Farmers often have to treat animals for invasive diseases. It is advisable to become familiar with sheep coenurosis and the peculiarities of its treatment first of all, since the pathogen can be found in water, on pastures, or on sheep’s wool. It should be taken into account that mainly lambs under two years of age or individuals with poor health suffer from the disease.
What is coenurosis
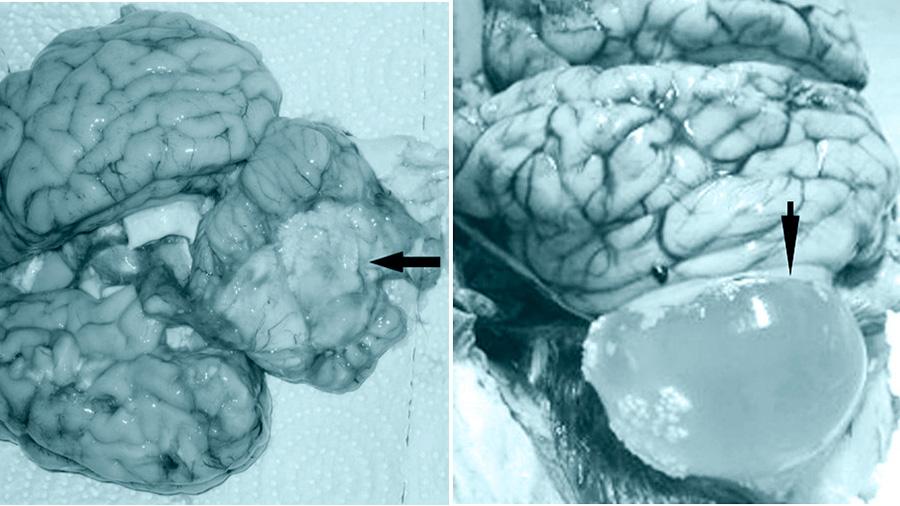
The disease of sheep, caused by helminths (tapeworms cestodes), lasts a long period in a chronic form.Characteristic signs of infection: impaired motor coordination, damage to parts of the brain (sometimes infection of the spinal cord occurs). Tumor-like formations can be present in the thoracic, abdominal cavities, in muscle fibers, directly under the skin.
Sheep are infected with the whirligig by eating grass covered with parasite eggs. Sources of the disease can also be water, soil, wool (in the case when ewes lick lambs). Sheep can become infected with the disease in any region.
Pathogen
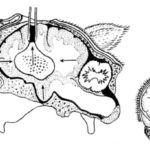
The larva belongs to the family Taenidae. Cestodes look like thin-walled blisters (coenuri) of varying sizes (from a pea to a chicken egg). Worms of different stages of development are attached to the inside of the shell. Eggs, entering the body of sheep, penetrate the blood vessels and are carried throughout the organs by the blood stream. Caenuri form in the brain (brain, spinal column) 70-90 days after infection.
Eggs located in the external environment quickly die in summer under high temperatures. If humid weather with low temperatures occurs (spring-winter-autumn months), then the pathogen remains viable for 2.5-3 months.
Types of disease
When treating coenurosis in animals, three forms of the disease must be taken into account. Features of the disease:
- in the central form, the brain is predominantly affected. There are cases when parasites are localized in the spinal cord;
- in case of serial coenurosis, the location of coenurs is muscle fibers, subcutaneous layer. The form of the disease occurs in rabbits and hares;
- Scriabin's coenurosis is observed mainly in sheep (the larvae parasitize the muscle tissue of animals). Tumor-like formations are localized on the neck, head, and torso.
In the East (regions of Kazakhstan, Tajikistan) there are cases of Geiger's coenurosis in sheep. The places where coenurs form in the animal’s body are subcutaneous spaces, kidneys, lungs, liver, muscle connective tissue, and eye mucosa.
Pathogenesis
The parasites produce a destructive effect within 1.5-2 days. First of all, the soft membrane in the brain is affected, and the blood vessels dilate. Winding passages up to 7-8 cm long appear 2-3 weeks after infection. The metabolic products of the larvae cause particular harm to the animal’s body (in the form of intoxication).
