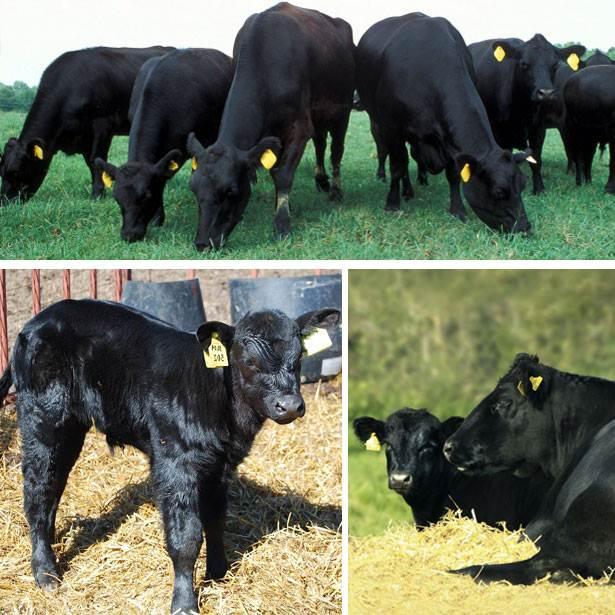
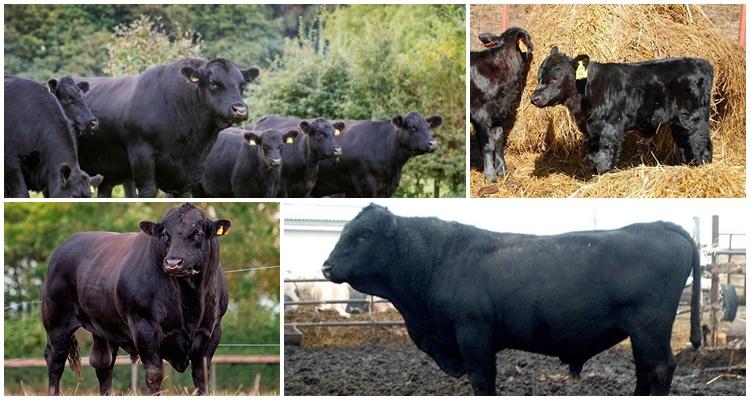
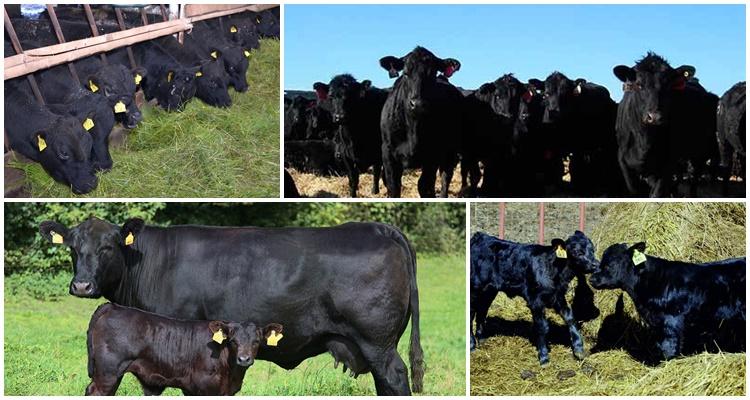
Among beef cattle, representatives of the Aberdeen Angus breed stand out. Their main feature is meat with thin layers of fat, called marbled meat. It is valued all over the world by those who love exquisite meat delicacies. Let's consider the description and productive characteristics of the breed, conditions of detention and feeding rules and features of breeding.
Origin and distribution
The Aberdeen Angus cattle breed was developed in the highlands of Scotland.The ancestors of the representatives of the breed were local polled black cattle. Work with the breed began in the second half of the 18th century; registration occurred a little later - in 1873.
During this time, it was possible to improve the exterior of bulls and cows, the yield of meat and its quality, the animals became precocious. Early maturity and excellent quality meat are the main qualities of the breed, for the sake of which it is kept in breeding farms.
In which countries is Aberdeen Angus grown?
After successfully breeding the Aberdeen breed in its homeland, it began to be exported to Europe and North America. Today, Aberdeen-Angus bulls and cows are raised in breeding farms in the USA and Canada, Russia (Kaluga and Voronezh regions) and the CIS, Australia and New Zealand, and Argentina. They are bred to produce distinctively flavored marbled beef, 80% of which comes from Black Angus.
Description and characteristics of the Aberdeen Angus breed
Aberdeen cows are built like meat. The animals are compact, short, 116-118 cm at the withers. They have a small head, short muzzle, short but large neck. The body is rectangular, muscular, level withers, back, voluminous chest. The legs are short and strong. The skin is thin, loose, with pronounced subcutaneous tissue. The color of the coat is pure black; when crossing Aberdeen-Angus individuals with other breeds, the calves inherit black color and polled hair.
Calves are born weighing 22-28 kg, but grow quickly; by six months, bull calves can weigh 150-180 kg. Cows gain 1 kg per day. In adulthood, cows weigh 500-550 kg, bulls - 750-950 kg, while fattening males gain up to 1 ton of weight. The slaughter yield of meat is 60-70%, such a high figure is explained by the fact that cows have thin bones.The meat of Aberdeen Angus cows is tender, with thin fibers and layers of fat. The milk production of cows is small - up to 1.7 thousand liters, a lot of milk goes to feed the calves.
