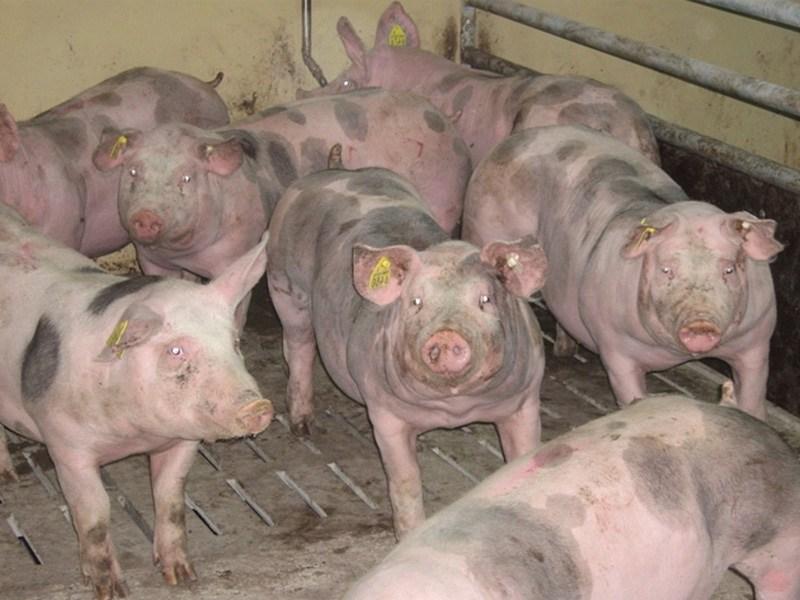
The European Pietrain pig breed is popular all over the world. The quality of Pietrain meat is at a high level; bacon is considered dietary. Despite the fact that representatives of this breed are demanding in terms of living conditions, they are bred in private farms in our country; piglets are raised for breeding and improving the gene pool of the livestock. The European breed is also suitable for industrial meat production.
A little history
The ancestors of the valuable breed are Belgian pigs, which were crossed with great white, Berkshire and Yorkshire species. This event took place at the beginning of the 20th century. Pietrain achieved special respect in Germany. Here these pigs are prized for their high-quality bacon, with thin streaks of fat.
In Russia, the breed is not very popular due to its demanding climate, care and living conditions; Pietrains, as a rule, are bred in order to improve the gene pool of the main stock. The breed is not included in the State Register of the Russian Federation.
Description and characteristics of the Pietrain pig
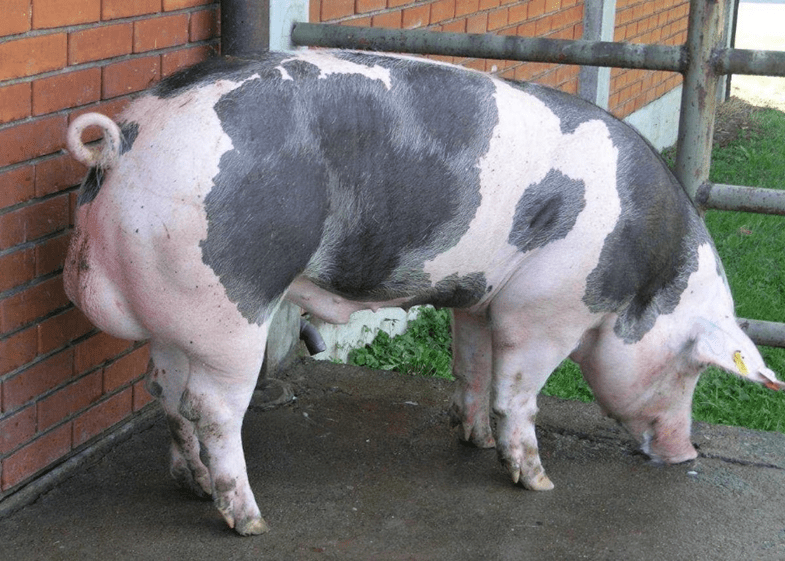
Representatives of the bacon branch of the Pietrain pig are not genetically predisposed to excess weight gain. The average weight of European pigs is 240 kilograms, the skeleton and bones are quite light. Appearance:
- The head is small in size with a short snout.
- The body is cylindrical, with well-developed muscles and a wide sacrum.
- Height at the withers is 80 centimeters.
- The color of the skin is white, the presence of gray and black spots on the back and head is acceptable.
- The ears are small and erect.
- The belly is underdeveloped, not saggy, the pig looks fit.
- Legs are short.
- The tail is in the form of a spring.
