Goldrich apricot has a high level of resistance to moniliosis. There is also a rich and regular harvest. The variety is classified as a commercial variety, but at the same time it is common among ordinary gardeners.
History of origin
Apricot Goldrich spread from America in 1971. It was bred to be grown in large quantities on farmland. When working on the variety, we used varieties such as Sun Glo and Perfection. For 40 years, apricot has firmly established itself in Western European countries and has earned high popularity there.In Russia it is still quite rare.
Description of the variety
Gold Rich apricot trees are medium-sized, have wide and spreading crowns. In order for fruit to set, apricots need pollinators. The best of them are the varieties that bloom at the same time.
The description of the variety states that Goldrich has a dessert purpose, so it is completely unsuitable for processing.
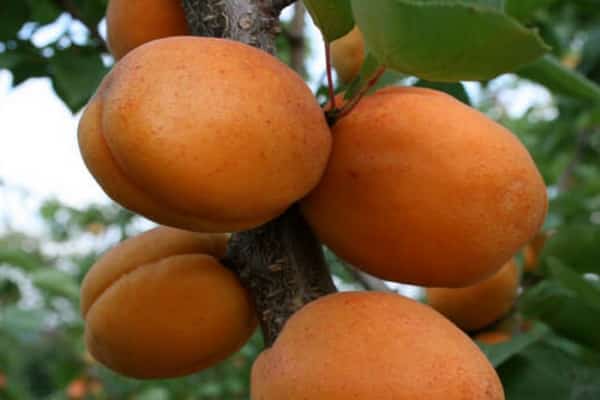
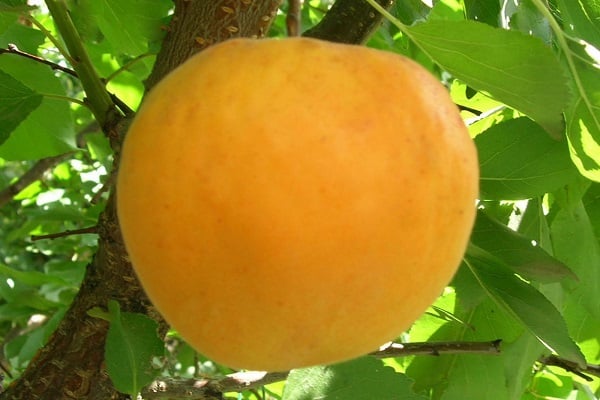
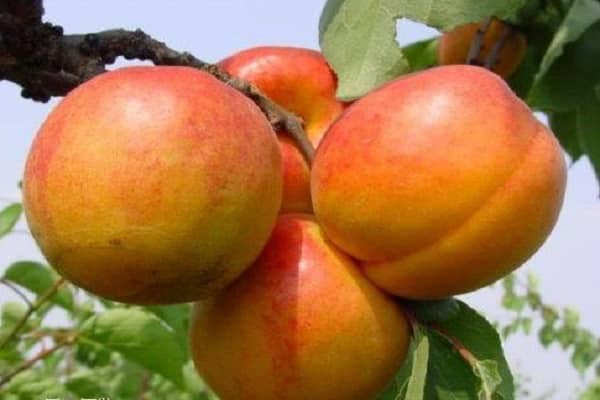
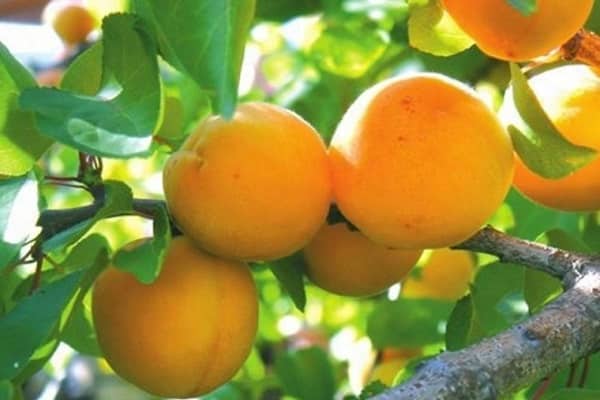
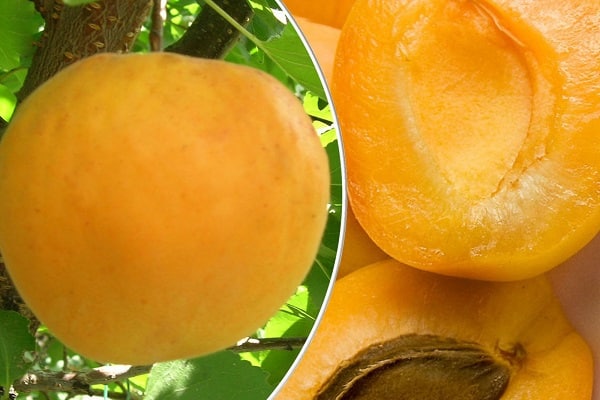
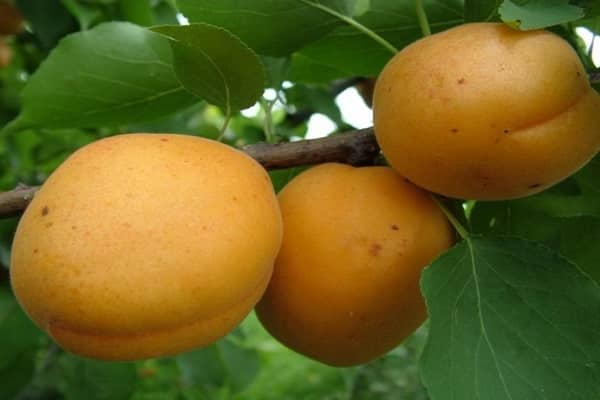
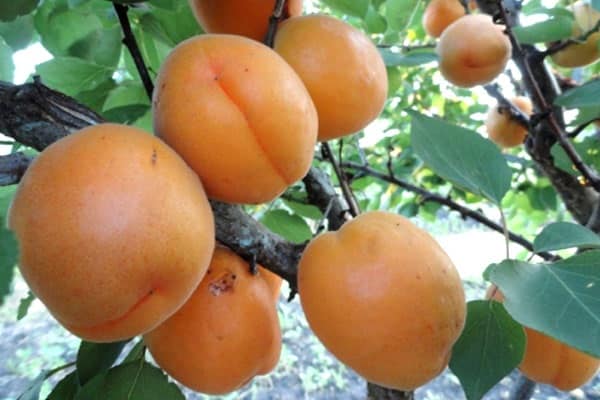
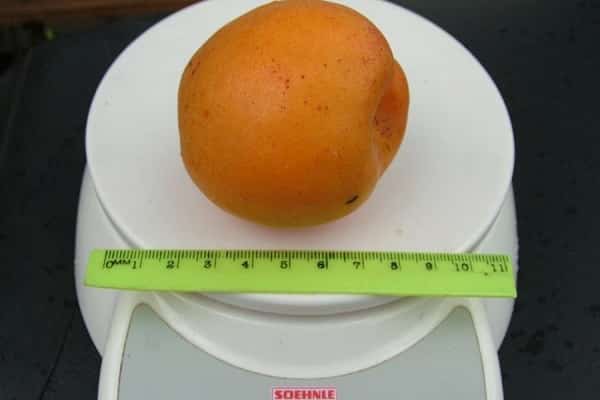
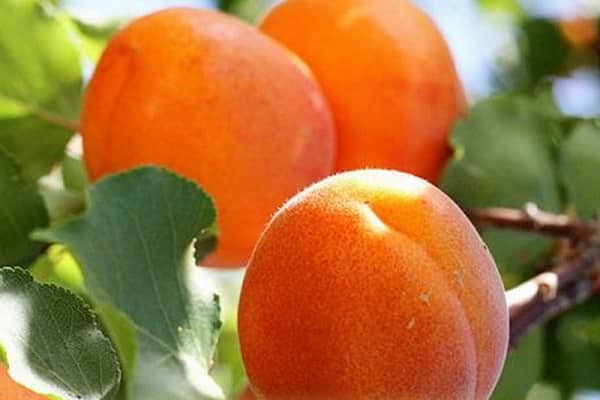
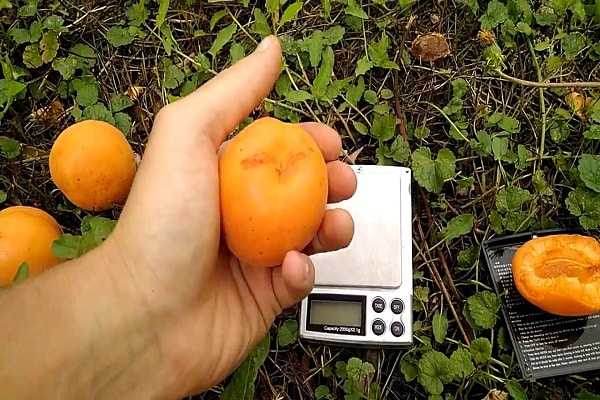
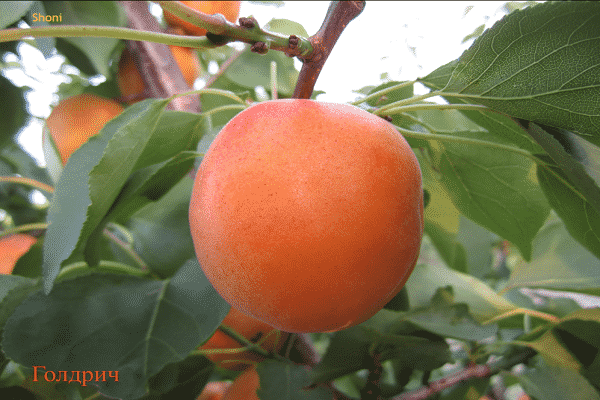
Apricots grow large and have an attractive appearance. The average weight of one is from 60 to 100 g. Sometimes they are especially large - up to 160 g.