With central coenurosis, after 1.5-3 months, deformation of the sheep’s brain is observed due to the development of parasites - the brain tissue is compressed, the cranial bones become thinner.
All these lesions lead to disruption of the activity of important centers of the animal’s body. Sheep experience disorientation in space, loss of consciousness, breathing problems, and tonic convulsions. If the parasite “settles” in the spinal cord, then the sheep will exhibit dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of the disease
Fearfulness, tonic convulsions, pinpoint hemorrhages - such signs are observed in sick lambs. Weakened individuals die. In stronger animals, the disease becomes latent. But after 3-6 months, characteristic symptoms of coenurosis appear in the behavior of young animals. Lambs may suddenly run or run into any object, hanging their heads low.
The behavior and postures of animals change depending on the location of the coenurus:
- the lamb throws back its head and backs away if the bubble is located in the occipital area;
- unsteady gait, death on the hind legs are typical when the parasite is localized in the spinal cord;
- impaired coordination of movements, paresis of the legs is noted with damage to the frontal lobe.
Animal behavior begins to change 2.5-3 weeks after infection. The prognosis for veterinarians is usually poor if lambs are already exhibiting behavioral abnormalities.
Diagnostic rules
Palpation of the animal's skull (thinned bones in the area where the coenurus grows) allows a preliminary diagnosis to be made. Also, when examining the nasal cavity, a characteristic discharge of mucus and pus is observed. The appearance of hemorrhages in the whites of the eyes is noted. An accurate diagnosis is confirmed by clinical studies (a popular method is the allergic method).
How to treat sheep coenurosis
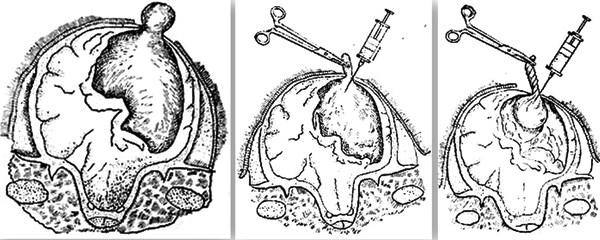
The disease is treated primarily surgically - by trephination of the skull, the fluid is sucked out from the bladder and the membrane is carefully removed. In this way, individuals of valuable breeds are saved.
An alternative to surgery is the destruction of parasites with Praziquantel, Niclosamide, and Albendazole. After chemotherapy, glucocorticoids must be used to suppress inflammatory processes. If treatment of coenurosis is started at the initial stage (at the stage of larval migration), then injections with the drugs “Febendazole” and “Praziquantel” are used. Medicines are administered to animals in the desired areas of the head.
Possible consequences
The disease poses a danger to humans, although cases of infection are quite rare. When a person is infected with a parasite, the same symptoms are observed as in sick sheep. Therefore, after any contact with pets, you should thoroughly wash your hands, since the larvae remain viable at low temperatures. There is no clear opinion on the safety of eating heat-treated meat from infected animals. However, you should definitely not feed raw meat from sick sheep to dogs.
Prevention measures
Keeping animals and pens clean is the main preventative measure to prevent infection. Other rules must also be followed:
- protect pastures from stray animals;
- regularly clean sheepfolds and carry out antiseptic treatment;
- The lambs’ diet is supplemented with vitamins and minerals;
- On farms with large flocks of sheep, dogs are regularly dewormed. It is also recommended to keep dogs separate from sheep;
- To prevent the development of the disease, at the first signs of infection, seek help from a veterinarian.
When carrying out preventive measures, you need to remember that coenurosis mainly affects young animals. Therefore, they carefully monitor the diet of lambs. The best food is a mixture of oatmeal, cake, and mixed feed. In case of a lack of vitamin D and minerals, the young animals begin to eat soil. It is necessary to add bone meal, chalk to the food and ensure regular walks on sunny days.
Coenurosis is a dangerous disease of sheep, causing significant damage to the business of producing meat and dairy products. Treatment of animals and disposal of dead sheep require serious expenses. Preventive measures, compliance with the rules of keeping and feeding animals are the main measures to prevent infection of the flock.