A dangerous and quickly transmitted disease among poultry must be detected in time by the breeder. Timely treatment will prevent its spread and preserve the livestock population. Therefore, it is important to distinguish the symptoms of pasteurellosis in domestic chickens from other diseases in the early stages of the disease, to know how to prevent it and how to deal with it.
- Characteristics of the disease
- Causes
- Symptoms of the disease
- Super acute
- Acute
- Chronic
- Methods for diagnosing the problem
- How to cure Pasteurellosis in chickens
- Kobaktan
- Trisulfone
- Levoerythrocycline
- Tetracycline and Doxycycline
- Prognosis and treatment time
- Vaccines and vaccination
- Possible consequences
- Danger to people
- Prevention
Characteristics of the disease
This disease, also called chicken cholera, is widespread throughout the world. It is transmitted through the digestive and respiratory tract, as well as through damaged areas of the skin, then spreading through the blood throughout the body.
Pasteurellosis is caused by bacteria of the species Pasterella multocida and Pasterella Haemolytica, which are weakly resistant to high temperatures and disinfectants. Not only poultry, but also other small animals are susceptible to the disease. The infection can also be transmitted to humans.
Pasteurellosis is especially dangerous for eggs and chickens. The infected embryo not only dies within 1.5 weeks, but also transmits the infection to other eggs through the shell. If death does not occur (if the future chick is infected with non-aggressive species of Pasteurella), the hatched chicken is already a carrier of pasteurellosis from birth, dangerous for its fellows.
Causes
The infection spreads through food and water contaminated with bacteria, through the bites of sick animals (mice, dogs), insects (botflies, mosquitoes) and parasites (bird mites), through the remains of the bodies of dead animals, by airborne droplets, and less often through contact with the manure of a patient livestock
The most dangerous is infection from a dead infected bird. Keeping chickens too closely in one room has a bad effect on the health of chickens.
Cool, damp weather observed in spring and winter is favorable for the development of bacteria.
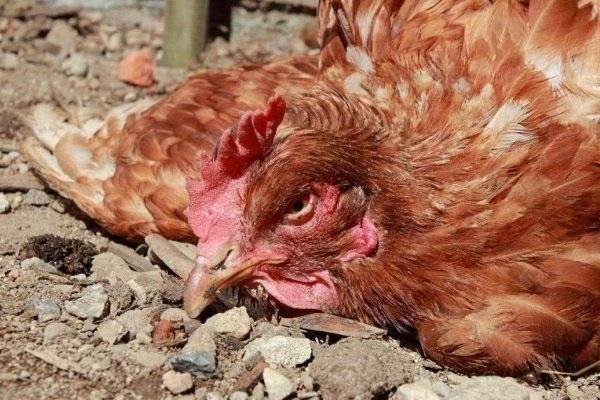
Symptoms of the disease
The incubation period of the disease lasts from several hours to 4 days.
Then the following symptoms appear:
- heavy intermittent breathing;
- discharge from the nasal cavity of the beak;
- darkening of the beard and comb;
- decreased appetite due to severe thirst;
- reduction in the number of eggs.
Signs of the disease may appear gradually or all at once.
Pasteurellosis in birds can occur in three forms: hyperacute, acute and chronic. Each form is characterized by its own symptoms and course characteristics.
Super acute
The hyperacute form of the disease entails mass death of birds. In this case, there are no symptoms, the infected individual suddenly closes its eyes and falls to the ground, dying. This form of the disease mainly affects waterfowl, but can also affect chickens.
Acute
The acute form is characterized by the sudden appearance of symptoms of the disease. The chicken's temperature rises to 44C, green diarrhea containing bloody spots appears, the bird breathes heavily, drinks a lot and refuses to eat.
The disease can quickly spread to the entire herd. With this course of the disease, chickens die within 1-3 days. Surviving individuals remain carriers of pasteurellosis for life. With timely treatment measures taken, up to 70% of the livestock can survive.
