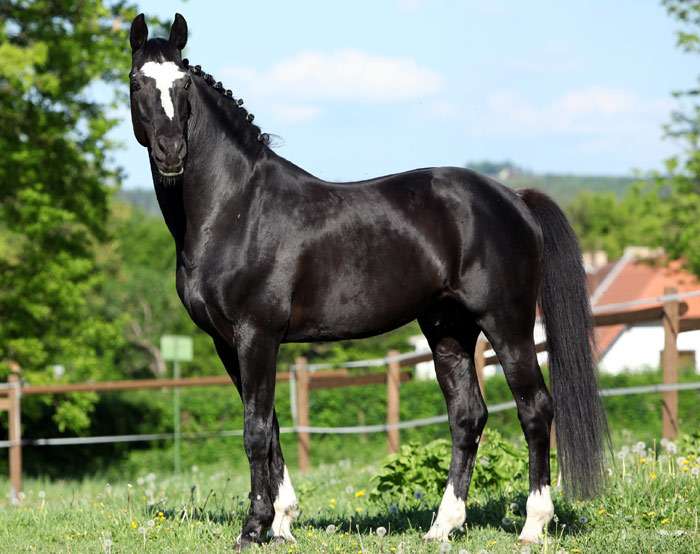
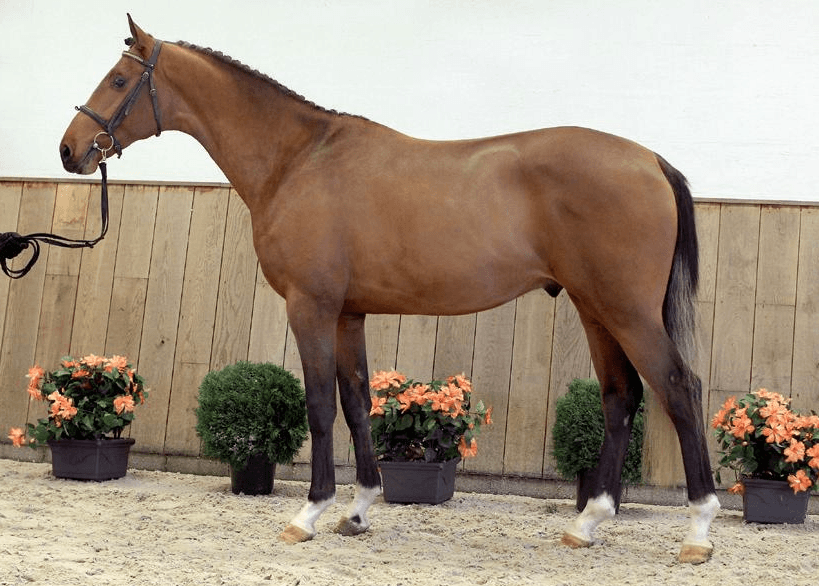
The elite color of Dutch Warmblood horses is popular all over the world. Proportional horses achieve success in equestrian sports and are distinguished by high intelligence. The Dutch Warmblood horse breed gained official status in the 20th century, during a period when horse riding was gaining popularity everywhere. Graceful horses are easy to train and are endlessly devoted to humans.
History of the breed
Warm-blooded horses are those bred by crossing purebred thoroughbred horses with draft horses. The Gelderlander and Groningen are recognized as the ancestors of the Dutch beauties. In addition, according to breeders, when creating the breed, different types of horses were used for mating. Thus, among the “Dutch” one can find Trakehner, Hanoverian, Westphalian, Holstein, Oldenburg and other characteristics.
The breed was officially registered in the KWPN studbook in 1959. At the same time, work on improving the breed continued, and after 20 years the species was improved. Another 10 years later, the Dutch warmblood received the royal title.
Description and characteristics of the Dutch Warmblood horse
The main purpose of Dutch warmblood horses is horse riding and participation in equestrian sports competitions. A correct, proportional body shape with a classic type of silhouette are the distinctive features of the exterior. Characteristics and description of the breed:
- classic type of croup;
- proper balanced physique;
- running – soft, fast, graceful;
- the average height of a stallion is 168 centimeters;
- different colors are allowed;
- the chest and neck are muscular and well developed;
- the legs are long, strong, the muscle relief is clearly defined on the hips;
- the character is peaceful, obedient, horses are devoted to humans.
