Mastitis occupies a leading place among diseases of dairy cattle in modern animal husbandry. The number of sick animals in some cases can reach up to a third of the total number of dairy animals. The damage from mastitis is expressed in a sharp decrease in milk yield and the inability to use milk from sick cows. Let's consider the causes of subclinical mastitis in cows, its symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment.
What is hidden mastitis?
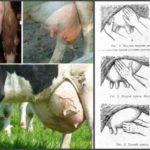
Mastitis in cows can manifest itself in different forms, one of which is subclinical mastitis. Its peculiarity is that it is difficult to determine this form of the disease by its symptoms, since they are practically absent. Subclinical mastitis can be diagnosed only by test results, since inflammation of the udder occurs unnoticed, and the milk has a normal composition and appearance.
However, if mastitis in this form is not detected in time, after some time it will become clinical. It has been established that subclinical mastitis occurs 2-10 times more often than clinical mastitis.
Causes of the disease
Inflammation of the udder is bacterial in nature, but no single pathogen has been identified that causes one or another form of mastitis. Bacteria enter the mammary gland through the nipple or from the body - with blood and lymph. However, even in the presence of bacteria, the disease develops only when the immune function of the entire body or udder tissue decreases. Weakening of the immune system occurs due to keeping cows in a cold, poorly ventilated and insufficiently lit room with drafts, on damp, long-standing bedding, and with limited physical activity.
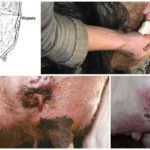
Mastitis can develop at the site of a bruise or wound on the udder, which the animal may receive during walking or transportation. Danger can also lie in wait for cows in the stall - bacteria are found in the bedding, which is often dirty and damp. Unsanitary conditions for keeping animals and lack of disinfection are one of the main causes of mastitis, as well as hypothermia of the udder on a cold floor or in a draft.
The disease can be caused by poor condition of the milking machine and errors during the milking process: if the machine is not configured correctly, this will lead to injury to the udder lobes or a lack of milk.Unsterility of any part of the milking machine and especially the teat rubber, which is in direct contact with the teats, is a common cause of mastitis in cattle.
Mastitis in cows can develop due to endometritis, an inflammation of the uterine lining that animals get after calving. In this case, the inflammation passes from the uterus to the udder, and mastitis develops. Swelling of the udder due to succulent feed can also cause inflammation of this organ.
Symptoms of the disease
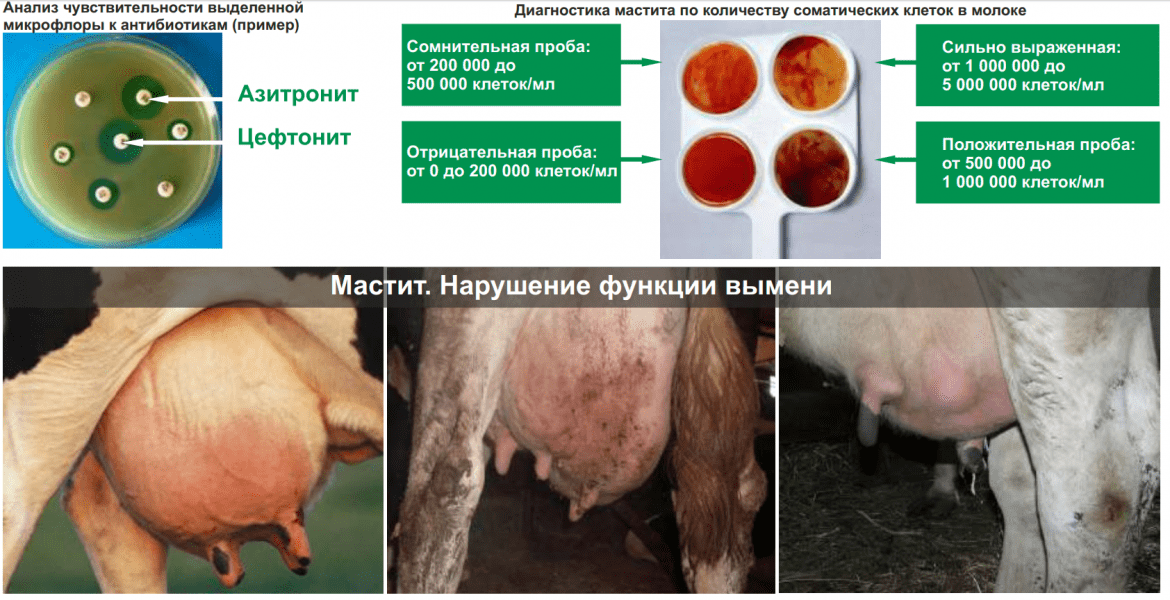
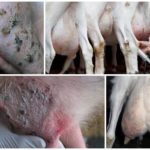
Subclinical mastitis occurs with the absence of clinical symptoms, only upon examination is pathogenic microflora detected, the physical and chemical properties of milk change (lactose content decreases, acidity shifts to the alkaline side, the number of somatic cells sharply increases).