Disadvantages and advantages compared to other breeds
The breed's disadvantages are not significant, which is why Aberdeen-Angus cattle are recognized as one of the best types of livestock for industrial breeding.
Subtleties of maintenance and care
Aberdeen are characterized by good adaptability, so they can be grown without creating special conditions for them. Cows can live in temperate, cold and hot climates. Only humidity has a negative effect on animals. With successful organization, they can manage to be kept open on pasture without reducing productivity.
In winter, especially in cold regions, they need to be kept in a warm barn; they simply cannot be kept outside.
It is recommended to keep bull calves free-stall so that they can easily approach the feed and drinkers. Animals should go for a walk every day and spend time in the walking area. A proper diet and moderate physical activity allow animals to stay healthy and fatten quickly.
The character traits of Aberdeen Angus cows dictate the rules for handling them. Animals love communication, they need to be accustomed to contact with people; lack of training leads to the fact that animals become wayward and aggressive.
Diet planning
Calves are kept with their mothers; due to their natural nutrition, they grow quickly and rarely get sick; they acquire natural immunity along with milk. Gradually they are transferred to adult food, fed with chopped grain, mixed feed, fresh grass, and premixes are added to the food. Animals are given fresh, clean water.
But there is a special fattening scheme using wet corn, which makes it possible to obtain premium quality marbled meat. Aberdeen Angus cows are fed according to an intensive feeding scheme, which gives an average daily gain of 1-2 kg. Fattening lasts 6 months. It is important that animals do not overeat; overfeeding makes them fat. If this happens, you need to immediately review the diet, as the quality of future beef will suffer.
Individuals are selected for fattening that will not replace animals in the breeding herd. At 8 months, at weaning age, they can weigh 200-230 kg. The best quality meat can be obtained from castrated bulls. Castration is carried out at an early age. As a result of the operation, the structure of the muscle fibers changes, they become thinner. But the advantages of castration are not only this, bulls can be grazed next to cows, there is no need to allocate pasture for them.
For an Aberdeen Angus cow to gain 1 kg of weight, 6.5 feed is spent.units, that is, 6.5 kg of oats or 32 kg of fresh grass from meadows or 13 kg of average nutritious hay. Slaughter is carried out at the age of 18 months. In practice, it has been proven that in animals older than this age, weight gain does not increase, but stabilizes. In older cows, the quality of meat deteriorates and it becomes coarser.
Fattening on corn allows you to get meat of impeccable quality. Beef is used to prepare steaks, cutlets, kebabs and other meat products. Aberdeen meat is soft, juicy, and has an ideal structure.
Breeding
Although the breed is known for its cows being able to adapt to different climates, you should try to buy calves that were raised as close as possible to where they will live. Then they will endure transportation and changes in conditions almost without stress.
Heifers of the Aberdeen Angus breed are ready for breeding at 15 months, but there is no need to rush to breed them at this age, their body is not yet fully formed. Pregnancy will stop the development of the cow itself, the offspring will be small, weak and sickly. Thanks to the small newborns, calving is easy, without complications, the cow does not need help, she copes with everything herself. Representatives of the breed give birth to 1, rarely 2 calves.
Like calves of other varieties, they require colostrum and maternal care immediately after birth. The babies can be left with the cow; the breed is not a dairy breed; almost all the milk is drunk by the calf.
The most pronounced characteristics inherent in the breed are possessed by purebred individuals, therefore, to obtain the famous marbled beef, it is recommended to keep purebred individuals. If this is not possible, crosses with other cattle breeds are bred.They receive valuable qualities from their Aberdeen Angus parent and acquire new ones, are distinguished by good health, vitality and live longer if used for breeding. This property of the breed is used to breed new promising breeds of cows.
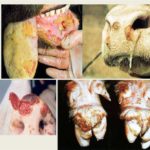
Diseases
The Aberdeen Angus breed is characterized by genetic diseases, which are especially common in purebred individuals, since they are carriers of recessive genes. Crossbreeds with other breeds do not get sick. Carriers of defective genes can be identified using a DNA test.
Diseases of Black Angus:
- Arthrogryposis multiplex. It manifests itself in serious birth defects and joint deformities, damage to tendons, muscles and ligaments in calves. The disease is detected in meat and dairy cattle breeds and causes significant damage to livestock production. In calves, joint mobility decreases, leg muscles are weakened or atrophied.
- Neuropathic hydrocephalus. Angus are born with a large deformed head.
- Contracture arachnodactyly. In newborn calves, the mobility of the hip joints decreases.
- Dwarfism.
Bulls and heifers with genetic diseases are always culled and not allowed for breeding so that defective genes are not passed on. Aberdeen Angus cows can suffer from infectious and other cattle diseases, but when they meet rearing standards and are in good conditions, they rarely get sick. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the premises where animals are kept, the cleanliness of pastures and walking areas, feeding troughs, and carry out vaccinations and routine veterinary examinations.
Aberdeen Angus cattle can be bred on farms and private farms to produce beef of a special structure and excellent quality.The animals are quickly fattened on a special diet, and the slaughter yield of meat is at a high level.