Chronic
After suffering an acute form, as well as when a non-aggressive type of Pasteurella enters the body, chickens develop a chronic form of the disease. You can notice this by the following signs:
- poultry exhaustion;
- heavy breathing, nasal discharge;
- poor appetite;
- swelling of the limbs, ridge, pain when moving;
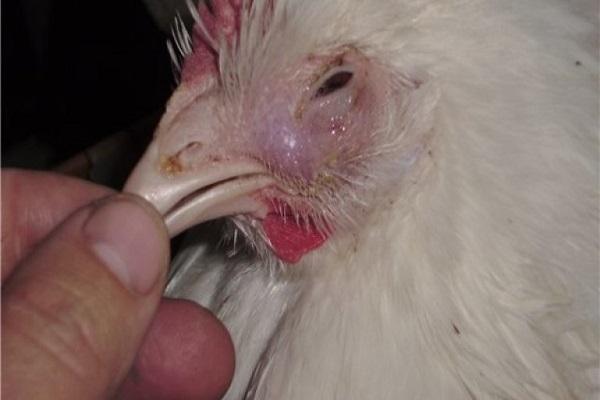
- eye inflammation;
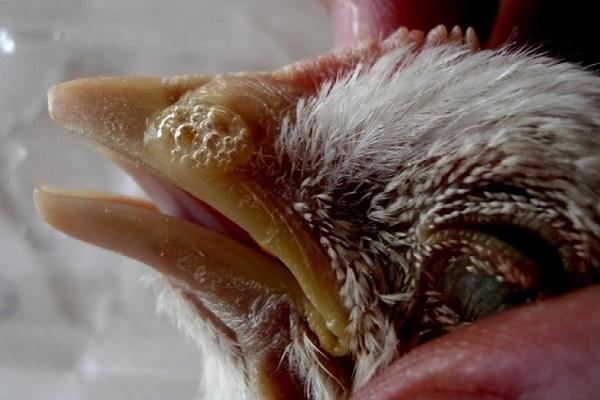
- the formation of bumps on the head;
- decreased egg productivity.
With this form of the disease, chickens live for several months. With proper treatment, recovery occurs, but the bird remains a carrier of bacteria for life.
Methods for diagnosing the problem
Since the symptoms of pasteurellosis are similar to those of other chicken diseases (bird flu, salmonella), identifying the disease by external signs alone is difficult.The diagnosis is made either on the basis of a post-mortem examination of a dead chicken, or after laboratory analysis of particles from the organs of dead individuals.
Therefore, if even a single symptom occurs in an individual, it is isolated from the rest as soon as possible, and the use of medications is immediately started.
How to cure Pasteurellosis in chickens
Pasteurellosis is treated with antibiotics and special serum. In this case, the bird needs a dry, warm room and increased nutrition. The effect will only be achieved if the medications were used in the first 2 hours after the onset of symptoms. In factories and large farms, sick chickens are immediately killed and disposed of. Eggs of sick individuals must also be destroyed.
The latest developments in the treatment of pasteurellosis in chickens are Cobactan, Trisulfone and Levoerythrocycline.
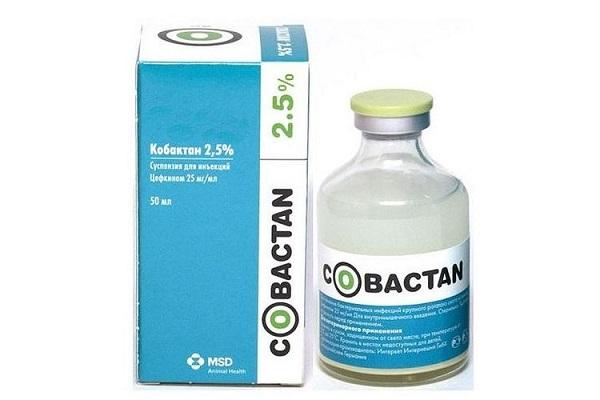
Kobaktan
A new generation antibiotic, available in the form of injection suspensions. It is administered intramuscularly once a day for 3-5 days. The dosage is agreed with the veterinarian. After administration, you need to monitor the condition of the bird, as allergic reactions are possible.
Trisulfone
Antibacterial drug in the form of white powder. It is given to the bird along with drinking water for at least 5 days. The solution must be prepared daily. Eggs of laying hens taking medication should not be eaten.
Levoerythrocycline
A complex preparation in the form of a viscous dark liquid. It is administered intramuscularly for 5 days. Can be used both for treatment and for prevention purposes. The dosage is determined by the doctor.
