Root rot of cucumbers leads to significant crop losses in greenhouses. Our advice will help summer residents pay attention to dangerous symptoms in time, understand their causes, and choose the best way to combat them. The information is especially useful for beginning gardeners who have unheated greenhouses or greenhouses.
- Pathogens of root rot
- By what signs do summer residents recognize root rot of cucumbers?
- Causes of diseases
- Mechanism of infection
- Ways to combat rot
- Traditional methods for fighting rot
- Chemical preparations for rot
- Biological products for cucumber rot
- Preventing plant infection
- Proper care of the greenhouse
- Follow the cucumber planting pattern
- What diseases of cucumbers do summer residents need to know?
- Mosaic on cucumbers
- Conclusion
Pathogens of root rot
Root rot on cucumbers is caused by a fungus from the genus Fusarium. A fungal infection can affect plants of any age. The disease is most often focal in nature, spread with soil and seeds. In some cases, the nature of the infection is not fungal, but bacterial.
Weak plants are susceptible to infection. Excessive humidity in the air and soil provokes fungal disease. Summer residents of any climate zone may encounter this disease. If the vascular system of a plant is affected by a fungus, the plant develops fusarium wilt. The entry of infection into the tissues of the root system causes rotting of the root part of the plant located in the soil.
A fungal infection can persist for a long time in the soil. By leaving unharvested plant residues in greenhouses, summer residents contribute to the occurrence of root rot of cucumbers in subsequent seasons and the gradual accumulation of fungal spores and other infections in the soil.
By what signs do summer residents recognize root rot of cucumbers?
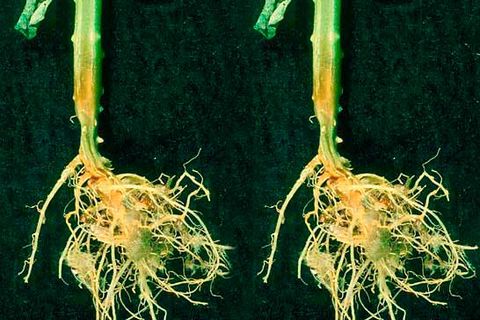
Let's figure out what signs can be used to calculate root rot in cucumbers. On seedlings, signs of root rot appear extremely rarely. Symptoms appear after transplanting cucumber seedlings into a greenhouse or soil. Droopy leaves on cucumber vines are a reason to think.
The mistake is made by the summer resident who runs for a watering can and waters fading plants in large quantities. Always check the condition of the roots of cucumbers before watering. You need to make sure there is no root rot. To do this, carefully scrape the soil away from the stem with your hand and go slightly deeper into the ground in the area around the stem.
Cucumbers are affected by root rot with the following symptoms:
- The stem at the base becomes thinner and acquires a yellow or brown tint.
- The plant has cracks at the bottom of the central shoot.
- The cucumber has brown roots that have begun to soften.
- Yellowing of leaves in the lower zone of the stem.
- Frozen, fading ovaries (advanced stage).
The presence of these signs in plants indicates that the cucumbers have root rot and treatment must be started immediately.
Causes of diseases
Knowing what can cause the development of root rot, you can avoid infection in the future, leading to the rapid death of cucumber bushes. Here is a list of factors that cause root rot of cucumbers in a greenhouse:
- violation of crop rotation;
- lack of autumn-spring tillage of soil and structures in the greenhouse;
- purchasing fungal-infected seeds for cucumber seedlings or when sowing them in the ground;
- contaminated soil;
- excessive watering;
- damp, cool weather;
- cold water for irrigation;
- daily fluctuations in air and soil temperatures;
- high air humidity due to poor ventilation of the greenhouse.
The water rate is 4 – 5 l/m² before flowering, 9 – 12 l/m² during the formation of ovaries (fruits). The optimal water temperature for irrigation is 25 °C.
Mechanism of infection
There are many ways a fungal infection can enter a greenhouse. The fungus can be brought by the summer resident himself on shoes or along with the soil, renewing the top layer of soil. The infection can accumulate in the soil for years. She chooses a weakened plant as her sacrifice - a cucumber that received mechanical injury when transplanted into the soil or during care.
Ways to combat rot
Let's try to figure out how to deal with root rot. You need to stop watering the diseased plant and use folk remedies.
Traditional methods for fighting rot
You can always find chalk, coal or ash at your summer cottage.Sprinkle the root collar, bare part of the rhizome and the base of the stem with these powdered substances. They will help dry the wounds and stop the spread of infection and slow down rotting.
A mash prepared according to a simple recipe will save plants from root rot. To prepare it you need chalk - 3 tbsp. l., copper sulfate - 1 tsp, water - ½ liter jar. Lubricate the lower part of the stem and the upper root part with the resulting solution.
