Growing cucumbers in protected soil includes the prevention and control of various diseases that lead to rotting of plants and fruits. The most common of them:
- white rot on cucumbers;
- gray rot;
- fusarium root rot;
- late blight root rot;
- fungal and bacterial rot of fruits;
- physiological blossom end rot of fruits.
Why do cucumbers rot in a greenhouse?
The main causative agents of putrefactive diseases are fungi.High humidity of protected soil and unstable temperature provoke the spread of infection. Water evaporated by plants is constantly retained inside the greenhouse structure. Excess moisture deposited on the stems and leaves becomes a favorable environment for the growth and development of fungicove.
Causes:
- irregular ventilation;
- poor ventilation due to dense plantings and improperly formed bushes;
- untimely removal of weeds;
- temperature in the greenhouse is below 18-16℃;
- the temperature in the greenhouse is above 28-30℃;
- contaminated soil;
- infected seeds;
- dirty tools and shoes;
- bushes are not rejuvenated, dry and yellowed leaves of cucumbers, spoiled and overripe fruits, and branches that bear fruit are not pruned;
- too much or unstable watering;
- watering with cold water (below 20-22℃);
- excess fertilizing with a high nitrogen content;
- insufficient fertilizing;
- allowing fruit to contact the soil;
- inaccurate collection of cucumbers, allowing mechanical damage to plants and fruits.
Autumn events
After the end of the season, all plant residues, along with roots, are removed from the greenhouse and burned. It is in them that the main part of the fungi overwinters.
Greenhouse growing conditions complicate crop rotation. Typically, a structure is built to grow one crop. Therefore, every year the fertile soil layer should be completely replaced. The soil quickly accumulates fungal diseases and pests.
Some vegetable growers practice treating the soil with fungicides and insecticides. Even with this method, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil 5-6 cm, in which the bulk of pests and fungi accumulate. Thermal treatment of soil with steam has proven itself well.
All parts of the structure and tools must be treated with an antiseptic, for example, bleach (400 g per 10 liters of water).
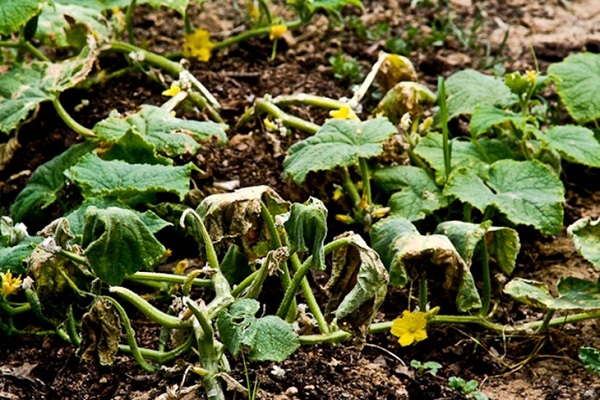
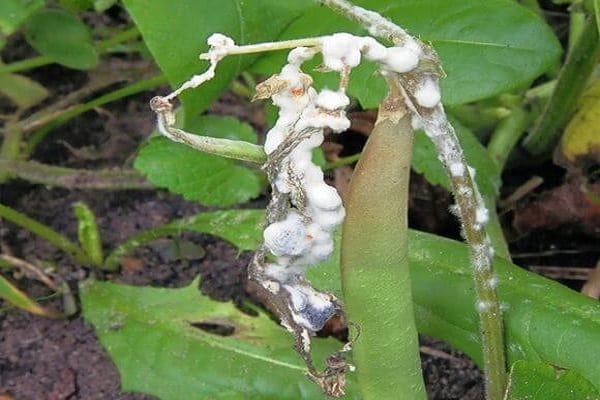
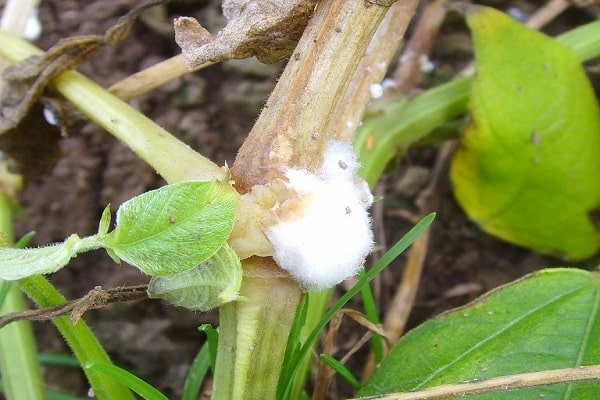
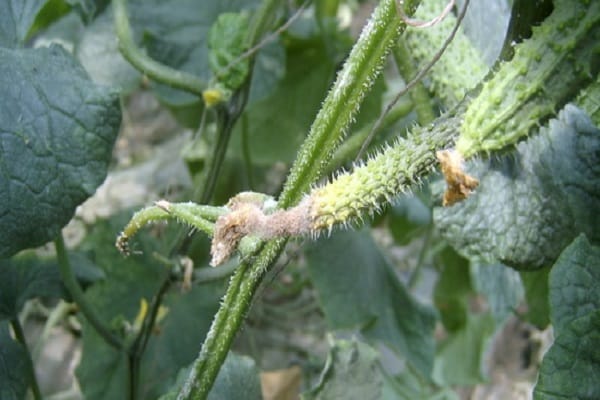
