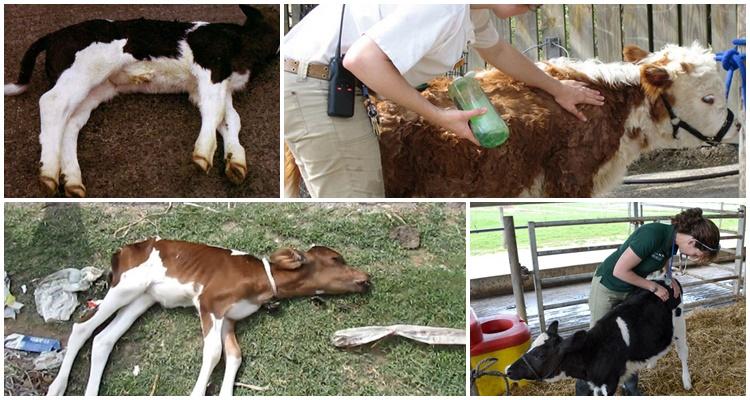
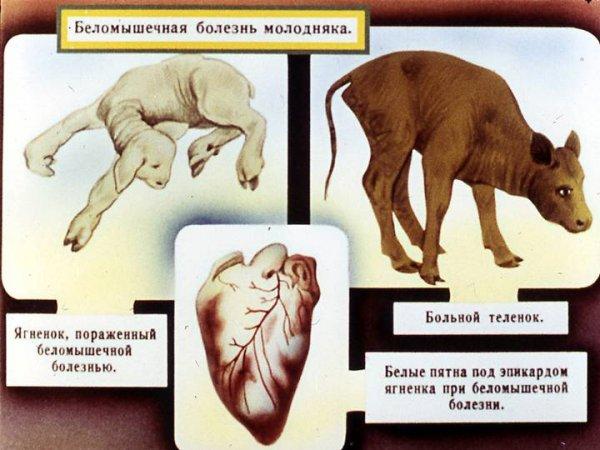
The development of white muscle disease in calves is often observed in the first weeks of life. This pathology is characterized by disruption of metabolic processes and problems with contractile functions. The danger of muscular dystrophy is that it cannot be eliminated. After illness, the calf will not develop well. If treatment is not started on time, mortality rates reach 60%. Therefore, the first symptoms of the disease require the help of a veterinarian.
What are the features of the pathology
White bone disease in cows is an endemic pathology. It mainly affects young animals. Currently, the disease is not well studied. The pathology usually affects calves. However, sometimes it occurs in other representatives of cattle.
If the use of conventional drugs does not give positive results within 3-5 days, it is recommended to urgently start using antibacterial drugs. As a result of the pathology, the heart muscle suffers, skeletal muscles are deformed, and morphological processes are observed in the structure of internal organs.
With the development of pathology in a sick animal, a decrease in the level of total protein and an increase in nitrogen are observed. A distinctive feature of the pathology is a violation of creatinine metabolism and increased phosphorus content. The pathology is more common in New Zealand, the USA, and Australia.
Symptoms of the disease
The pathology has several development options, each of which has specific symptoms. The duration of the acute stage is 7-10 days. The pathology is characterized by the following signs:
- general oppression;
- development of tachycardia;
- heart weakness;
- increased breathing;
- the appearance of symptoms of conjunctivitis, which are accompanied by clouding of the eyes;
- severe nasal discharge;
- disorders of the alimentary tract;
- bloating;
- profuse salivation;
- paralysis and paresis - in this case, the calf experiences a disturbance in motor activity;
- gnashing of teeth.
Other forms of the disease are characterized by less severe symptoms. However, only a veterinarian can make an accurate diagnosis.
Forms
There are several options for the development of the disease. Each of them has a specific clinical picture.
Acute
The acute form of the white mouse is characterized by general weakness of the animals. They suffer from stiffness of movement. It is not uncommon for calves to experience trembling and convulsions. After some time, other signs appear. These include paralysis of limbs or other parts of the body. Paresis may also occur. With this course of the disease, there is a clear disruption of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. This condition is characterized by increased heart rate, which reaches 140-180 beats per minute. In this case, weak and muffled heart sounds occur.
