Broiler chickens are more susceptible to bacterial and viral diseases and poor quality living conditions than chicks of conventional breeds. To preserve young livestock, poultry farmers use certain medications. Below is detailed information on how to properly feed chickens with antibiotics and vitamins; the table shows the procedure diagrams.
- Features and expediency of drinking
- What diseases are chickens susceptible to?
- Drinking schemes
- The most common drugs
- Vitamin
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Water-soluble complex
- Antimicrobial
- Traditional antimicrobial agents
- Professional antimicrobials
- When and how are chickens vaccinated?
- Relocation of chickens to the poultry house
- Advice from experienced poultry farmers
Features and expediency of drinking
Farmers have an ambiguous attitude towards drinking. Some believe that the procedure is extremely important for the preservation of young animals. Others believe that it is enough to follow the rules of care and feed the chicks well for them to survive. Some poultry farmers give antibacterial and vitamin preparations to chickens already in the first days of their life, others use only vitamins.
The need for watering is influenced by the breed of young animals. If the chickens are ordinary, then the procedure is not necessary. If you purchased a broiler or hybrid breed that is susceptible to unfavorable conditions, then it is necessary to solder it. Otherwise, there is a high probability of losing the entire livestock.
The drugs used for drinking not only prevent fatal pathologies, but also have a positive effect on the development of the body, the functioning of the digestive system, and help increase the productivity of birds in the future.
To choose the right drinking regimen, you should ask the seller:
- whether any drugs were used before the sale of young animals;
- what medications were used;
- whether young livestock were vaccinated;
- whether any illnesses occurred in the parents of the brood.
What diseases are chickens susceptible to?
The body of newly hatched chickens is susceptible to infection and other adverse factors. If you ignore the rules of care in the first few days, you can lose 40-100% of the livestock.
Purchased chicks raised in an incubator are especially sensitive.
The most severe mortality of broilers is observed on days 10-14.
Newborn chicks are susceptible to pathologies associated with:
- weakened immunity;
- previously used drugs;
- drafts, temperature fluctuations and other unfavorable conditions.
A sick chicken is identified by the following symptoms:
- inactive behavior, constant sleepiness;
- poor appetite;
- lack of reaction to the switched on light and other stimuli.
A sick chick is separated from its brethren, as it can become a spreader of infection.
Drinking schemes
Choose one of two drinking schemes.
In the first regimen, the use of antibiotics is postponed. The principle is based on the fact that in the first days of life, chicks have a sterile intestinal microflora, so good nutrition and the use of vitamins are enough to populate the intestines with beneficial microorganisms and form a strong immune system.
Table of the first drinking regimen.
| First day | Newborns should be given dissolved glucose to drink so that the residual yolk is absorbed faster. The solution has an immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory effect, strengthens the digestive system, and reduces susceptibility to stress. Use a 3 or 5% solution. You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself: 1 teaspoon of sugar per liter of water. |
| 2-7 days | The use of vitamins begins. A good option for drinking is the Lovit complex (5 ml dissolved in a liter of water). |
| 8-10 | Antibiotics are administered according to the instructions: Baytril, Enrostin, Enroflox. |
| 11-18 | Pause between courses. |
After a pause, the course is repeated, and so on throughout the life of the bird.
In the second scheme, shown in the table below, broilers are given antibiotics from birth.
| Until 5 days | Antibiotics are used: Baytril (1 ml ampoule per 2 liters of water), Enroxil - according to the instructions. |
| 6-10 | Vitamins used: Chiktonik complex or Aminovital (2 ml per liter of water). |
| 11-14 | Prevent coccidosis. Usually the drug Baycox is used (1 ml ampoule with a 2.5% solution per liter of water). |
| 15-18 | Repeat the course of vitamins according to the same scheme. |
| 19-22 | Repeat the course of antibiotics. |
The most common drugs
There are a large number of drugs available on the market for feeding day-old and week-old chicks. Before carrying out the procedure, you should carefully study the instructions for the antibiotic and vitamin complex.
Vitamin
Vitamin complexes for drinking are divided into fat-soluble and water-soluble.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Experienced poultry farmers use the following vitamins for feeding:
- Fish oil, saturated with vitamins A, E, D, important for the full development of the bird's body. When using the product, you should carefully monitor its shelf life, which is no more than 6 months under correct storage conditions. Spoiled fat is extremely harmful to chicks.
- Trivit, based on vitamins A, E, D. To prevent hypovitaminosis, the solution is instilled into the nostrils of birds and mixed with food.
- Tetravit. The composition is similar to the previous one, plus vitamin F (unsaturated fatty acids).
Water-soluble complex
Vitamins for drinking:
- Chiktonik, which is a mixture of vitamins A, D, E, amino acids. The liquid solution has an anti-stress effect, so it is given not only to young animals, but also to transported chickens to calm them down (within 3 days before and after transportation).
- Aminovital. The composition is similar to the previous one, but minerals and ascorbic acid are added.