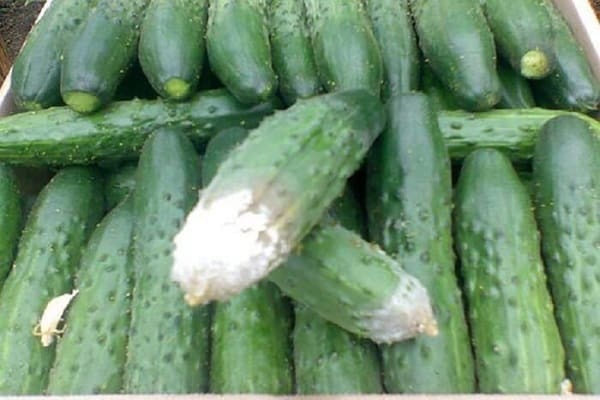
White rot
The sclerotinia fungus, also called white rot, affects many cultivated plants, including the pumpkin family.
Most often, outbreaks of fungal diseases of cucumbers in a greenhouse occur in early spring and autumn, when it is most difficult to achieve normal temperature and humidity conditions.
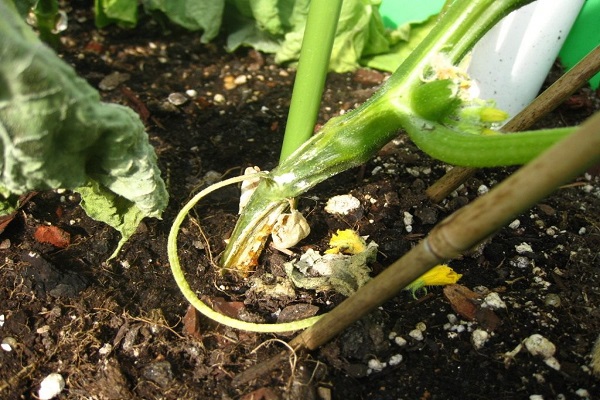
The optimal temperature for the development of sclerotinia is 12-16℃. Foci of white rot are usually located on the forks of the stem and in the root part. Any place with mechanical damage is especially vulnerable. With thickened plantings, white rot quickly spreads in the bed between the plants.
Foci of infection first take on a rotten, weeping appearance, and then they are covered with a white cottony coating. This is the sclerotinia mycelium growing, which gradually falls off and hardens. Hard round inclusions are formed inside - sclerotia. The plant part in this place becomes soft and slimy. The stem becomes macerated and breaks, the affected fruits become flabby.
Treatment
Treatment of white rot on cucumbers in a greenhouse consists of:
- removing deeply affected branches of the bush;
- cutting and cleaning shallow areas of decay with a knife;
- treating superficially affected and cleaned areas of the stem with a mixture of chalk and copper sulfate (1:1)
- treating all bushes with fungicides: copper oxychloride (2.4 kg/ha), foundationazol (0.8-1.0 kg/ha), Bordeaux mixture (1%).
If you do not get rid of the infected parts of the bushes at the beginning of the disease, the fungus will kill the entire plant and begin to spread microscopic pieces of mycelium through the air. After contact with infected cucumbers, tools, gloves and clothing should be washed with soap and treated with fungicides.
Advice!
Removed bushes should be immediately burned outside the site, since white rot can affect most cultivated plants.
If the disease is detected at an early stage of development, you can try to treat the areas affected by rot with a mixture of chalk and copper sulfate.
It is also necessary to take the following control measures:
- treat all cucumbers in the greenhouse with fungicides;
- reduce watering to a minimum for 10-14 days;
- ventilate greenhouses twice a day;
- feed the cucumbers with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers;
- achieve an increase in temperature to 25-26 ℃.