How to determine hidden mastitis in a cow at home
An accurate diagnosis can be established in the laboratory by the content of somatic cells in milk and the reaction with special reagents. Mastitis is determined by changes in the thickness and color of milk. At home, subclinical mastitis can be determined by the settling method - pour milk milked from suspicious udder lobes into a small container, put them in the refrigerator for 15-18 hours, and keep them at a temperature of 5-10 ˚C. Then you need to inspect the milk, if it is white or with a bluish tint, there is no sediment in the container - the cow is healthy, if sediment appears in the container, flakes are present in the cream, this may indicate mastitis.
How to treat the disease
First of all, the sick cow must be separated from the rest of the herd and placed separately from the others. The stall should be dry, warm, ventilated, and light. The animal is put on a diet, reducing the amount of food to reduce milk secretion. If the udder is swollen, reduce the volume of water.
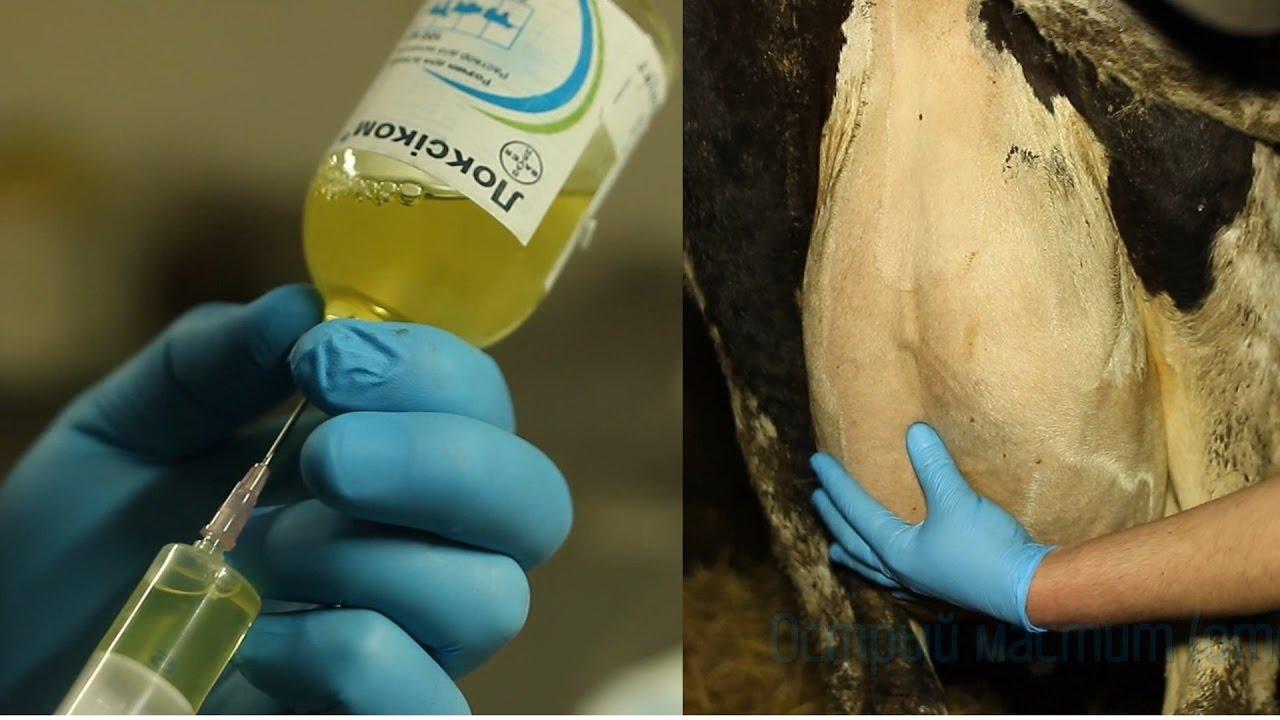
To treat a cow for mastitis, antibiotics are used (Penicillin, Erythromycin and others, depending on the type of pathogen), special medications for mastitis and other drugs in combination to support the body, warming compresses, heating with lamps, light massage of the udder. Therapy should begin immediately after the disease is identified.
