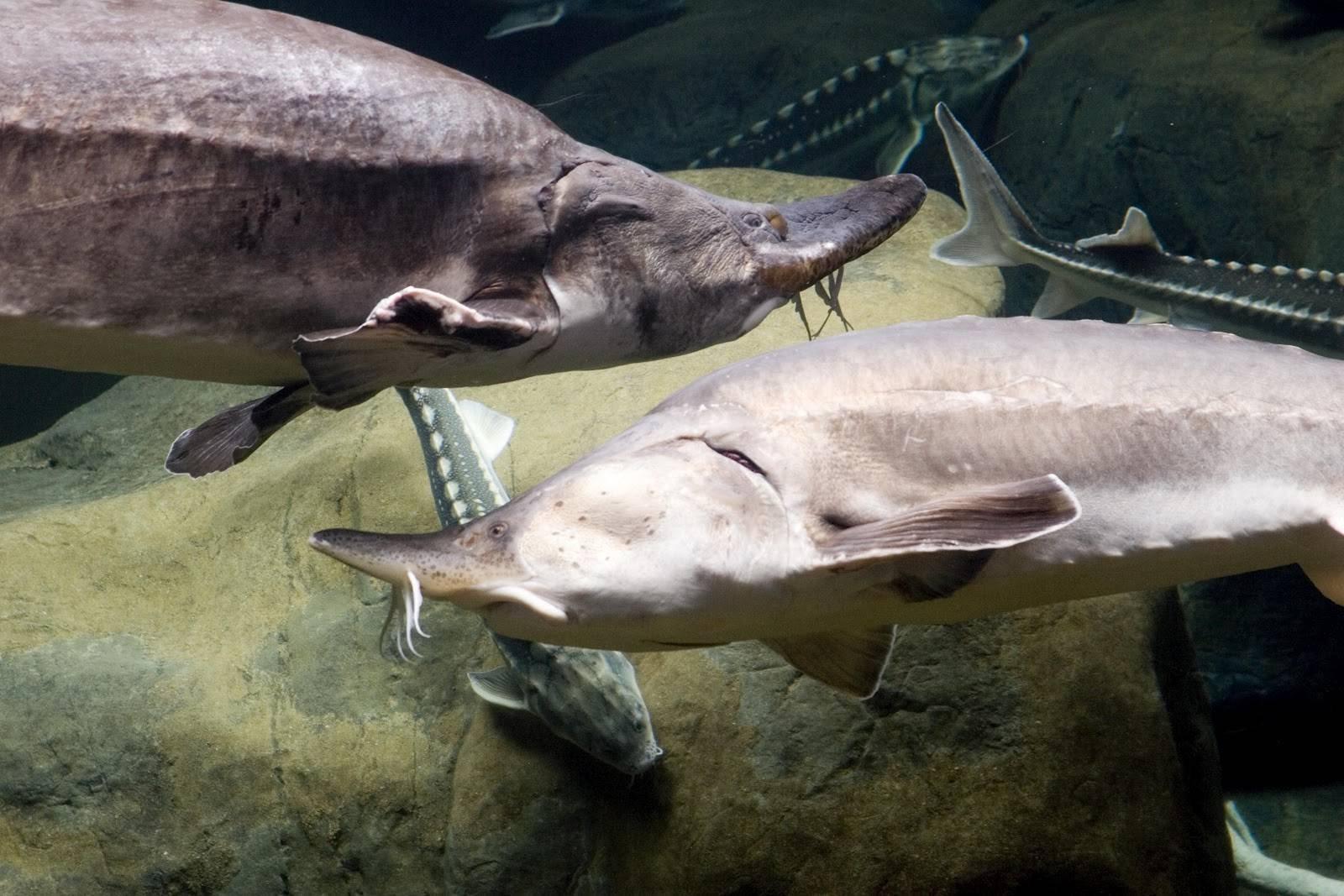
However, unlike other fish, beluga has virtually no pronounced sexual dimorphism. This means that there are no noticeable external differences between males and females, other than some anatomical features.
What size does it reach?
It is one of the largest freshwater fish in the world. An adult beluga can reach impressive sizes, reaching lengths of up to 5 meters and weighing up to 1.5 tons. The largest representatives live in Siberia and the Russian Far East, where they reach a weight of up to 2 tons.