Tetracycline and Doxycycline
Broad spectrum antibiotics classically used to treat pasteurellosis. They are administered intramuscularly, the dose is determined by the veterinarian.Can be used topically as ointments to treat skin lesions and eye infections.
Prognosis and treatment time
Pasteurellosis is considered an incurable disease.
Even if the chicken does not die, it remains a carrier of the bacteria for the rest of its life. Only preventive treatment of healthy individuals makes sense. The course takes five or more days.
Vaccines and vaccination
Disease prevention is the most effective way to combat pasteurellosis. The following drugs are used for vaccination:
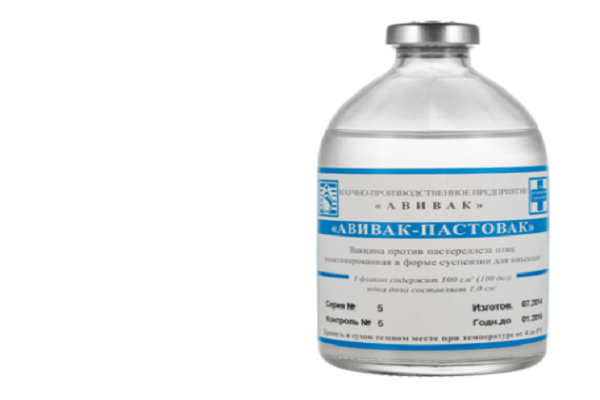
- Avivak-Postavak or Avivak in the form of a suspension;
- Diavak;
- VGIIVIP (suspension).
Chickens begin to be vaccinated at one month of age. After this, immunity to Pasteurella develops in the bird within six months.
Together with vaccines for the prevention of chickens give Floron, Avidox or Norsulfazol, add antibiotics to the food (chloramphenicol, doxycycline, tetracycline), and use other antibacterial drugs. It is recommended to vaccinate only in areas unfavorable for pasteurellosis.
Possible consequences
In case of frequent epidemics of chicken cholera, it is recommended to stop breeding birds for several years.
Danger to people
When contacting sick chickens, a person can also contract pasteurellosis through microcracks in the skin.
Therefore, it is important to only wear special clothing and gloves in an infected chicken coop.
At the first suspicion of infection, you must immediately contact a medical organization.
Despite the fact that Pasteurella dies during heat treatment, and cooked chicken meat is not dangerous to humans, it is still recommended to dispose of the carcasses of sick birds.This is due to the fact that it is impossible to guarantee proper cooking of meat, which means there remains a risk of infection.
Prevention
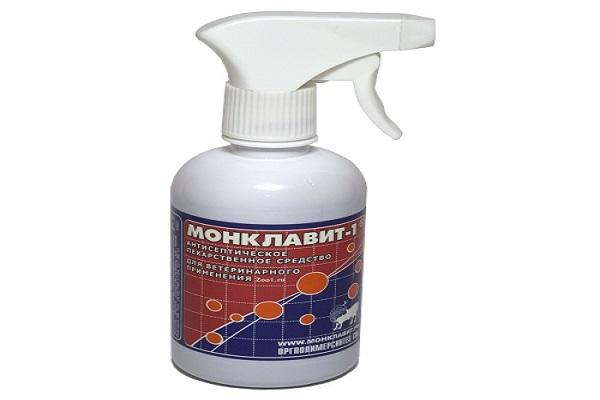
The most effective method of prevention is disinfection of the chicken coop. The treatment takes place in the presence of chickens in order to kill bacteria in the bird's feathers. Aerosol Monclavit and its analogues are used for this.
After the first treatment, the chickens are transferred to another room, and the chicken coop is sprayed with 5% bleach. After this, the room is whitewashed. Whitewash the walls and ceiling three times, each time allowing the previous layer to dry for an hour.
The area where the chickens roam is also treated. The grass is mowed off, the area is left in the sun, and two weeks after that the ground is dug up with lime.
To prevent the disease, it is important to monitor the quality of water and feed, pay attention to hygienic conditions, and protect the poultry house from possible contact with potential carriers of pasteurellosis.
Infection with pasteurellosis always causes great damage to the breeder. Since treatment is ineffective, the best way to combat the disease is prevention.