It happens that a seemingly healthy cow begins to produce milk with a noticeable bitter taste. The deterioration of the taste of dairy products is a serious problem for the farmer, associated not only with difficulties in selling the product, but also with the need to treat livestock. The most common reason why a cow’s milk often tastes bitter is the consumption of spoiled feed and bitter plants, but sometimes the unpleasant taste of the product is a consequence of serious pathologies.
Why can a cow's milk taste bitter?
Rancidity of taste is associated with deteriorating cow health, poor diet, or ignorance of hygienic rules for keeping cattle.
Helminths
Milk tastes bitter due to fascioliasis - damage to cow liver tissue by helminths. Helminthiasis is the cause not only of deterioration in the quality of dairy products, but also of depression in the physical condition of the cow. An infected individual's temperature rises to 40-41 °C, loss of appetite, and vomiting. The liver is enlarged on palpation, the muscles of the peritoneum are compacted.
Symptoms of helminthiasis are most pronounced in the summer months. During the cold season, the only sign may be a bitter aftertaste of the product.
If there are suspicious symptoms, it is necessary to send the cow's feces for laboratory analysis.
Fascioliasis is treated with injectable drugs based on closantel. The injection is given once, the dose is 10 ml per 200 kg of body weight. Powdered medications based on fenzol and fenbendazole are also effective. They are given 2 times with a 2-week interval in the morning during feeding.
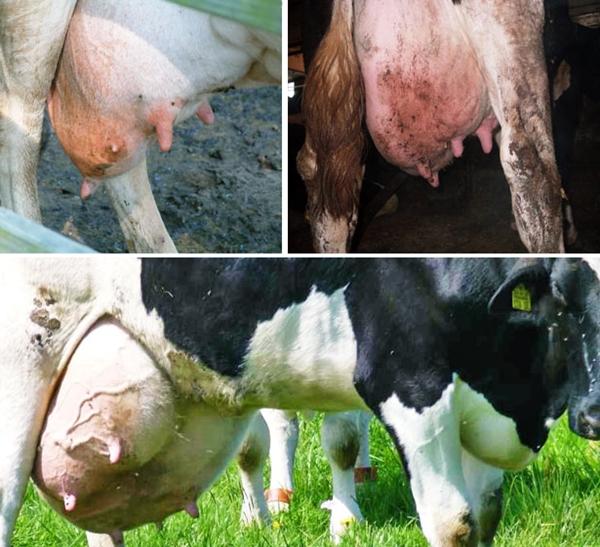
Mastitis
Of all cattle diseases, mastitis is the most common reason why milk tastes bitter. Provocateurs of inflammatory pathology are genital tract infections, mechanical damage to the udder, improper pumping, and ignoring sanitary rules. Milk obtained from a sick cow cannot be used for drinking or making fermented milk products. In cattle, veterinarians diagnose chronic mastitis more often than acute mastitis. The acute form is accompanied by:
- udder swelling;
- development of gangrene;
- purulent and bloody inclusions in milk.
The chronic form is asymptomatic in many cases. The only sign is a change in the quality of the product:
- heterogeneity, presence of clots;
- low fat content;
- bitter taste.
Mastitis is treated with injectable antibiotics “Mamifort”, “Masticide”, “Antimast”. They are used once daily. You should also regularly treat the udder with antiseptic solutions: manganese, ichthyol or Furacilin. Medicinal liquids are injected into the nipple slowly, with extreme caution, without allowing too much pressure. Before the procedure, be sure to express milk.
Other health problems
A common reason why cow's milk tastes bitter is liver dysfunction caused by a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection.
Functional liver pathologies manifest themselves, in addition to rancidity of the product:
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- increased temperature;
- increased breathing;
- swelling and tenderness of the palpable liver;
- decrease in milk yield;
- watery consistency of milk.
Milk becomes bitter and turns yellow due to curvature of the gallbladder and abnormalities of the bile ducts. These pathological conditions are common in cattle; because of them, bile is released in small quantities and accumulates in excess, affecting the quality of the product.
A bitter taste is a consequence of impaired metabolism, leading to fluctuations in blood sugar and excessive accumulation of acetoacetic acid.
Another reason why the product is bitter is an increase in the acidity of gastric juice. If laboratory analysis shows that the milk is harmless and can be consumed, then to eliminate rancidity the product should be heated to 40 °C and then cooled.
When a cow eats soil, gnaws tree bark, or licks concrete and brick walls, a lack of mineral elements should be suspected. Bitter milk suggests that the deficient microelement is cobalt.