In the last century, there have been cases of beluga caught in the Caspian Sea of impressive weight: in 1922, a fish was caught that weighed 1200 kg, and in 1924 - weighing 1000 kg. However, in our time, the mass of caught specimens has greatly decreased. In the period from 2013 to 2015, several representatives were caught in the Ural River, but their weight did not exceed 125-130 kg.
Moreover, the size of the fish varies depending on the region in which it lives. For example, in some North American rivers, beluga whales tend to be smaller in size, reaching a length of about 2-3 meters.
It is also worth mentioning that the size of the beluga depends on its age. Young beluga whales are usually around 60-80 cm long, and by the time they reach sexual maturity - at about 15-20 years - they can be between 1.5 and 2 meters long and weigh between 20 and 30 kilograms.
Habitat
The beluga's natural range covers marine areas including the Caspian, Azov and Black Seas. During spawning, these fish migrate to the mouths of rivers flowing in these seas and rise up the rivers. Rivers known for finding large numbers of belugas where they can be caught include the Volga, Dnieper, Don and Southern Bug. The Caspian Sea has the largest population of these fish, and they can be found in almost any river belonging to the sea basin.
Previously, they traveled upstream for many hundreds of kilometers, but due to the construction of hydroelectric power stations and reservoirs, their path to natural spawning grounds is closed. In the Black Sea, belugas are found off the coast of Crimea, off the coast of Turkey in the area of the Kyzylyrmak and Yeshilyrmak rivers, and off the Caucasus coast, at the mouth of the Rioni River.
Beluga is a species of fish that has an anadromous life cycle.Some species spend most of their lives in the sea and then move to fresh waters to spawn. Other species live only in rivers and lakes. They live at depths of up to several hundred meters and are often found in areas of strong currents, close to the surface of the water or on the bottom.
The construction of dams and dams has a significant impact on fish populations and their habitat. Beluga prefers to migrate long distances along rivers to spawn and feed, and barriers created by dams and dams interfere with its movement. The water behind dams and dams also heats up and accumulates toxic substances, which negatively affects the beluga population.
Features of fish life
Beluga is a predatory fish of gigantic size that has a complex lifestyle. It is difficult for her to feed herself in the river; she hunts mainly in the sea, where sufficient food is available. Occasionally it enters river mouths in search of food.
Belugas lead a solitary lifestyle if environmental conditions do not allow them to live in groups. During the spawning period, small groups are formed, which consist of 2-3 individuals, sometimes more. In a group, they not only search for food and defend their territories, but are also able to protect each other from predators. They lead an active lifestyle, always in search of food.
In the spring, individuals usually begin to actively move and feed in order to regain strength after hibernation. They become more mobile and often move in search of food. However, like most fish, beluga prefers to be in places with warm water, especially on the coasts, where currents and winds create zones with elevated temperatures and abundant food. It also chooses places where river streams flow into the sea, because there the water is warmer and rich in food.
Metabolism in fish slows down in winter. This phenomenon is called thermoregulation and is typical for many species. This allows the fish to save energy and survive in conditions where there is less food and they cannot move quickly. Then the fish goes into hibernation, its heart rate can drop to several beats per minute.
In spring, it goes to rivers to spawn. Water quality is one of the key factors influencing the life cycle. If the water quality is low, this can negatively affect her ability to spawn, to the point that the eggs in the female simply dissolve. This problem is especially acute in Russia, which significantly reduces the fish population in natural reservoirs.
Life cycle
Beluga fish has a fairly long life cycle. She begins life as a fry, which hatches from eggs in rivers, where the first stage of her life cycle occurs. In the first years of its life, the beluga grows and develops in rivers, where it feeds on insects, fish and other small animals. During this time, she does not leave the river and is constantly in it.
When the beluga is about 5-7 years old, it begins to migrate to the sea, where it will spend most of its life. The transition from a river to the sea is an important stage in its life cycle. At sea it becomes much larger and begins to feed on fish and squid.
When the beluga reaches about 20-25 years of age, it begins to migrate back to the rivers, where the second important stage of its life cycle occurs - spawning. She chooses rivers upstream, those where the conditions for spawning are most suitable. At this stage of the beluga's life cycle, the female lays her eggs on pebbles or sand at a depth of 2 to 5 meters.