Subacute
This form is characterized by less severe symptoms. The main signs of the disease include a noticeable deterioration in appetite, the appearance of wheezing in the sternum area, and mild depression of the animal.
With the development of the subacute form of the pathology, a sharp decrease in the parameters of the body's resistance is observed.
As a result, he becomes more vulnerable to various pathologies. This leads to the occurrence of inflammatory processes and pleurisy in the calf. This form of pathology is present for 14-30 days. Moreover, in 60% of cases it provokes the death of the calf.
Chronic
The chronic course of the disease is characterized by a clear depletion of the body of cattle and a slowdown in its development. In this case, symptoms of heart failure occur, and anemia develops. Subacute and chronic forms of pathology in calves can cause dangerous health consequences - gastroenteritis and bronchopneumonia.
Diagnostic rules
If white muscle disease is suspected, it is important to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of animal myopathy. It is important to take into account the clinical picture and research results. It is also worth comparing test data with the age category of the animal in order to exclude the development of pathologies with a similar clinical picture.
Fluoroscopy is of no small importance. To assess the functioning of the heart, electrocardiography is recommended. This procedure helps detect damage to the heart muscle. If the calf died, pathological changes help identify myopathy. These include the following:
- severe damage to skeletal muscles;
- an increase in the size of the heart and lungs;
- swelling in the layers of fiber;
- softening of the brain.
Carrying out differential diagnosis is of no small importance. In this case, it is necessary to distinguish the pathology from enzootic ataxia.
How to cure disease in cattle
To cope with the disease at home, you must strictly adhere to the veterinarian’s recommendations and maintain the animal’s normal condition. Once an accurate diagnosis has been made, the sick calf should be immediately isolated. He definitely needs to lay a warm bedding. It will protect the animal from hypothermia and other pathologies.
Compliance with a special diet is of no small importance. It consists of introducing the following products into the diet:
- carrot;
- quality hay;
- bran;
- fresh dairy products.
It is very important to maintain a proper drinking regime. In addition, it is important to monitor the cleanliness of the box and systematically clean it of food debris and manure.
At the same time, there are no specialized medications that help cope with the pathology today. For treatment you should use the following:
- Sodium selenite solution - this helps to replenish selenium deficiency in the animal's body. The product is recommended to be administered subcutaneously.
- “Methionine” - this amino acid allows you to restore impaired metabolic processes.
- “Tocopherol” – ensures the normalization of metabolic processes.
- "Cysteine".
The dosage of medications is determined by the veterinarian - this is done taking into account the stage of the disease.
Folk remedies
Pathology is usually not treated with folk remedies. Camphor oil can be used as an addition to the usual course of therapy. It is also permissible to use Cordiamin. These substances improve the functioning of the heart muscle.
Prevention of white muscle disease
After recovery, calves have difficulty growing and experience many problems. Therefore, the main method of combating the disease is not therapy, but prevention. Even with a selenium deficiency, a healthy calf may not get sick. Therefore, proper nutrition of the female at the end of pregnancy is of particular importance.
During this period, it is recommended to adhere to two-phase feeding with low nutritional value in dry wood 3-8 weeks before the planned calving. However, in the last days it needs to be increased little by little.
The recommended concentrations of calcium and phosphorus, as well as their ratio, also differ. In recent weeks, preventive measures are required that are aimed at preventing ketosis. This violation provokes the birth of weakened calves. To avoid problems, it is recommended to supplement the cattle diet with energy supplements. These include "Felucene" and "Propylene glycol".
A high content of vitamins, especially fat-soluble ones, is of great importance. A lack of carotene increases the need for antioxidants.Therefore, it is worth carrying out preventive administration of “E-selenium”. This product is used by injection.
A couple of months before the birth of a calf, it is recommended that the cow be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Usually 15 milliliters of the substance are used per individual. In this case, 3-4 injections are required with an interval of 2 weeks. White muscle disease is a serious pathology that can cause death in a calf. To avoid this and prevent growth retardation, you must consult a veterinarian in a timely manner and strictly follow his recommendations. However, it is much better to prevent the development of pathology.