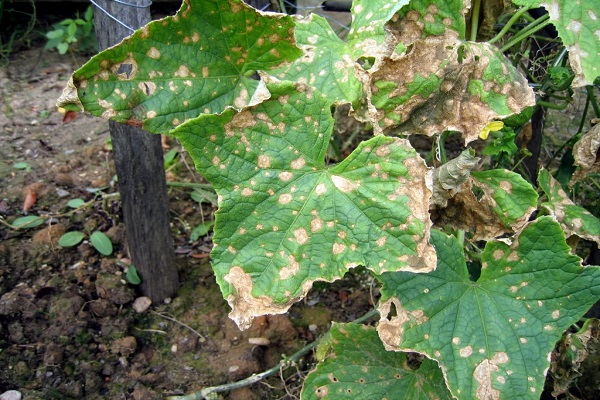
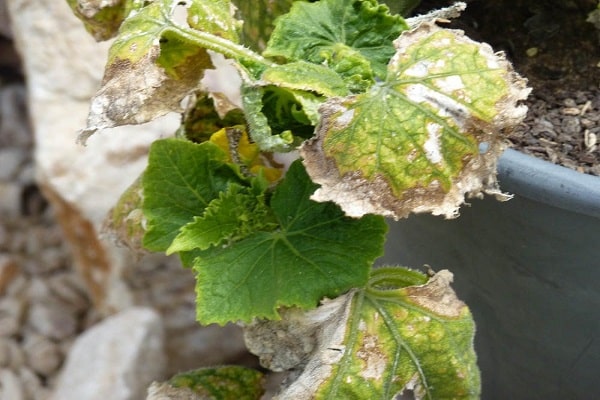
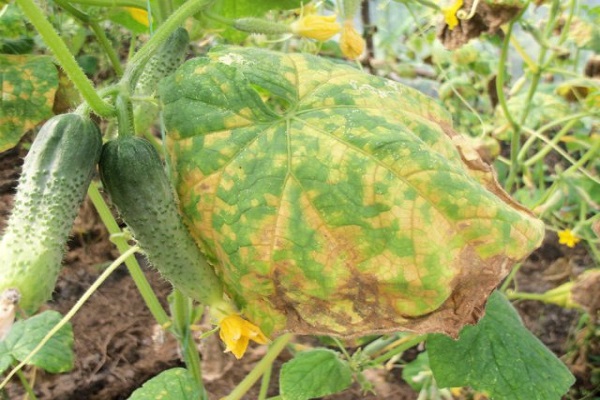
Gray rot
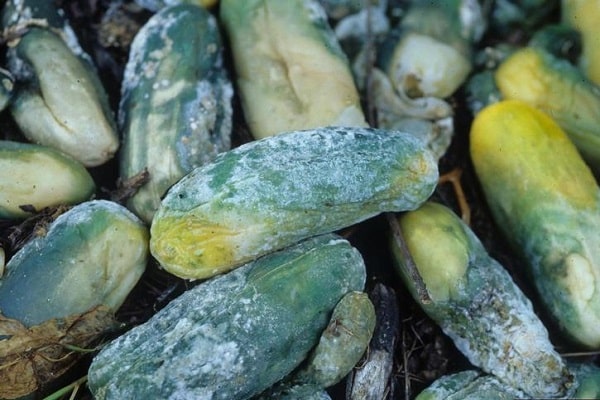
Another type of fungus called Cucumber Gray Rot (Botrytis cinerea) is also a common unwanted guest in greenhouses. Most often, foci of infection occur at the site of mechanical injuries. The ovary becomes infected through the pistil scar.
High humidity (above 90%) at a temperature of 15-16 ℃ are optimal for the development of gray rot. The initial source of infestation is usually untreated greenhouse structures, contaminated soil, and uncollected plant debris.
Signs of the onset of the disease are wet, loose spots, which over time become covered with a fluffy gray coating. The plant part under the fungus quickly softens and rots.