After spawning, it can spend several more years in the sea, feeding and growing to large sizes, or it can immediately return to the rivers. Its general life cycle lasts from 30 to 60 years, depending on living conditions and habitat.
These fish spawn in spring and autumn. Depending on the time of year chosen for this process, 2 types of fish are distinguished: spring and winter representatives.
The first species goes to spawn in the spring, after the end of hibernation. This occurs at different times depending on the region, usually March, April or May. When the rivers begin to fill with meltwater, the water level rises and the fish reach the uppermost channels.
Winter beluga, in turn, spawns in the fall, in September-October. It is not often found in one place and tends to migrate long distances to find a suitable spawning site.
This fish has a very good memory and remembers migration routes over a distance of 10 thousand kilometers. It is also capable of staying in rivers for long periods to search for food and suitable conditions for reproduction.
Diet
Beluga is a predator, and the bulk of its diet consists of smaller fish. In the first years of life, beluga fry feed on zooplankton, including crustaceans and mollusks, as well as small fish. They use their small tentacles to catch food in the water. As the fry grow, they begin to consume larger and larger fish, including other small species of salmon, grayling and large insects that enter the water bodies.
In addition, they sometimes hunt waterfowl and Caspian seal pups. Among the fish that they usually eat are carp, roach, pike perch, crucian carp, and herring. It also eats small sturgeon fish such as sterlet and sturgeon.
Although she is a predator, and not the smallest in the world, her diet is not limited to live food. Its diet also contains algae and other plant components and insects.
Spawning
Beluga does not grow quickly, so it reaches sexual maturity quite late.
Azov beluga females reach sexual maturity at approximately 16-17 years of age, when their size reaches about 120-130 cm. Males are usually ready for spawning a year earlier. The Caspian variety lags behind in terms of performance by about 4 years.
Fish are long-lived, on average they live about 100 years. But age may vary depending on living conditions, feeding and other factors. Female belugas go to spawn once every 4-6 years, while males are ready to spawn every year. During spawning, females lay up to 30% of their mass in eggs, which are released into the water for fertilization by males.
The fertility of a female beluga depends on her weight. Typically, large females are able to produce more eggs than smaller individuals. However, the amount of eggs produced by one female may vary depending on her age and general health. Female belugas spawn every few years, and the amount of eggs they produce may decrease with age. Some studies have shown that at the age of 20, a beluga produces an average of about 6 kg of caviar, while at the age of 50, the amount of caviar may be only about 2 kg.
When it's time to spawn, the beluga, which spends most of its life at sea, heads upstream to the spawning grounds.
She chooses places with fresh water, usually rivers or lakes, which allow her to return to her place of birth. The water should be deep and cold, with good oxygen levels and moderate current. For better egg laying and the survival of offspring, clean and transparent water is important. At the same time, it swims several thousand kilometers.
Females lay eggs, and males swim up to fertilize. The eggs are all covered with an adhesive substance, which allows them to stay in place and not be carried away even in strong currents.
About the offspring of belugas
Its caviar is large in size and has a unique shape. Each egg is a small bubble with a diameter of about 4 cm, inside of which there is an embryo. Typically, caviar is dark gray or black in color due to its high content of melanin, the pigment that gives the dark color. Depending on the age of the female and other factors, the size and quantity of eggs varies greatly.
The time it takes for the eggs to hatch depends on the temperature of the water in which they are found. This usually takes from 5 to 12 days. At low temperatures (0 to 4 degrees Celsius), hatching can take up to 20 days. However, at high temperatures (7 to 10 degrees Celsius), hatching can occur in as little as 4-5 days.
At high temperatures, water contains more oxygen, which promotes the rapid development and hatching of beluga larvae. However, if the water temperature is too high, it can cause the larvae to become deformed and weakened, reducing their chances of survival.
After hatching, the larvae quickly turn into fry and begin to search for food on their own. They live in shallow water and feed on plankton, various types of algae and other fry.
Most of the fry are in a hurry to go downstream into the sea. However, some individuals stay in the river until they are 5-6 years old before heading out to sea.
When young beluga whales go to sea, they are often found along shallow shores with low-salinity water. However, over time, they begin to move further and further into the salty and deep areas of the sea.
Features of caviar
Beluga caviar is one of the most expensive and luxurious delicacies in the world. It is gray-black in color and large in size, reaching a diameter of approximately 3.8 mm, and its weight ranges between 30 mg.