Hot in summer
In the warm season, pasture farming is used, so rancidity of dairy products is rarely observed. But on hot days, a cow can become infected with leptospirosis.
The disease affects the vascular system, kidneys, liver, and muscle tissue. A sick cow has diarrhea, fever, yellowness of the integument, and dark urine. Leptospirosis is treated with hyperimmune polyvalent serum. A subcutaneous injection is given, 0.4 ml of the drug is taken per 1 kg of weight.
Problems in winter
In winter, the situation when milk tastes bitter is observed more often than in summer. At low temperatures, bacteria that cause rancidity multiply more actively than microorganisms that cause the product to sour. To prevent the problem, cattle are kept in an insulated and ventilated barn during the colder months. Cows should not stay in stalls all winter; they are periodically taken out into the fresh air. The winter paddock must be regularly cleared of snowdrifts and manure.
Pregnancy
For natural reasons, milk becomes bitter in a cow that is 1-2 months away from calving. Due to hormonal changes in the product, the concentration of leukocytes and casein increases. The milk yield drops and the cow enters the dry period. A few days after birth, the quality of the product returns to normal.
Violation of milking hygiene
If unwashed dishes are used during milking, bacteria and dust particles end up in the milk. Before each milking, the container must be thoroughly washed and the remaining milk from the previous milking must be poured out. Before milking, the worker puts on clean clothes, washes his hands with a hygiene product, thoroughly washes the cow's udder with boiled water, and wipes it with a clean towel.
The first streams of milk are milked into a separate container to be poured out, because they contain a high concentration of reductase, an enzyme that makes milk taste bitter.
Errors in content
If hygienic and sanitary recommendations in the barn are not followed, infection and dirt penetrate the cow’s body, negatively affecting the quality of dairy products. To eliminate factors leading to rancidity of the product, the farmer must:
- Regularly clean the barn and disinfect it;
- maintain optimal microclimatic conditions in the barn;
- wash feeders regularly;
- Replace soiled and rotten litter daily.
Poor quality feed poisons the cow’s body and increases the acidity of gastric juice. To prevent milk from becoming bitter, the following should not be given to livestock:
- rotten, moldy hay, grain;
- poisonous herbs;
- spoiled cake;
- flax seed meal;
- yeast.
Bitter herbs in the diet
The aromatic substances contained in plants accumulate in the mammary glands. Products obtained from a cow that has eaten:
- rowan;
- sagebrush;
- yarrow;
- spicy crops - dill, garlic and onions, cumin;
- vegetables - potatoes, rutabaga, carrots.
In order for the milk to become bitter, the cow must eat the listed plants for several days. In the spring, a cow may eat horsetail, and its milk will become foamy and have a soapy taste. And excess beet silage gives the taste of herring.
How to prevent the problem from occurring
In order not to experience changes in the taste of dairy products, you must follow the recommendations listed in the table.
| Problem | Preventive measures |
| pre-calving period | the problem goes away on its own, signals the start of the start |
| mastitis | the veterinarian recommends antimicrobial drugs for injection into the nipple in prophylactic doses |
| helminthiasis | antiparasitic treatment 2 times a year |
| decreased blood sugar | feed is enriched with a small portion of sugar |
| high acidity | using licking stones containing soda, adding soda to the food (1 small spoon per 10 l) |
| cobalt deficiency | cobalt chloride tablets are used, the prophylactic course lasts a month, 2 tablets per day |
| leptospirosis | walking the herd away from wetlands and floodplains, organizing a watering point, gradual transition from winter to summer housing |
| poor hygiene | the stalls are regularly cleaned, the barn is ventilated, the udders are washed and wiped dry before milking |
| poor quality feeding | hay and grain feed must be fresh and of high quality; daily portions of beets, potatoes, tops must not be exceeded |
Why is sour cream bitter when the milk is normal?
Good milk can spoil due to improper storage, resulting in sour cream and other fermented milk products turning rancid. At enterprises, products are pasteurized, so they are stored longer, but homemade milk quickly spoils and bacteria multiply in it.
Milk prepared for making sour cream begins to taste bitter when it sours if taken from a cow that has undergone antibiotic therapy.
Sour cream begins to taste bitter when:
- standing in direct sunlight;
- storage at high temperatures;
- using iron or copper utensils;
- improper handling of storage containers.
Spoiled sour cream should not be eaten due to the risk of poisoning. Heat treatment will not help restore the product's suitability for consumption.By observing sanitary and hygienic standards and following preventive recommendations, the farmer will receive only tasty and sweet milk from the cow.