Fighting methods:
- cessation of foliar feeding;
- reducing humidity in the greenhouse;
- removal of infected bushes and fruits;
- treatment with fungicides (“Euparen multi”, “Trichodermin”)
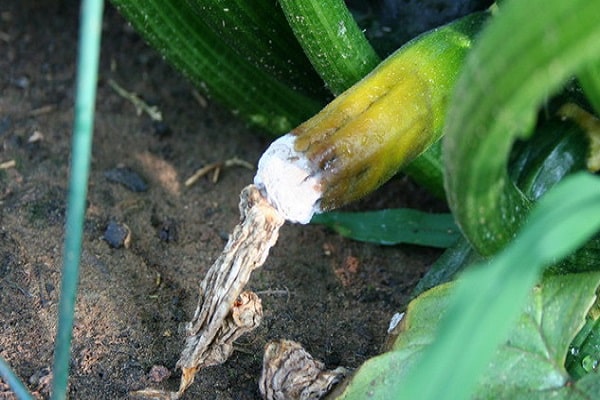
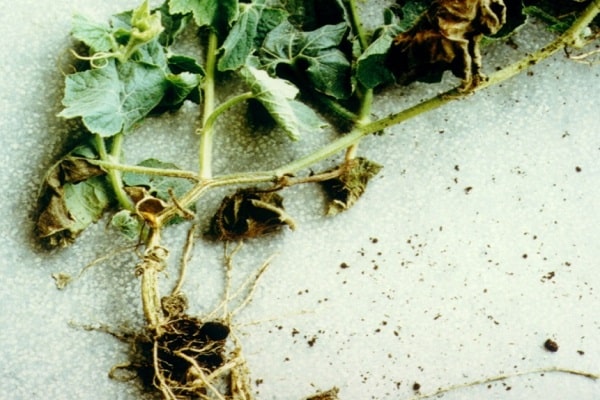
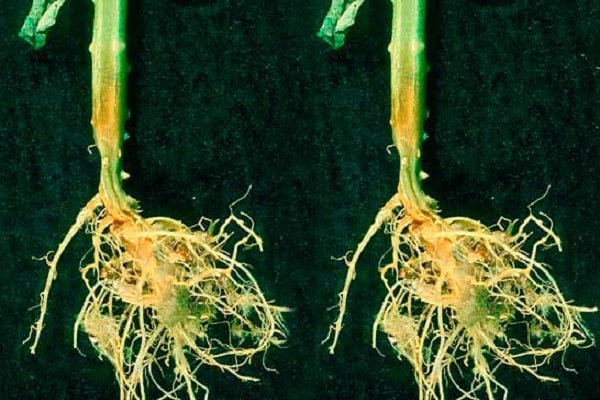
Fusarium root rot
If in the middle of the growing season the plant suddenly stopped developing, began to wither, drop flowers and ovaries, most likely the cause was damage to the roots by fusarium. A brown coating of rot appears at the base of the stem. Underneath, the plant part softens to a mushy state.As a result of rotting, the root part becomes loose and quickly dies. The main control measures are the removal of diseased bushes along with the underground part. The resulting hole is watered with a solution of copper sulfate.
You can try to re-root strong stems by cutting off the diseased root and treating the end with a growth stimulator.
Provoke the development of fungus:
- watering with cold water;
- excessive watering;
- excess mineral fertilizers.
The fungus lives in the soil for a relatively short time, so this disease practically does not occur in open ground with proper crop rotation. But in greenhouses, when growing one crop every year, the acute question may arise of what to do with the constant infection of plants with fusarium. The main method of combating the disease is to completely replace the soil.
Late blight root rot
The disease usually suddenly affects developed bushes ready for fruiting. The plant quickly and irreversibly withers as the roots rot. The disease is provoked by stagnation of moisture in the soil. The roots become covered with black, watery rot, which can be seen at the base of the stem.
Since it makes no sense to fight the disease of already affected bushes, measures are usually taken to prevent it:
- preparing high beds for planting cucumbers to improve drainage;
- avoiding compaction of the top layer of soil by loosening and mulching;
- avoiding prolonged, frequent watering and high temperatures.