If the cow was milked with a milking machine, then you need to switch to more gentle manual milking. Drinking milk until the cow has recovered is prohibited due to the presence of antibiotics in it. After completing the course of treatment, you need to wait a few more days, as indicated in the instructions for the drug, so that it has time to be eliminated from the animal’s body. Due to the unsuitability of milk for consumption during the period of treatment of a cow, it is necessary to select milk from another animal for the calf.
The frequency of milking a sick cow should be increased, this is necessary so that bacteria are removed from the udder along with the milk and swelling is reduced.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment are effective only at the very beginning of the development of the disease. A popular method of treating subclinical mastitis in cattle at home is application of a mixture of clay with a decoction of medicinal herbs: plantain, nettle, yarrow. The mixture is applied to the udder at night, the clay relieves swelling and reduces pain, the herbs act as antiseptics.
Applications can be made from warm paraffin, cabbage leaves, grated carrots, potato starch mixed with butter, baked onions, pork fat mixed with calendula flowers. All products must be warm, not hot; strong heating activates the growth of bacteria and worsens the condition of the cow.
In addition to applications, garlic tincture is used, which is administered through the nipple canal 2 times a day, 15 ml at a time.
Preventive actions
First of all, this is a clean bedding, a warm, dry, bright room with good ventilation. Proper feeding and compliance with milking rules. Regular inspection of the animal's udder; if any diseases are detected, treatment should be carried out. Particular attention should be paid to whether there is swelling of the udder, which is a predisposing factor for the development of mastitis.
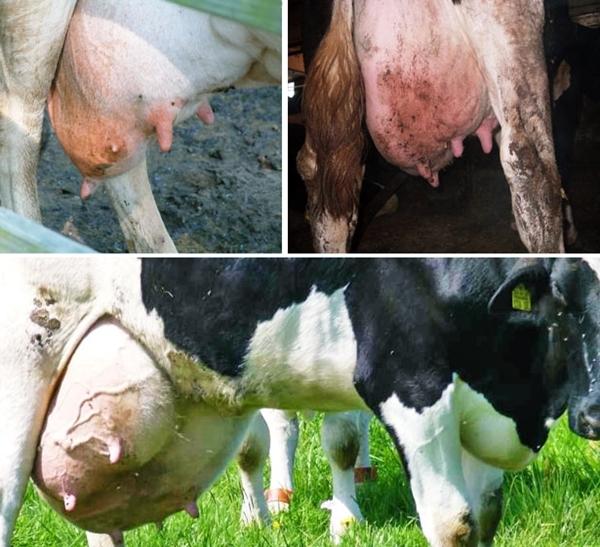
If detection and treatment are not timely, subclinical mastitis easily turns into clinical mastitis, the consequence of which can be atrophy of the udder lobes. The danger of this form of the disease is that without the presence of characteristic signs it is difficult to identify the disease, meanwhile, at this time, the milk from such cows contains bacteria and it is unsuitable for consumption.
Raw milk can cause illness in humans, and if used as a raw material, it reduces the quality of dairy products. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are important in preventing subclinical mastitis.