Chemical preparations for rot
If the cucumber bushes turn yellow and there is severe wilting, folk remedies alone will not do. You will have to resort to chemical pesticides. Adhere to the following scheme:
- If the cucumbers show signs of severe wilting, dilute 20 ml of Previkur pesticide in 10 liters of water and pour over the cucumbers.
- After 5 days, apply watering with a “Fitolavina” solution prepared from 20 ml of the product and 10 liters of water.
- Treat the soil in the greenhouse against fungus with the preparations “Gamair” and “Alirin-B”. Treatment is necessary to restore beneficial microflora that have been damaged by the use of chemicals.
Biological products for cucumber rot
Bacterial preparations can be used to treat rot in cucumbers. You can purchase Alirin-B. The product is available in tablet form, does not accumulate in fruits and leaves, and is not dangerous for humans. Purpose: fight against various types of fungi. In plants treated with this product, the level of nitrates decreases, and the content of ascorbic acid in cucumbers increases.
Greenhouse plants can be treated with Gamair fungicide, which is available in powder or tablet form. The biological product helps against many types of fungus.It is used not only to treat disease manifestations in greenhouse cucumbers, but also to disinfect soil in a greenhouse, greenhouse or open ground. A rotten root can be treated with a Gamaira solution prepared from 5 liters of water and 1 tablet.
Treatment with Glyokladin, an effective microbiological fungicide, will stop cucumber rot. It helps especially well with fusarium of plants planted in soil fertilized with organic matter above the norm.
Almost all biological products can be combined with insecticides and mineral fertilizers, humates. These preparations are easy to use, soluble in water, and can be sprayed on leaves and applied to the soil using drip irrigation systems for greenhouses.
Preventing plant infection
Prevention should begin in early spring, treating the seeds before planting, because one of the ways the infection spreads is through poor-quality planting material.
The simplest and most affordable way to disinfect (seeds, soil) is a solution of potassium permanganate. This is an old and time-tested method, but for reliability, you can purchase the drug “Fitosporin” and treat the seeds with it before planting. This is much better than treating root rot in cucumbers.
Potassium permanganate and Fitosporin can be used to treat the planting soil. Do this not on the day of planting, but a week or two before. Disinfecting the soil will save cucumbers from many diseases and pests.
Proper care of the greenhouse
Annual autumn cleaning of the greenhouse prevents the accumulation of harmful fungi in the soil and structural elements. Mandatory measures to maintain the structure:
- Treating wooden structural elements with copper sulfate.
- Using a solution of laundry soap to wash metal and galvanized parts.
- Wash greenhouse glass or polycarbonate with soapy water and rinse with a hose.
- Carefully remove all plant debris, mating and other functional debris that has accumulated in the greenhouse over the summer.
If there were sick plants in the greenhouse in the summer, disinfection can be carried out in the fall using a sulfur bomb, taking into account the fact that beneficial microorganisms in the top layer of soil die in the same way as harmful ones. In the spring, to restore the microflora, treat the soil with any modern biological product.
Follow the cucumber planting pattern
We must not forget about crop rotation. If you plant the same vegetable crop in the same place every year, an infection will accumulate in the soil - an outbreak of the disease is inevitable. Reuse of the plot for cucumbers is possible only after 3 years. In greenhouses, the top layer of soil is changed every two to three years. They take soil from the beds where the following plants grew:
- onion;
- early cabbage (white cabbage);
- garlic;
- salads;
- beet;
- potato.
Failure to follow the cucumber planting scheme recommended by the manufacturer is the most common mistake made by summer residents. In pursuit of a large harvest, cucumbers are planted too densely, provoking diseases. Due to the close proximity of the bushes, both pests and diseases spread through them at high speed. It is very difficult to treat dense plantings; even early diagnosis of diseases is difficult.
What diseases of cucumbers do summer residents need to know?
Difficult weather conditions, poor agricultural technology, and lack of nutrition are the main causes of diseases that lead to decreased yields and even death of plants. Cucumbers, both greenhouse and ground, have the following diseases:
- powdery mildew and downy mildew;
- gray and white rot;
- fusarium;
- olive spot;
- copperhead;
- mosaic;
- leg rot.
Outbreaks of powdery mildew usually occur in wet weather accompanied by a decrease in daily air temperature. At first, a white coating may be noticed on the surface of the leaves.
Leaves affected by the fungus turn yellow and dry out. Spores persist on plant debris and in soil. Spores are easily transported by air movement.
Mullein infusion helps to cope with yellowing of leaves. Strain 1 liter of infusion and add 1 tbsp. l. urea. After the fertilizer is completely dissolved, you can spray the cucumber bushes infected with powdery mildew with the solution. Yellow leaves should be removed and destroyed.