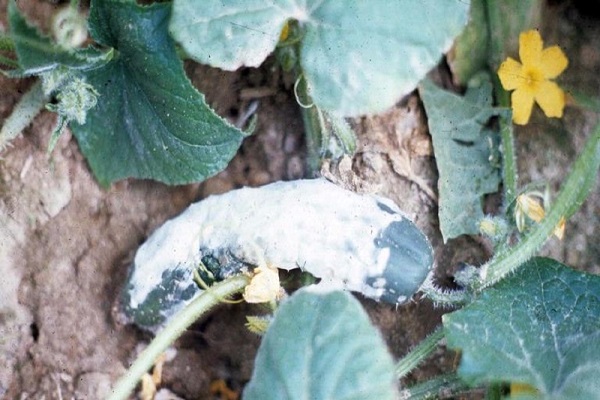
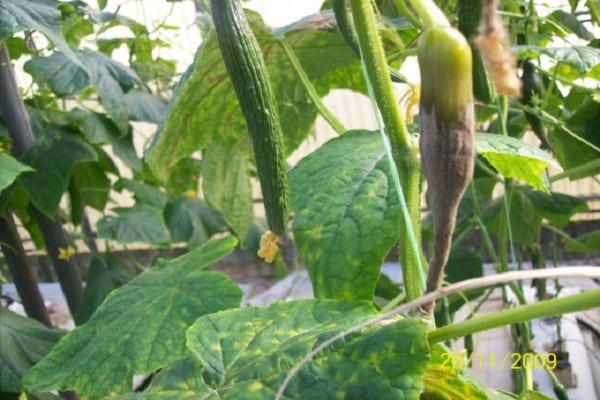
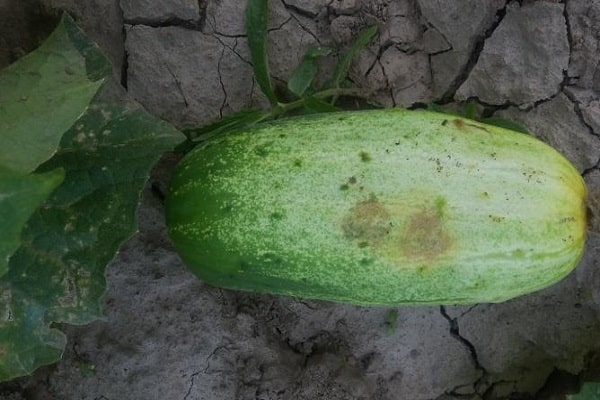
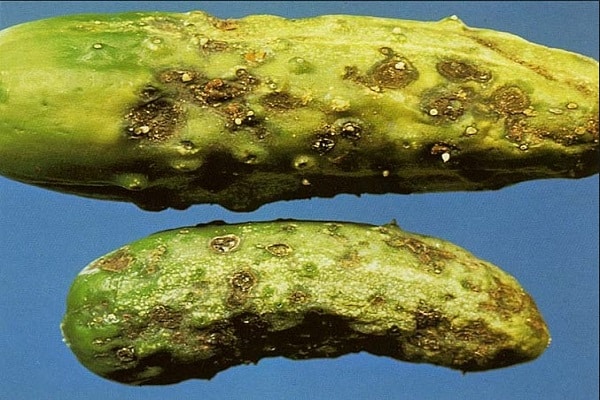
Fungal and bacterial rots of fruits
Infection of fruits by fungal and bacterial rot in a greenhouse can occur for many reasons:
- inaccurate formation and tying to trellises, allowing cucumbers to come into contact with the soil;
- mechanical damage to fruits;
- secondary infection of fruits by bacteria and fungi, after damage to the integrity of cucumbers due to other diseases.
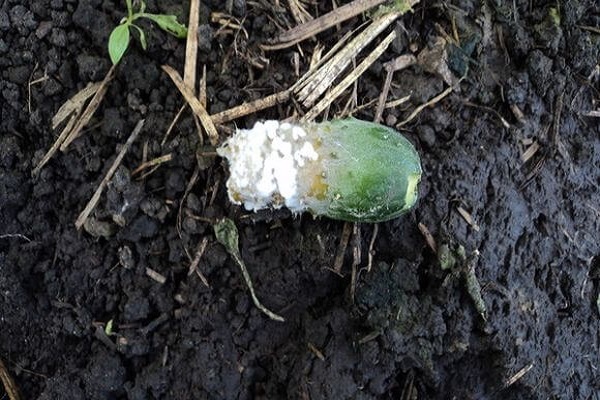
Most often, the source of the disease is at the top of the cucumber at the point where the flower is attached.
Fruit blossom end rot
Sometimes the tops of the fruit begin to darken and take on a rough, leathery appearance. Gradually, the tips of the cucumbers turn black and rot. This physiological disorder is called apical rot and there may be several reasons for it:
- damage to the root system;
- unstable watering;
- lack of calcium in plant nutrition;
- excess nitrogen.
If the tips of cucumbers rot in the greenhouse, you must:
- mulch the soil, which will help avoid sudden jumps in soil moisture;
- carry out mineral fertilizing of plants with a high calcium content and minimal nitrogen;
- establish stable watering.