The ability of animals to participate and win in equestrian sports is determined by genetic endurance and a tendency to learn and train. Currently, a strict selection is being carried out among representatives of the breed; artiodactyls with minor defects are quickly discarded.
Note: horses with a height at the withers higher than 170 centimeters are not suitable for equestrian competitions; with such a physique, a huge load is created on the joints and tendons.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of the breed include:
- intelligence and humility;
- strong muscular body and “light” legs;
- endurance and perseverance;
- ability to adapt to changes in environment and region of detention;
- aesthetic appeal of purebred representatives of the breed.
A wide, powerful chest, combined with strong legs and correct body proportions, allows horses to carry a team with their heads held high, which makes the Dutch beauties unique in the class of draft horses.
The disadvantages of Dutch warmbloods include:
- in tall specimens, joint injuries are likely;
- Due to the frequent birth of foals that do not meet all breed criteria, a strict system for evaluating breeding stallions and mares is necessary.
Even after an animal is recognized as a purebred representative of the breed, it will have to be periodically sent for re-evaluation throughout its life. Observation of representatives of the breed, according to the rules, is carried out throughout their lives.
Subtleties of maintenance and care
In order for a horse to be happy, healthy and delight its owner with its achievements, it is necessary to provide the animal with regular care, create a balanced diet, and equip the stable.
Stable
Dutch Warmblood horses can be kept in three ways:
- in the stable;
- herd;
- stable-pasture method.
The most practical method of keeping is considered to be the stable method. The bedding on the floor needs to be changed. The building where horses live should not be allowed to become stuffy, but the wind should not blow around either.In regions with cold climates, the walls, floor and ceiling of the room should be insulated. An important requirement for creating comfortable conditions for animals is maintaining cleanliness. Regular cleaning and disinfection of stables is recommended.
Hygiene
Thoroughbred horses need regular care: washing, combing the mane and tail, maintaining healthy legs and hooves. Horses must be washed frequently, once a week; in hot weather, the cloven-hoofed animals are given a bath even more often. The mane and tail are washed with shampoo and conditioner. After a shower, the animals are wiped dry and combed. To avoid diseases of the legs and hooves, take care of clean and dry bedding.
After each training or grazing, the hooves are wiped with a stiff brush, and dirt is thoroughly cleaned from the hooves. The water should not be ice cold or very hot.
Nutrition
Features of feeding Dutch horses:
- the optimal number of meals is 3 times a day;
- food must be fresh and balanced;
- the calorie content of the diet is determined by the age of the animal, depending on physical activity and the characteristics of its maintenance;
- in the autumn-winter period, the amount of vitamins in food is increased with the help of supplements;
- horses should always have table salt in their diet;
- after feeding, the horse is sent for walking or training no earlier than 1 hour later;
- the water should be clean and not cold;
- The feeder and drinking bowl are periodically disinfected and washed thoroughly after each meal.
The basis of the working horses' menu is hay, vegetables and feed. Fresh vegetables, seaweed, garlic, yeast, and nettle are used as fortified supplements.
Disease Control
Dutch warm-blooded horses are genetically endowed with strong immunity and are excellent at adapting to new conditions.But this positive quality does not mean that you can refuse vaccinations and routine deworming.
The main factors provoking the development of diseases include:
- improper maintenance of horses;
- birth defects;
- dirty, damp bedding, presence of mice and rats in the stable;
- lack of ventilation in the room where animals are kept;
- an outbreak of infection among individuals housed in the same stable;
- the diet is not balanced, the quality of the products is questionable.
Artiodactyls need regular examination for signs of disease. Decreased appetite, unmotivated aggression, loose stools, bloating, fluid leaking from the eyes, skin defects, unpleasant odor and increased body temperature are reasons for urgent examination of animals by a veterinarian.
Features of crossing and breeding
Working on the breed, creating standards, culling animals is the work of breeders who gave the world a unique breed. It is important to take a responsible approach to selecting a pair to create offspring. The best age for producing offspring in horses is 3-4 years, although animals reach sexual maturity earlier. To obtain high-quality offspring, a novice breeder is recommended to turn to professionals.
Modern use
The Dutch breed of warmblood horses is multifaceted and versatile. Currently, foals of this species are purchased for participation in equestrian competitions and for harness riding. The horse is ideal for riding and is capable of working on a farm.
The cost of elite horses can reach huge sums, so representatives of the breed are valued by collectors, and the royal status of the breed is recognized throughout the world.