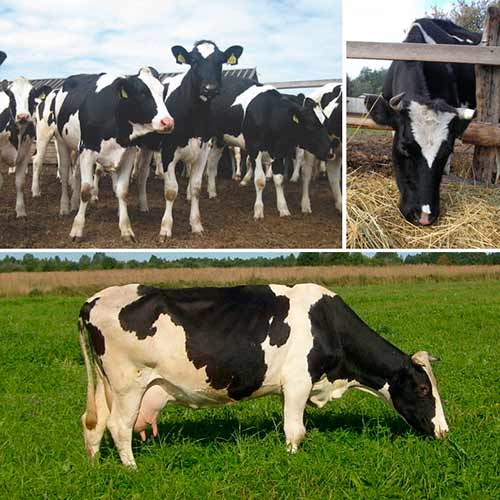
Fattening for cattle meat is a system of complex measures used on large livestock breeding farms, which are aimed at quickly increasing the live weight of farm animals, bringing the livestock to the required weight standards before slaughter. They put it on fattening replacement young stock, culled adult individuals of meat, dairy, dairy and meat breeds.
Goals and technology
The main goals of cattle fattening are to obtain in the shortest possible time a large amount of the highest quality meat (beef, veal) with good taste with minimal feed costs, increasing the growth of economic indicators of industrial livestock complexes. It is equally important to achieve a reduction in the share of imports of beef and veal from other countries, to stabilize prices for meat products by reducing the cost of final products.
Cattle fattening goals:
- increase in the fatness of farm animals in a short period of time;
- change in the biochemical parameters of the carcass for the better;
- reduction in the amount of water and protein compounds in tissues in the final product;
- reduction of fat deposits in subcutaneous tissue, muscle tissue, and internal organs;
- increasing the slaughter weight of cattle, improving the taste parameters of all parts of the carcass (meat, offal);
- minimizing the percentage of waste.
The main criterion for raising cattle for meat is an indicator of live weight. Estimated at six months, one and a half years of age. In 12-13 month old calves, the weight should increase by 7-8 times compared to birth weight, and by 17-18 months of age - by 11-13 times.
Intensive livestock rearing in our country on specialized farms is carried out using different methods. Cattle feeding technologies are based on compliance with the feeding regime, proper selection of feed, gradual changes in diets, use of high-quality feed, and proper organization of feedlots.
When fattening farm animals on an industrial scale, different diets are used (succulent feed, silage, compound feed, grain).
The diet is supplemented with mineral supplements. An increase in nutritional value occurs by adding concentrated corn silage and high-quality hay to the main feeds (cereals, succulents). The daily diet of cattle must fully cover the body's energy costs and contain all the necessary nutrients, minerals, and vitamins. When fattening livestock, high quality feed is used.
Important! The structure of diets can change with the progress of fattening to prevent obesity in young animals and adults.
Feeding technology involves stall (in enclosed spaces without walking), stall-pasture, and open housing of cattle in feedlots. Animals are divided by age groups, condition, initial weight, and breeds. Based on the intensity and speed of cultivation, technologies are classified into:
- extensive, with a long production cycle;
- moderate-extensive. The average daily gain is 420-800 g;
- intensive technology, in which the live weight gain of young animals is 900-1000 g.
The choice of comprehensive measures for maintaining cattle depends on the climatic conditions of the region, the specialization of livestock complexes, the economic tasks set for enterprises, and the availability of feed.
How to choose calves for fattening
Young animals of meat, meat and dairy domestic and foreign breeds are most suitable for intensive rearing. A good increase in live weight is noted in calves of the Kazakh, Kalmyk, Simmental, Aberdeen Angus, Hereford, Limousin, Kian, Galloway breeds. They also use cattle of hybrid breeds of zebu origin (Braman, Santa Gertrude).
The placement of bull calves for fattening begins immediately after the end of the milking period and the weaning of calves from lactating cows. Weaning of young animals is carried out in the fall or at the age of 6-8 months.
Before using or choosing intensive rearing technologies, young animals must adapt to new living conditions and get used to new feeding rations. On average, this period takes from three to five weeks. The fattening period includes two main stages:
- live weight gain, 400-420 kg;
- weight increase up to 650-700 kg.
