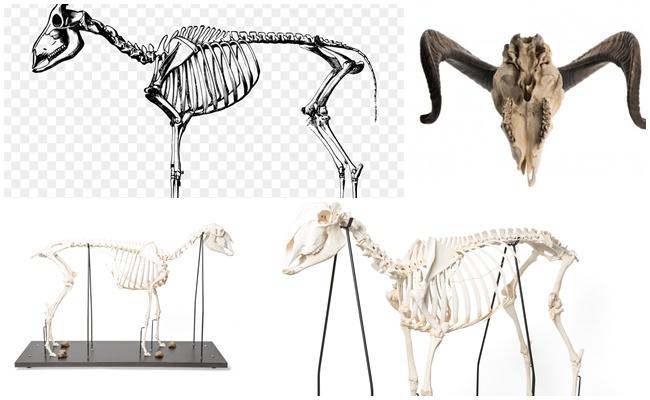
Knowledge of the features of the sheep's skeleton allows owners to control the changes occurring in the animal's body depending on the conditions of keeping and feeding. Sheep have an anatomical structure that is partly similar to other mammals, but they also have their own characteristics, in particular regarding the mechanics of movement, which are associated with anthropogenic influences.
Axial skeleton
The anatomy of a sheep has characteristics of several species. They differ from each other depending on age, gender and breed. The guard skeleton of the animal is divided into two parts:
- Passive – this includes tendons, bones and cartilage. This part is designed to fix the sheep's body in a certain position.
- Active - this part consists of muscles. It allows the animal to move and protects internal organs from mechanical damage.
The anatomical structure of the head consists of the brain and facial parts. The cranial bones form a cavity in which the brain is located. Thanks to the skull, it is reliably protected. The cavity also contains the organs of smell, touch, and vision. The brain is the center of concentration of the main systems in the body. Here are the regulatory parts of the nervous system, which is built on innate and acquired reflexes.
Rams have one peculiarity! There are only 12 molars in the upper jaw.
The basis of the spine of the skeleton is the spine. It consists of:
- 6 lumbar vertebrae;
- 7 cervical;
- 13 breasts.
5 false and 8 true ribs are attached to the vertebrae. False ones are attached to the sternum using costal cartilaginous arches. And the true ribs are directly connected to the sternum. The vertebrae, ribs and sternum together form the rib cage. It contains the heart and lungs. The shape of the chest depends on the length and curvature of the ribs.
Anatomy of sheep limbs and diagram of movement mechanics
The anatomy of the limbs of rams has its own characteristics, which were formed due to the movement of the animal on its hooves. The front legs consist of:
- humerus;
- shoulder blades;
- forearm bones;
- fingers;
- wrists.
The girdle of the hind limbs consists of the bones of the metatarsus and tarsus, femur and tibia. It is attached by the hip joint.
Important! Animal owners need to provide them with a proper diet, enriched with all the necessary vitamins and minerals. This ensures the strength of the skeleton.
Movement is ensured through the interaction of the articular, ligamentous and muscular systems. Muscles are fibers that are covered with a connective membrane. They are attached to bones by tendons. If an animal is fed too much, fat deposits form between the muscles.
Are there skeletal differences between a sheep and a ram?
The general structure of a sheep and a ram is the same. The only differences are in the reproductive system, bone size and the presence of horns. Rams are larger and more powerful than sheep; they have a more developed chest. In addition, rams add horns to their skeletal structure, which sheep do not have.
Knowing the characteristics of a sheep's skeleton, pet owners can monitor the characteristics of their development and promptly detect possible negative changes associated with improper nutrition or maintenance.