Diseases and pests of cabbage can destroy the entire crop. To prevent the problem, you need to know the main signs, treatment methods and preventive measures. If an infection is detected at the initial stage, all plantings can be protected.
Fungal infection
Here are the most common diseases of cabbage seedlings and an adult plant, which you need to know how to prevent and start treatment on time when the first signs are detected.
One of the common diseases is clubroot. The fungus only affects young white cabbage seedlings planted in a greenhouse or open ground.The pathogen that causes clubroot in cabbage beds is carried by wind or rain, and can also be spread by insects.
Initially, the root branches begin to be damaged. Growths appear on them, which prevent them from fully absorbing moisture and essential microelements. As a result, the cabbage withers and develops poorly.
It is easier to prevent an infection than to fight it. To do this, you need to strictly select seedlings; you do not need to plant weak seedlings. The soil where cabbage is supposed to be planted must be disinfected. Regular watering, hilling, loosening and applying lime fertilizer will help prevent the disease.
If an infection is detected, cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables should not be planted on the site for 5-7 years. This is exactly how long it takes for the infection to disappear.
In open ground, cabbage can often be attacked by downy mildew (experts call the disease downy mildew). The first symptoms of the disease include:
- formation of light yellow spots on cabbage leaves;
- a white coating is observed on the inside of the cabbage leaf;
- leaves affected by the fungus wither and fall off;
- cabbage does not develop well.
The fungus is active in a humid environment. The infection spreads very quickly, so urgent measures need to be taken. You can treat cabbage with drugs such as Phytophtorin or Bordeaux mixture. The drug Topaz shows good results.
Preventive actions should include proper watering, disinfection of the soil, and maintaining a distance when transplanting seedlings. Another main condition is that cabbage cannot be planted in the same place for several years in a row. It is better to plant where potatoes, beans or cucumbers were previously harvested.
Fusarium disease is considered common among cabbage. Fighting a fungal infection should not cause any difficulties, provided that the infection was detected in time. The first signs of the disease are:
- Numerous yellow spots appear between the leaf veins;
- gradually the entire surface of the cabbage leaf begins to turn yellow and, as a result, dries out;
- the head of cabbage forms poorly and slowly, and the shape is deformed.
The disease is provoked by lack of soil moisture and not too warm weather (below 18 degrees).
The diseased cabbage should be removed from the garden along with the roots and a lump of earth. The remaining vegetables and soil must be disinfected. For this purpose, the drugs Benomil and Topsin are used. You can use potassium permanganate or copper sulfate.
Another cabbage disease is Alternaria blight, or otherwise called black spot. When infected, black spots appear on any part of the plant. As the disease spreads, the spots darken and a fungal coating appears.
Black spot is spread by pests that overwinter in vegetable residues and seeds. That’s why it’s so important to remove the tops and dig up the soil after harvesting in the fall. Cabbage seeds must be disinfected and heat treated before planting.
Fungal disease Blackleg leads to rotting of the roots and lower part of the stem of seedlings. As a result, the stem dries out and the plant withers and dies. The infection quickly spreads to healthy shoots.
The development of fungal infection is facilitated by high acidity of the soil or excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers. The fungus may remain in the soil from the previous harvest.
To prevent the development of blackleg, before planting seedlings, the ground must be disinfected, a solution of potassium permanganate will do, or you can simply water the area with hot water. It is recommended to treat cabbage seeds with special preparations, for example, Fundazol.
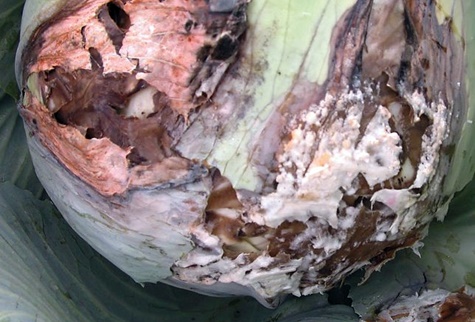
Cabbage disease White rot is also quite common. The most important factors in the development of rot are excessive watering and frequent rains. The risk of developing the disease increases towards the end of the growing season.
Recognizing the signs of white rot is easy. There is a fungal coating and mucus on the leaves. White cabbage rots quickly. The disease can develop not only in the garden, but also during storage of the already harvested crop.
Preventative measures include timely harvesting, before the onset of autumn rains; you should not plant cabbage in the same place for several years in a row. Be sure to disinfect the place where the harvested crop will be stored.