Plant leaves suffer from downy mildew. Brown spots can be seen on the outer surface, and a gray-violet coating on the lower part. As a result, the plant loses leaves, which dry out and fall off.
Recommended measures to prevent downy mildew:
- Eliminate drafts in the greenhouse.
- Fertilize with potassium and phosphorus, introducing them into the soil.
- Ventilate the greenhouse to maintain the required air humidity.
Plants can be treated with drugs. “Topaz” and “Oxychom” help. Solutions must be prepared according to the instructions supplied with the preparations. After treating the plants with a solution of the drug, the soil under them should be sprinkled with ash.
You can clearly name the reasons for the occurrence of olive spot in plants:
- drafts;
- high soil moisture;
- using low temperature water for irrigation;
- low temperature (air, soil).
A sign of plant infection is dry sores appearing on cucumber vines. They are covered with an olive-colored coating. The leaves suffer from fungus and become covered with spots with a light brown color.The cucumber skin becomes uneven with olive-colored indentations. The dents gradually turn into irregular ulcers.
Olive spot on plants needs to be treated in a system. You need to stop watering the sick plant. The next stage of treatment is the treatment of cucumber leaves and stems. The treatment can be carried out using 1% Bordeaux mixture or another popular agent among summer residents, Oxychom. An aqueous solution is prepared from Oxychom: 20 g of product per 10 liters of water.
Fusarium is found in the soil. It enters the stems through the root system. The first visible signs of cucumber infection are wilting leaves at the bottom of the stem. Later, the leaves located higher on the stem turn yellow.
At the last stage of the cucumber whip disease, the leaves become very thin and turn brown. The plant dies. It is impossible to cure a cucumber. The bush must be destroyed by burning. Fusarium plant disease is better prevented than treated. To do this, you need to sow only treated cucumber seeds in fungicide-treated soil.
Gray mold spreads through the air or through liquids through the spores of the fungus Botrytis cinerea Pers. Factors influencing the degree of plant damage:
- A sharp change in air temperature from high to low.
- Using cold water to water plants.
- Lack of ventilation, humid air, condensation on leaves and stems.
The disease can be determined by the appearance of cucumbers: weeping, brown spots are visible on the fruits. Diseased plants have cucumber vines with signs of rotting, leaves with brown spots. After some time, the affected areas of the plant become gray from plaque.Plaque is fungal spores that are carried throughout the greenhouse by drafts and infect healthy plants and soil.
You can stop the development of a fungal infection and prevent the plant from rotting. To do this, prepare the powder: 1 tsp. copper sulfate, 1 glass of ash. Powder the fungus-affected areas of the stems and leaves with this powder. The soil under the plants can be sprinkled with ash. To reduce air humidity, you need to regularly ventilate the room with plants. If the measures do not give a positive result, you will have to remove the damaged parts of the plants and destroy them.
Fungal spores (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) living in the soil infect the root zone of the stem. Weeping spots form on the stem, overgrown with white mycelium. The infection gradually covers the entire plant and affects the fruits.
As a measure to prevent white rot, it is recommended to monitor the level of air humidity in the greenhouse. Mulch the soil in the greenhouse with dry grass. At the initial stage of the disease, lubricate the areas of plants affected by fungal infection with a paste made from chalk, potassium permanganate, and water. In advanced cases of the disease, remove diseased plants along with a clod of earth.
The cucumber stem rots if the bush is infected with a bacterial infection. At the initial stage, you can try to save the plant by sprinkling the affected area with wet peat. Water the cucumbers carefully so that water does not get on the vines and leaves. In case of a large number of damages, it is better to destroy the cucumber bush.
Medyanka is a fungus that attacks the leaves and fruits of the plant. In the initial stage, brown spots form on the leaf blades, which over time enlarge, turn black, dry out and crumble.
Cucumbers affected by the fungus are not suitable for consumption due to brown dents 3–7 mm in diameter. The causative agents of cucumber copperhead persist in a 10-centimeter layer of soil and spread through seeds obtained from the fruits of diseased plants.
Mosaic on cucumbers
The mosaic virus can remain active in the soil and on the roots of weeds. Cucumbers infected with the virus can be identified by yellow, curled leaf blades. The fruits are covered with yellow spots, the vines of the plants are cracking.
The mosaic virus is transmitted between plants by aphids. The fight against aphids is the main preventive measure against mosaic on cucumbers. In addition, you need to keep the soil of the beds clean - regularly remove weeds and loosen the rows. Plant mosaics are treated with Actellik and Aktara.
Conclusion
Now you know what to do when the first symptoms of disease appear on greenhouse cucumbers, why plant stems and roots of cucumbers rot in a greenhouse, and what effective drugs need to be used to cure diseased plants.