Important! Bulls of beef and mixed breeds gain weight faster than heifers. At one year of age, their weight can reach 400-450 kg. Early castration of animals (1-3 months) leads to developmental delays, decreased daily weight gain, and early obesity.
In order for calves to have a stable daily gain in live weight, clinically healthy, strong individuals with normal body condition for their age are selected during purchases or from the general herd. Young animals must have a good gene pool, healthy parents, and all the necessary vaccinations. The best period for acquiring young animals is mid-to-late spring.
Types of cattle fattening
There are two types of fattening young animals and adults:
- Stall (standard). Suitable for all breeds, age groups. It differs in the type of nutrition, diets depending on the availability of certain feeds, the availability of food resources, and the time of year.
- Intensive. Aimed at quickly building muscle mass, achieving high average daily growth rates.
The success of fattening and the choice of activities for intensive cattle rearing depends on:
- sex of animals;
- condition, condition of cows;
- frequency, intensity of feeding, type of feed;
- method of maintenance;
- organizing the necessary activities for keeping livestock;
- age;
- genetics, physiological characteristics;
- health conditions;
- growing conditions.
The duration of fattening, regardless of the type, is influenced by the presence of systematic veterinary control, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards in barns, a competent approach to the preparation of diets, and the use of high-quality feed.
Important! Daily weighing of cattle will help you understand how effective a particular technology used when choosing a technology for intensive fattening at an enterprise is.
On average, it takes 1.2-2 months to fatten adult individuals. With properly organized fattening, young animals show stable daily weight gains.
Intensive fattening
Rapid, or intensive, fattening of cattle is used to quickly obtain increases in live weight in young animals. The method is suitable for raising bulls, heifers of meat, dairy, meat and dairy replacement breeds, as well as calves from the first calving, which appeared by crossing dairy cows and beef bulls. The resulting meat products have excellent taste and high nutritional value. The meat is juicy, tender, and low in fat.
Fattening of calves begins after the end of the milking period, the cessation of lactation of cows, or upon completion of artificial feeding of newborn animals. The diet consists mainly of hay, grains, concentrated feed, and corn silage. Young animals are given probiotics, mineral premixes, and vitamins.
Stall fattening
Used on farms for fattening cattle of any age and breed. Includes three stages:
- Initial, lasting one month.
- Intermediate – 40 days.
- Final – 20 days.
The choice of feed when preparing diets is selected separately for each stage of fattening.
Important! Changing diets requires adaptation. The transfer of cows to new feeds is carried out gradually.
At the initial stage, it is permissible to use any feed. At the finish line, the main part of the diet consists of concentrated feed. The daily amount of food is divided into three to four meals. But at the same time, cows must have constant access to drinking water.
What food do you need?
The diet of fattening cattle must be balanced and contain the components necessary for a rapid increase in live weight. According to the composition of the feed, there are basic, mineral, and concentrated feeds.
Basic
The entire diet of animals is based on basic feed for fattening cattle. Must meet the following parameters:
- have at least 30-35% dry matter;
- contain crude fiber (200 g/kg), crude protein (73-90 g/kg);
- have sufficient energy value for metabolic processes above 10.5 MJ/kg.
Important! Basic feed should be absorbed by the animal's body by 70-73% and contain biologically active substances necessary for stable gains in live weight.
When preparing diets, the nutritional value and quality of feed are taken into account. If necessary, some feeds can be replaced with others. For example, corn silage can be replaced with cereal silage.
Concentrated
Concentrated feeds are intended to supplement the basic diets of cattle. They have energy and nutritional value. Contains proteins, vitamins, minerals. Promotes satiation. Have a beneficial effect on metabolism.Compound feeds include: legumes (peas, broad beans), sunflower, rapeseed, soybean meal; wheat grain, oats, barley and dry pulp.
The daily menu should contain at least 2-3 kg of concentrated feed. When compiling a diet, the period and stage of cattle fattening are taken into account. So, if the weight of young animals does not exceed 400-410 kg, feed takes up 40% of the total volume of dry food. With increasing body weight, their content gradually decreases.
Mineral
Mineral supplements supplement the daily diet of cattle. Stimulate weight gain, have a positive effect on the growth and development of young animals, increase resistance and immune defense of the body. Minerals accelerate metabolism and stimulate the secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! The body of calves needs calcium, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and sodium.
Mineral supplements are supplemented with special vitamin complexes. The daily norm is 60-80 g.