During winter storage, heads of cabbage are often subject to gray rot. The leaves are covered with a gray coating, mucus is observed, and an unpleasant odor is felt. In the cellar or basement it is necessary to carry out disinfection and maintain the temperature regime. While cabbage is growing, you need to add fertilizer to the soil.
Dangerous viruses
Less common, but still found among cabbage, are viral diseases. They spread at an even faster rate than a fungal infection and have a detrimental effect on the entire crop.
The mosaic virus is considered the most dangerous. Small, numerous dark dots form on the leaves. Mosaic cannot be treated, so it is best to prevent the disease in time:
- cabbage seeds should be immersed in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection;
- when a diseased seedling appears in the garden bed, it must be uprooted and taken away from the garden bed;
- a prerequisite is the removal of weeds that can carry pathogens;
- spray plants several times a season against pests.
Black cabbage ringspot appears as light green spots. Over time, the spots darken, join together, and the leaf becomes deformed and falls off. The pathogen thrives in cold weather, overwintering on seeds or plant debris. The disease is also spread by pests (aphids and mites).
Before planting seeds, they must be disinfected and heat treated. Weeds and tops from last year need to be removed from the beds on time.
The reason is bacteria
Mucous bacteriosis of cabbage can affect the plant at any stage of development. Rotting may begin in the outer leaves. They resemble a mucous structure and smell unpleasant. Gradually the entire head of cabbage is subjected to rotting.
There is an option for rotting to start from the inside of the head of cabbage. Bacteria can be carried by pests or get in with the soil. The leaves become milky and soften.
The cause of the disease can be excessive fertilization of the soil with nitrogen, excessive moisture, or lack of proper care of the beds.
Preventive measures include choosing cabbage varieties that are resistant to this disease, timely treatment of vegetable crops from pests, compliance with conditions in the harvest storage room, and disinfection of planting material.
Vascular bacteriosis is spread by pests or enters cabbage beds during rainy weather. The first signs are yellowing of the edges of the leaves and blackening of the veins. A characteristic feature is the appearance of a grid-like pattern on the leaves.Then the leaf completely darkens and falls off. The cabbage stops growing and developing and as a result dies.
You should not plant cabbage on the same piece of land every year; you should choose varieties that are resistant to vascular bacteriosis.
It is imperative to carry out preventive treatments against pests. At the initial stage, you can treat with the drug Binoram.
If any diseases of white cabbage are detected, the fight against them must be started immediately. This will help save not only the diseased plant, but also the entire crop in the garden plot.
Pest Infestation
Pests and diseases can cause yield reduction or complete loss. Pests of white cabbage not only eat and damage cabbage plantings, but also transmit diseases, which is why regular preventative watering and spraying is so important.
One of the common parasites that can settle on cabbage is aphids. The insect is small, about 2.5 mm. In the pictures you can better see this pest. They develop their activity on the lower part of the plant leaf, almost at the base. They eat cabbage juice.
Aphids often attack cabbage in the spring, when young seedlings have just been transplanted. The problem can be identified by the following signs:
- cabbage begins to develop slowly;
- leaves become pale with a pink tint;
- Over time, the leaves become deformed and fall off.
To combat aphids, drugs such as Iskra, Corsair, and Karate are often used. It is useful to plant cabbage beds next to tomatoes and carrots. Among folk remedies, infusions based on garlic and onions are considered effective. Insects do not like their smell.
Cabbage can be attacked by the cabbage fly.The insect is approximately 6 mm in size, gray in color. The danger to the vegetable is posed by the larvae that the fly lays in the soil. After a week, the larvae begin to eat the root system first, and then move on to eating the stems, making tunnels in them. White larvae reach 8 mm in length. In addition, they can cause the development of a viral, fungal or bacterial disease.
The appearance of cabbage will indicate a fly infestation:
- the roots begin to rot and the plant is easy to pull out of the ground;
- leaves wither and grow poorly;
- the lower row of leaves darkens and acquires a grayish tint.
A solution of Chlorophos or Thiophos, as well as drugs such as Corsair, Rovikurt, helps against cabbage fly. People try to cope with the insect using a mixture of tobacco and lime.
Cabbage cutworm can cause the loss of an entire cabbage crop in a matter of days. During the daytime, it hides in cabbage leaves, and with the onset of night it begins to be active. The insect is similar to a butterfly, approximately 5 cm in size. The wings are light brown with white stripes and spots. The greatest danger comes from the caterpillars of these butterflies. They are green with yellow stripes.
If cabbage cutworms are detected, you need to treat the beds with insecticides such as Sumicidin, Cyanox. To prevent the invasion of butterflies, you need to pick weeds in time and dig up the ground in the fall.