Among all types, beluga caviar is considered one of the most valuable due to its high protein content and low fat level. It is rich in important minerals such as iron, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc and calcium, which support healthy bones and blood.
In addition, beluga caviar contains vitamins A, B12 and D, which are essential for maintaining healthy skin, teeth and immunity. These vitamins also improve metabolism and maintain a healthy weight.
Beluga caviar also contains high levels of essential fatty acids such as Omega-3 and Omega-6, which are essential for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. These fatty acids improve brain activity, memory and concentration.
Beluga eggs are highly valued for their delicate taste, which is comparable to the aroma of the sea breeze and light corned beef. However, not every beluga caviar is so highly valued - in order to get a real delicacy, you must comply with many rules and requirements. The first rule is to use only caviar collected in a certain period of time. It is also necessary to take into account the temperature of the water in which the fish was before collecting the eggs.The cooler the water, the more valuable the caviar will be. On average, the price per kilogram of beluga caviar ranges from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Natural enemies
Adult belugas living in the seas have virtually no natural enemies due to their enormous size, which prevents other fish from attacking them. However, many small fish pose a danger to eggs, larvae, fry and young beluga fish: gudgeon, sturgeon, pike and others.
It’s a paradox, but belugas are considered enemies of their own population, since they sometimes engage in cannibalism. This happens when larger individuals attack smaller ones or their own little ones. Cannibalism is observed both among adults and between fry, capable of eating “brethren” or eggs.
However, for adult belugas, the most serious enemy is man. Previously, before the ban on catching belugas during the spawning period, every year from 1.5 to 1.9 thousand tons of belugas were caught on the Volga River alone. Despite the ban on beluga fishing, poachers still hunt these fish, which seriously reduces the number of belugas.
Population of the species
Over the past eight to ten decades, the beluga population has declined to alarming numbers. It began to decline catastrophically at the beginning of the 21st century, and this process continues today. The Caspian beluga, which has become an endangered species, is included in the Red Book of Russia and the International Red Book. Over the past 80 years, the population has declined by more than 85%.
The decline in the population of beluga fish in nature occurs for several reasons:
- Overfishing. Beluga is a valuable commercial fish and is caught in large quantities. Overfishing can lead to the disappearance of fish from certain water bodies.
- Negative impact on the environment. Pollution of water resources, changes in their temperature regime, disruption of the hydrological regime of watercourses, the presence of barriers on rivers and other factors negatively affect the living conditions of the beluga and lead to its extinction.
- Construction of hydraulic structures. Culverts such as hydroelectric power stations and dams block beluga migration to spawning grounds, reducing their numbers.
- Climate change. Climate change in the regions where belugas live may reduce the quality of their habitat and make it more difficult for them to reproduce.
Is this fish farmed?
In 1952, Russian scientists obtained a hybrid of sterlet and beluga, called bester, from the words “beluga” and “sterlet”. Bester is raised in fish farms and its hybrid nature gives it some advantages, such as a fast growth rate inherited from the beluga and early sexual maturation inherited from the sterlet.
The beluga breeding process can be described as follows:
- The eggs are placed in an incubator where they remain until hatching. The larvae are transferred to special nurseries and raised until they reach a weight of about 3 grams.
- Then the fry are transferred to small ponds, where both natural and artificial feed are used. Young fish eat not only minced fish, but also other additives that promote healthy growth.
- To ensure normal growth and development, the temperature and purity of water in ponds must be optimal, similar to natural conditions in the sea.
- In winter, it is transferred to special wintering ponds, in which there is no bottom vegetation, but greater depth. The fish continue to feed, but in smaller quantities.
- In the spring, the fish are returned to the feeding ponds, where they continue to grow and gain weight.
- When it reaches a weight of up to 2.5 kg, most fish are sent for sale to stores and catering establishments.
Application
Since ancient times, beluga has been a valuable commercial fish due to its enormous size and high quality meat and caviar. Now catching it is prohibited to preserve the species. It is grown in fish farms for commercial purposes. In its natural habitats it is protected by prohibiting fishing.
This is one of the most prestigious and expensive fish in world cuisine. Salted beluga is a real delicacy, which is prepared using the dry or wet salt method. Smoked has a distinct taste and aroma, ideal for sandwiches and snacks. Also used for preparing various salads and hot dishes.