The fruits are light orange in color with a faint blush. The taste of apricots is sweet and sour, the aroma is pronounced. Shelf life 2 weeks.
Experts claim the winter hardiness of the variety. But at a temperature of -28 degrees, cases of trees freezing have been recorded.
Apricots bloom mid-early, and this often leads to freezing of the buds when frost returns.
Features of cultivation
Before you start growing Goldrich apricots, you should know the specifics of the procedure. Then the yields will be high, and the tree will not be affected by diseases and pests.
Time and place of landing
For the seedling, a place is chosen that is well lit by the sun. Plants require protection from gusts of wind. Buildings on the site are suitable for this.
Planting is done away from groundwater and closer to pollinating trees.
Goldrich is planted in early spring in holes prepared in advance at the end of last season.
Soil preparation
Before planting, a drainage layer is laid on the bottom of the hole. For this, sawdust, humus or vegetable tops are used. Fertile soil is poured on top.
After planting the seedlings, abundant watering is carried out.It is recommended to pour 18-20 liters under each tree.
Then the young apricots are shaded. To prevent the soil from drying out too quickly, it is mulched with organic matter - peat or humus chips.
Proper care
Agrotechnical rules for Goldrich apricots are no different from caring for other varieties.
Watering
During the season, the soil is moistened abundantly, but not frequently, to a depth of 30-40 cm. Apricots are watered during the following periods:
- bloom;
- growth of fruits and shoots;
- after harvesting;
- at the end of autumn.
Top dressing
At each time of the year, Goldrich apricot trees must be fed with special fertilizers:
- spring - with nitrogen;
- summer - potassium;
- autumn - with phosphorus.
Organic matter is added every 3-4 years.
Reproduction
The process is carried out by planting seeds and vegetatively. But most apricot varieties are cross-pollinated. In this regard, it is difficult to say exactly what will grow from the seed.
Vegetative propagation allows you to breed offspring without unpleasant surprises.
Among gardeners, the most common method is propagation by grafting.
But if you plan to grow exact copies of Goldrich on the site, the surest method is used - propagation by shoots or root shoots.
Diseases and pests
Goldrich is affected by the following diseases:
- Moniliosis. Flowers are the first to become infected and quickly wither. The fungus then moves to the shoots, leaves and branches. As a result, cracks appear and the wood dries out.
- Clusterosporiasis. Appears on leaves in the form of brown spots, gradually turning into holes. The shoots also become covered with similar spots that form cracks. Gum leaks out of them.
- Valsa mushroom.An infection characterized by the formation of orange growths and sores.
- Verticillium. The lower leaves turn yellow, but the upper ones remain green. The accumulation of fungus occurs in the petiole and veins of the leaf. From there, the disease moves into the soil, from there it spreads to other young plants.
- Smallpox. A viral disease that forms on fruits in the form of depressed brown stripes and spots, under which the pulp gradually dries out.
Apricots are attacked by the following pests:
- Aphid. It sucks the juice from the leaves, which then weaken. Sooty fungus may appear next.
- Codling moth. Feeds on apricots. Overwinters in the soil or in cracks in the trunk. The offspring are left on the petiole of the leaf and on the ovary of the fruit.
- Leaf roller. Spends the winter in the bark of the tree, as well as in the ground. Actively eats apricot foliage and buds.
Disease Prevention
Apricots do not have many diseases and pests, but it is better to prevent their occurrence than to fight them later. The best preventative measures are considered to be cleaning the garden from fallen leaves, burning plant residues, digging up the soil around the tree trunk, as well as annual spring and autumn treatments of trees.