Fitosporin is a modern and effective remedy for combating fungal and viral plant diseases. The drug is suitable for any crops - both flowers and fruits and vegetables, which is why it is very popular among gardeners and gardeners. Let's look at the instructions for using the fungicide Fitosporin and figure out how and in what cases it is most effective to use this product.
- Description, release form and principle of action of the drug
- Advantages and disadvantages of the fungicide Fitosporin M
- Application area
- Dosage and timing of application
- garden flowers
- For cabbage
- For potatoes
- For cucumbers
- For tomatoes
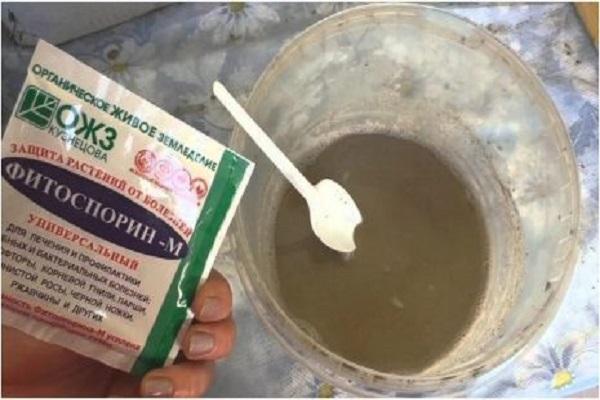
- Preparation of working solution
- Features of use
- For indoor flowers
- For vegetables
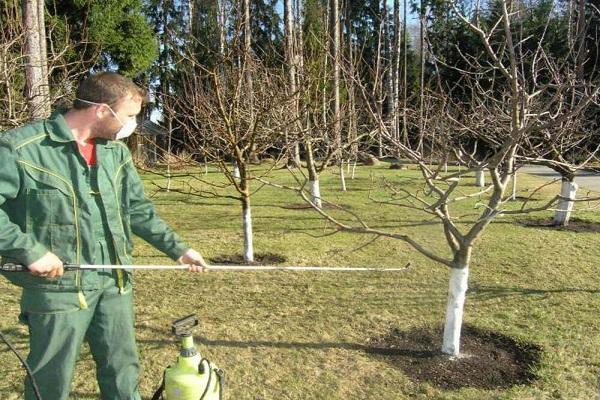
- For trees and shrubs
- For seedlings
- Greenhouse disinfection
- Soil treatment
- Safety precautions
- Toxicity of the drug
- Compatibility with other substances
- Terms and conditions of storage of the product
- Analogs
Description, release form and principle of action of the drug
Fitosporin is one of the most powerful fungicides used to treat plants. The drug belongs to the class of bacterial fungicides. It contains only components that are harmless to plants..
After treating the plant with the drug, the spore bacterium is activated, it begins to feed and produce waste products. Those, in turn, have a detrimental effect on fungi and harmful microorganisms. The fungicide is available in the form of powder, paste, and liquid suspension.
Advantages and disadvantages of the fungicide Fitosporin M
The main advantage of the product is its safety for plants, as well as the ability to maintain its properties at low and high air temperatures. Under unfavorable conditions for the life of spore bacteria, which are the basis of the drug, they suspend their activity, but when conditions improve, they continue to act.
Application area
The product is used to combat and prevent almost any diseases of plant crops caused by the action of fungi and harmful bacteria. It helps well in the fight against any types of rot, bacteriosis, powdery mildew, mold, rust, and so on.
Dosage and timing of application
The dosage and timing of Fitosporin application depend on the specific crop, processing method and diseases for the prevention or treatment of which the drug is used.
garden flowers
To prevent diseases of indoor flowers, use a dosage of half a teaspoon of powdered preparation per two liters of water.
To treat flowers from diseases, the ratio of powder to water should be doubled.
For cabbage
To treat cabbage, a dosage of six grams of fungicide per ten liters of water is used. Cabbage is treated by spraying the leaves, the procedure is repeated after two weeks.
For potatoes
For potatoes, the optimal dosage is ten grams per five liters of liquid.
For cucumbers
The dosage is similar to that used for potatoes. Spray three times, at intervals of approximately two weeks.
For tomatoes
For tomato crops, use a dosage of five grams per ten liters.
Preparation of working solution
The solution must be prepared immediately before use, no more than two hours, as it quickly loses its properties. When using powder, a teaspoon will contain approximately three grams of product. Use soft water at room temperature, no less than fifteen and no more than thirty-five degrees Celsius.
Features of use
There are certain features of using the product for different types of crops.
For indoor flowers
Indoor flowers are treated by spraying. Treatment should be carried out during the growing season. The optimal proportions for processing are ten drops per liter.
For vegetables
When processing vegetable crops for most varieties, the procedure should be repeated approximately once a month.
For trees and shrubs
For spraying fruit trees, a dosage of four teaspoons per liter of liquid is used.
For seedlings
Fitosporin is used to treat seedlings.It can be used both when treating seeds and at the stage when the plants grow their first leaves. When fighting fungal diseases, the first result becomes noticeable after a few days.
Greenhouse disinfection
The preparation can be used to treat the greenhouse at any time of the year, before planting. The walls are sprayed with the solution and the soil is disinfected.
Soil treatment
It is recommended to till the soil in the spring, before planting. Five grams of powder per liter of water is enough to treat one square meter of area.
Safety precautions
When carrying out the processing procedure, be sure to use special suits, masks and rubber gloves. Avoid contact of the solution with exposed skin and eyes. The drug can cause a rash and damage to human mucous membranes. If the drug comes into contact with your skin, rinse the affected area thoroughly with clean water. If the drug enters the esophagus, gastric lavage should be performed.
Toxicity of the drug
Fitosporin belongs to the fourth class of danger to humans. If it comes into contact with exposed areas of the body, the solution can cause rashes and damage mucous membranes.
Compatibility with other substances
Fitosporin is compatible with almost any fungicides, insecticides and plant growth stimulants. However, Fitosporin in the form of a paste is not recommended to be combined with stimulants. This is caused by the content of humic acids in the paste, which conflict with the active substances of the stimulants.
To check compatibility, you need to mix the two drugs in small quantities.
If no precipitate forms in the solution, then the products can be considered compatible.
Terms and conditions of storage of the product
The powder should be stored in a dry place, out of reach of children, at a temperature of zero to thirty degrees Celsius.
The solution should be prepared immediately before treating the plants, carefully calculating the required amount, since the remnants of the prepared solution cannot be used the next time.
Analogs
The closest analogues of the fungicide Fitosporin are the drugs Alirin and Gamair. They contain the same spore bacteria as Fitosporin, so the principle of action and effectiveness of the products are similar.