The arrangement of beds in a greenhouse depends on the size of the building, the crops grown, and the materials available. To get a good harvest even from a small area, it is necessary to make optimal use of the internal space. There are many nuances in the operation of a greenhouse that are recommended to be taken into account before construction and when arranging the territory.
Features of beds in greenhouses
Before placing beds in a greenhouse made of polycarbonate or other material, you must adhere to some rules, which will allow you to get a high-quality harvest and prevent the death of crops:
- It is recommended to plant plants from north to south (according to Mittleider). This is necessary to ensure uniform illumination and heating of crops by sunlight.
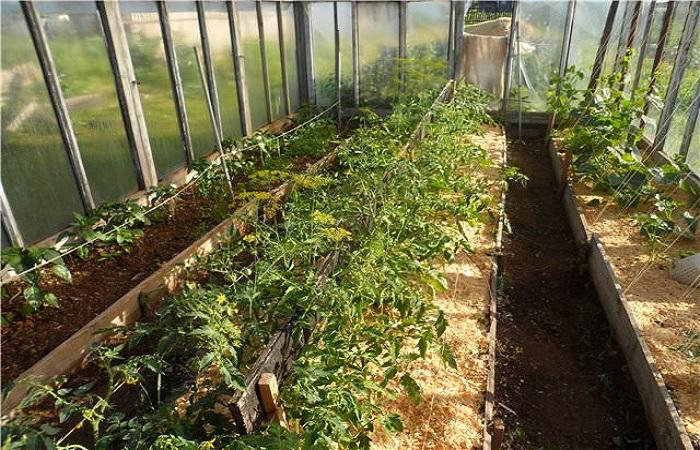
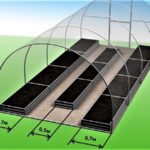
- To avoid problems in caring for the beds, it is recommended to make them narrow and high. If the size of the greenhouse allows, then you can arrange several areas for planting.
- Plants with similar characteristics must be planted in the same area. When choosing, you should take into account frost resistance, height, moisture consumption, resistance to diseases and pests.
- A distance must be left between planted crops so that adult bushes do not come into contact with each other.
- It is best to allocate a greenhouse for one specific crop.
How to choose sizes and placement
The rules for arranging beds in a greenhouse are the same for buildings of any size. They need to be known and taken into account during the installation phase. This will allow you to optimally organize the space.
Principles for arranging beds in a greenhouse, greenhouse and other structure:
| Name of the principle | Characteristic |
| Optimal width and height | Height affects the normal development of culture. Depends on the type of soil.
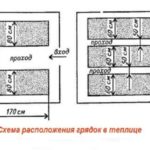
Low beds (10-15 cm) are recommended to be organized on fertile soil. Nutrient soil mixture is not used in this situation. Medium-height beds (25-30 cm) are intended for plants with shallow roots. Suitable for low-fertility soil. A nutrient substrate is used. High ridges (up to 60 cm) are intended for lands with low fertility levels and in marshy areas.Filling is carried out with special nutritional mixtures. Suitable for plants with a long and well-developed root system, growing at a large distance from each other. In this situation, regular watering is necessary. The width depends on the method of caring for plants. If the greenhouse has one-way access, then the optimal width is 45-50 cm. For two-way access, a width of 0.9-1 m is suitable. The recommended greenhouse sizes for a family of four are 3*6 m and 3*4 m. |
| Orientation depending on the cardinal direction | Optimal orientation from west to east. This ensures uniform lighting throughout the day, regardless of the size of the beds. It is necessary to place the plant from north to south for tall varieties and for greenhouses that are built on sloping terrain. |
| Features of the greenhouse design | The location also depends on the height of the building and the type of roof. A flat roof is considered universal. Suitable for any variety. Allows you to plant crops in several rows.
A gable roof is recommended for structures designed for tall varieties. The arched roof is suitable for medium-growing and low-growing varieties. A passage is left in the center, and crops are planted along the edges. |
How to make them correctly with your own hands
Do-it-yourself construction guarantees quality construction and long service life. Also, when organizing such a greenhouse, the owner takes into account such nuances as: crop variety, soil type.
Beds according to Mittleider
Mitlider conducted experiments for half a century, as a result of which the recommended width was established - 45 cm. In this case, the passage is not less than 90 cm. This placement of crops allows them to develop correctly and receive the necessary amount of light and oxygen.
In this case, it is recommended to place the beds from north to south. Loosening of the soil is excluded. In areas with difficult soil, it is recommended to use boxes.
Raised beds
The height is up to 0.6 m. Not suitable for all types of soil. Filling occurs due to the nutrient substrate. High beds are recommended for varieties that have developed roots. It is necessary to water the area regularly, otherwise drought will cause death.
Warm beds
There are several types of warm ridges:
- biological;
- electrical;
- water;
- raised;
- in the form of a hill;
- combined.
Warm beds allow crops to be planted in early March. The best option is tall structures. Suitable not only for heating plants, but also the root system. Household waste is used, but there is an unpleasant smell of rotting.
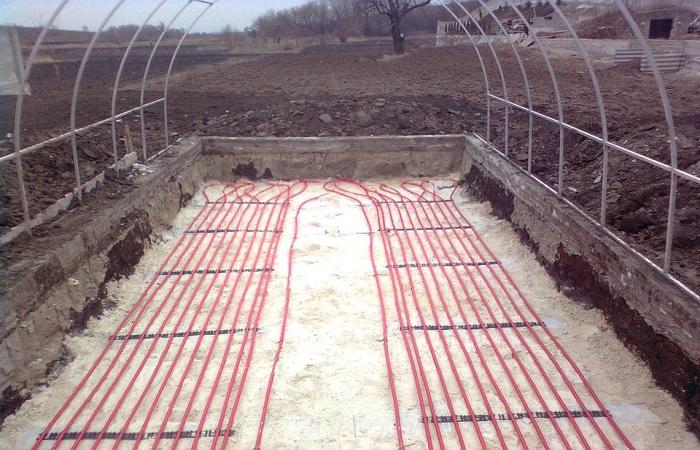
How to make a heated bed
The arrangement depends on the chosen type. Electricity, heated water using special devices, or compost are used for heating. Also, when arranging, it is necessary to take into account the type of structure. Properly made beds, including those made from metal structures, will last up to 15 years. Laying occurs in layers.
Creating a warm ridge:
- Digging a hole of the required depth.
- Laying out sand, material or mesh.
- Layer of drainage and mulch.
- Filling the bed with nutritious soil mixture. After this, a good watering is carried out.
Features of the fence
You can fence the garden bed with available materials. The fencing will depend on the type chosen. Common options:
- Boards, timber.
- Metal fencing.
- Stone and concrete.
- Border tape.
- Plastic bottles and other available materials.
Beds in a greenhouse are a necessary structure that helps not only to obtain a rich, high-quality harvest, but also to properly organize the space. There are several types; choosing the best one depends on several nuances.