Productive characteristics of the breed:
- Well developed hams.
- The yield of meat from the carcass is 85%.
- Fertility is average - 9-10 piglets.
- The average daily growth of young animals is 550 grams.
- The thickness of the subcutaneous fat is no more than 10 millimeters.
On a note. Males are distinguished by a strongly expressed sexual instinct, so boars are often used for inbreeding with tallow and meat-fat pigs.
As for Pietrain's temperament, these pigs are considered peace-loving, rarely show aggression, and are suitable for keeping together with other pets.
Advantages and disadvantages of the breed
The main advantages of the European breed include:
- High quality meat, low fat content.
- The meat yield from the carcass is more than 80%, the average weight of the ham is 12 kilograms.
- Strong immunity, including in young animals.
- Pietrain boars are the best producers.
Negative aspects of the breed:
- Poor acclimatization and adaptation to new conditions and regions of detention.
- Weak milk production, piglets need complementary feeding from the first days after birth.
- A thin layer of fat makes pigs susceptible to cold and drafts.
- A specific diet requires vitamin supplements and high-calorie nutrition.
Pietrains must be kept in insulated and clean pigsties. The meat of European pigs is dietary; good quality of the product can only be achieved with a properly selected diet for the animals and compliance with the conditions of detention.
Conditions of detention
The genetic predisposition of Pietrain to minimal accumulation of fat determines the characteristics of the maintenance and diet of these productive animals. Features of pig care:
- A warm barn with good ventilation and lighting, drafts are not allowed.
- Clean litter.
- Constant access to drinking water.
- Walking area for animals in the warm season; it is necessary to create a rest area for pigs with a canopy from the sun's rays.
- Regular deworming of livestock, vaccinations.
- Give pigs enough space when feeding.
It is not recommended to change the living conditions and place of walking for animals; Pietrains do not tolerate a change of environment and the associated stress.
What to feed?
Meat pigs require high-calorie nutrition and vitamin supplements.At the same time, it is not recommended to use stimulants; such agents worsen the taste and quality of bacon, the meat oxidizes and becomes loose. The basis of the diet of the European breed should be proteins and easily digestible carbohydrates; Pietrains have a fast metabolism. The diet may include the following products:
- Waste from the meat and dairy industry.
- Boiled potatoes and finely chopped vegetables.
- Legumes and grains, greens.
Piglets that are born immediately need complementary feeding; from the second day of life, babies begin to be fed yogurt and whole milk.
It is necessary to add vitamins and minerals to the diet of animals: chalk, phosphorus, salt, fish meal, fish oil.
If Pietrain’s diet includes a lot of cereal feed, then the average daily gain will sharply decrease, corn, barley, and oats fade into the background. Many farmers use aspirin as a growth stimulant for young animals.
Breeding rules
Pietrain males reach sexual maturity at eight months of age, females at six months. The best age for breeding is 11-12 months. Breeding rules:
- It is recommended to cross Pietrains with representatives of their own breed, as well as with Landraces, Durocs and Great Whites.
- Provide animals with a balanced diet and drinking water.
- After farrowing, the female and her cubs are kept in a separate pigsty.
- Provide piglets with additional complementary foods from the first days of life.
Most often in our country, male sires of the Pietrain breed are purchased in order to improve the quality of meat of the main breed; boars of this breed have a pronounced sexual instinct.
Disease Control
By nature, representatives of the European Pietrain breed are endowed with strong immunity, in particular to cyclovirus infections.But this positive quality does not mean that you can refuse vaccinations and routine deworming of the tribe. The main factors in the development of diseases include:
- Animal stress associated with moving, changing diet or living conditions.
- Drafts, excess humidity in the pigsty.
- Dirty, damp litter.
- Lack of ventilation in the room where animals are kept.
- Outbreak of infection among the main population.
- Incorrectly selected diet.
Livestock should be regularly inspected for signs of disease. Decreased appetite, unmotivated aggression, loose stools, bloating, drainage from the eyes and increased body temperature are reasons to examine animals by a veterinarian.
Prevention measures for pig disease:
- Routine vaccination.
- Immunization.
- Balanced diet.
- Regular disinfection of the premises.
- Creation of a quarantine zone for animals with signs of disease.
Pietrain pigs are susceptible to pneumonia and gastrointestinal disorders. You must be careful when selecting food for animals; pigs often suffer from poisoning, especially from unwashed, dirty fruits and vegetables. When keeping Pietrain pigs, it is not recommended to make sudden changes in housing conditions, change the diet or transport animals to a new place; stress is the main factor in the development of diseases and poor health of animals.