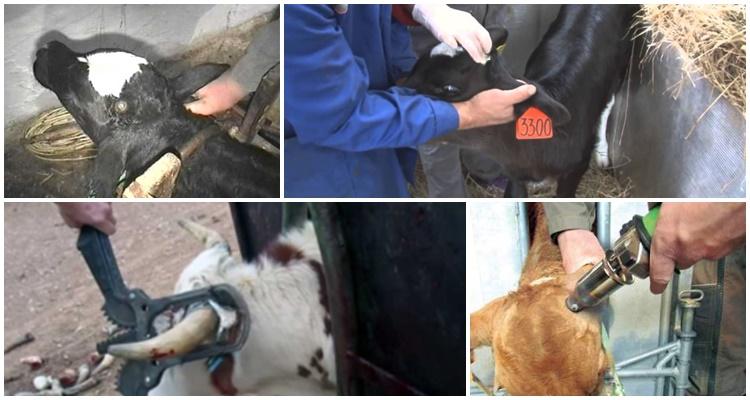
There are polled breeds of cattle that do not grow horns. For some reason, other breeds try to get rid of horns. This is a common practice on a livestock farm, and cows are also dehorned at home. After the operation, calves do not grow horns; dehorning is also carried out for adult animals. Let's consider the reasons for dehorning calves, why it is carried out, what methods are available and how to do it correctly.
Why do they do this?
Horns are removed from cows that will be raised on freestall farms.Since animals can move freely around the premises, contact is inevitable, which can lead to conflicts, fights and injuries from horns, sometimes serious.
It has been proven that where cattle are kept without horns, productivity increases by 10%. Without horns, the cattle become calmer, since they are deprived of the opportunity to sort things out, the cows are busy eating feed, as a result, there is an increase in meat and milk. Hornless cows cannot injure not only their relatives, but also humans, and it becomes more convenient to work with them. You can remove the horns of calves on your own farm if you invite a specialist to do this.
At what age?
Dehorning can be carried out at different ages, it all depends on the method of treatment. For example, horns can be removed chemically from calves as young as 3-5 days old. At the age of 2-3 weeks, the horny tubercle is cauterized with thermal cauteries. At 1-2 months of age, calves have their horns cut out with a tubular knife. When they are 3-6 months old, the horns are excised with pruning shears. It is recommended to remove horns for calves before 2 months of age. The younger they are, the easier it will be for them to undergo the operation.
What are the ways?
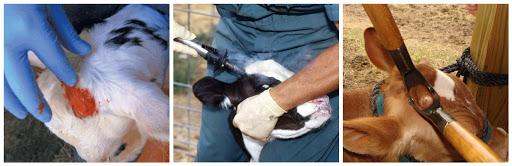
Horns are removed in several ways, using different materials and devices. For example, thermal, chemical and surgical methods are used.
Thermal
This method is considered simple and safe. Around the rudiments of horns (horny tubercles), the hair is first cut off, then each tubercle is cauterized with an electric device. Exposure time – 10-15 minutes.
After cauterization, the tubercles are lubricated with antiseptic preparations; in the summer months, repellents are additionally used to repel flies.
Chemical
The method is suitable for processing small calves.The same preparation is carried out, that is, first the hair around the tubercles is cut. Then wipe with alcohol and apply small scratches with a metal brush. Afterwards, the tubercles are lubricated with a caustic mixture of antimony trichloride (28%), collodion (65%) and salicylic acid (7%). Treatment options: nitric acid, caustic soda, caustic potassium. There are also ready-made ointments that are used to treat horns to prevent growth.
Surgical
The effectiveness of the method is based on the fact that the base of the horn and the rudiment are loosely connected. The operation is performed using a metal tube, which is pointed on one side. Removal sequence: determine the center of the horny tubercles, cut off the hair around it, treat the skin with an antiseptic or alcohol. Anesthesia is performed using novocaine.
The skin adjacent to the tubercle is cut with a tube, reaching the bone of the head. By tilting the tube, the base of the horns is trimmed. If there is bleeding, the injury site is treated with hemostatic agents.
The method requires practice, so only specialists can perform it. The result and normal healing can only be achieved if the operation and subsequent treatment are performed correctly.
Means for dehorning
An ointment that prevents the growth of horns is used on 2-3 day old calves. The product is rubbed into the area with the rudiments of the horns in a thin layer, covering an area of no more than 2 cm. The boundaries of the tubercles must be processed carefully so as not to touch adjacent tissues. After a week you need to check the result. You need to wear rubber gloves when working with the paste.The ointment should only be applied to calves up to 2 months of age; in older animals, the effect may be unsatisfactory: the horns will grow and become deformed. The same thing happens when applied incorrectly.
Another method of dehorning is thermal cautery treatment. The device operates from an electrical outlet or a gas cartridge; the second option is preferable due to mobility. The horns are cauterized with a thermal cautery when they first appear. Exposure time is about 5 seconds. It is important to set the time correctly; deviations in one direction or another will lead to the horns growing deformed or causing skin burns.
How to dehorn a cow
For adult animals, the horns are cut off, this is done using hacksaws, special saws, scissors or jigsaws. Pain relief is performed with anesthetic drugs, for example, Novocaine solution. You need to choose the right time for the operation. Pregnant animals should not be dehorned, especially in the 2nd-1st half of pregnancy, stress can cause abortion.
The right time for treatment is autumn, at this time there are no insects that could carry infections. If there is an error in the technique, bleeding and injury to the head bones may occur. The height of the cut is 3 cm from the warp. If you cut lower, bleeding and infection are possible. After the operation is completed, treat the saw cut with antiseptics.
Dehorning of calves and cows is a standard procedure on many cattle farms. The procedure has a positive effect on animal behavior, reduces the risk of injury, which ultimately leads to increased productivity of cows.A skilled specialist carries out the procedure quickly and professionally, painlessly for calves, the animals tolerate it well.