- Nutril Se is a powder complex used as an immunostimulant. The amino acid composition is small, but there is selenium - a strong antioxidant.
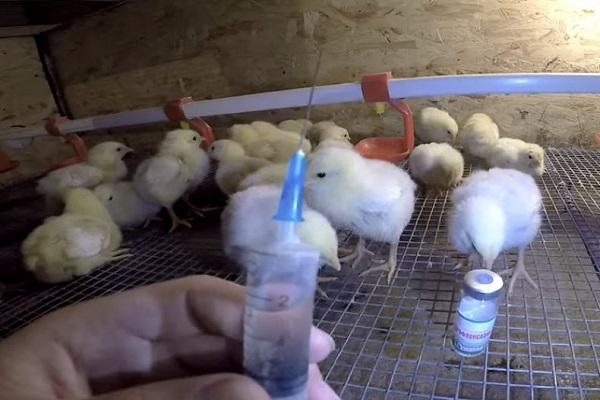
Antimicrobial
If vitamins are completely harmless for both chicks and people who eat chicken meat, then caution should be exercised with antibiotics.There are time limits for consuming poultry that has taken medications. But it is difficult to do without antibiotics.
There are simple antimicrobial agents used in private farmsteads, and professional ones for poultry farms.
Traditional antimicrobial agents
Owners of private farmsteads usually use antibiotics:
- injectable Penicillin (ampule per day of drinking sick chickens);
- Tetracycline;
- Levomycetin;
- Biovit is a product derived from tetracycline, saturated with B vitamins.
The problem is that the listed medications should be used extremely carefully so as not to harm either the chickens or yourself. Some farmers abuse antibiotics, and then eat themselves and send harmful meat and eggs for sale.
Professional antimicrobials
Poultry farmers use antibiotics during the most dangerous periods of chicks’ lives: on the first, fifth and eighth days.
It is unacceptable to give medications to 4-week-old broilers, since the chemicals will not have time to leave the body before slaughter.
Antibiotics are used:
- Enroflox. 0.5 ml per liter of water. Use within 5 days.
- Enromag. The dosage is similar. Water change daily.
- Keproceril. 10 g per 10 liters of water. Reception within a week.
- Tylosin. 5 g per 10 liters of water on days 1-3 of life. For consolidation - a single application at 4 weeks of age.
- Tromexin. 5 g per 10 l. Use from 5 days of age for 5 days.
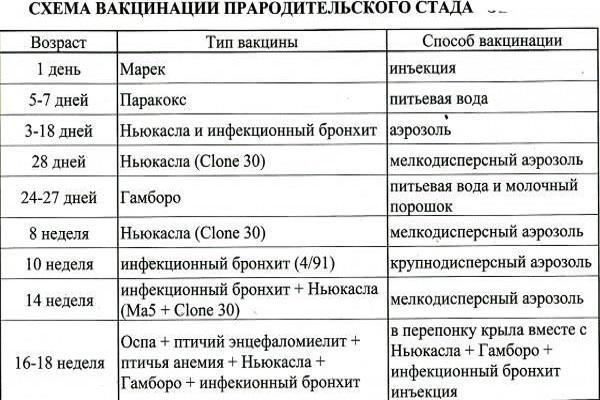
When and how are chickens vaccinated?
Vaccination is a good way to protect young animals from infectious diseases. The procedures are carried out according to a strict scheme, including 3 stages:
- Prevention of bursitis and bronchitis. The Nobilis vaccine is used for 2-week-old chickens.The contents of one ampoule are dissolved in warm water and the birds are given water.
- Repeated use of the Nobilis vaccine for 24-day-old chicks. Take 7.5 ml of ampoule solution per individual.
- 3 days after the previous one. The La Sota vaccine against Newcastle disease is used, it is diluted in water for drinking or instilled into the nostrils and eyes. Take 7.5 ml per individual.
Relocation of chickens to the poultry house
Before chicks are moved, new cages should be disinfected. Biodez-R and Virkon-S 2% concentrations are used. The treated chicken coop should remain closed for 30 minutes, then it must be ventilated. Next, treatment is carried out with the antiparasitic agent Butox (dissolved in water in a ratio of 1 to 2). Ventilate the chicken coop again for 5 hours.
Advice from experienced poultry farmers
Recommendations from poultry farmers regarding drinking:
- Antibiotics are given strictly according to the schedule. If you do not follow the course, pathogens will develop resistance (immunity) to drugs.
- The preparations are diluted in settled water.
- Drinking solutions are not prepared in advance. The next day they are no longer useful. Fresh medicine is made for each appointment.
- All drinking bowls are thoroughly washed before the next course of antibiotics.
It should be remembered that excess antibiotics are harmful. If the young animals are healthy, then there is no need to be zealous with prevention. However, it is unlikely that it will be possible to do without medications at all, especially when raising hybrid and broiler breeds with weak immunity.