Growing large, juicy, ripe tomatoes is the dream of every summer resident. In most regions of our country, this is difficult due to the unpredictability of the weather and the short summer. Tomatoes, when grown in a greenhouse, ripen earlier, produce a larger harvest, and have better taste and presentation. Let's look at the features of the greenhouse method of growing tomatoes.
- Advantages and disadvantages of growing tomatoes in a greenhouse
- Deciding on a variety for greenhouses
- Step-by-step technology for planting tomatoes
- Sowing seeds
- Germination of seedlings
- Transplanting into a greenhouse
- When to transplant
- Preparing the ground
- We apply fertilizers
- Tomato planting scheme
- Planting seedlings in the beds
- Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse
- Growing tomato bushes
- Regularity of irrigation
- How and what to feed seedlings and adult bushes
- Garter and bush formation
- Treatment against pests and diseases
- Nuances of caring for tomatoes
- In the winter greenhouse
- In an unheated greenhouse
- How to achieve a good harvest in greenhouse conditions
- Harvesting tomatoes
Advantages and disadvantages of growing tomatoes in a greenhouse
Growing tomatoes in greenhouse conditions has pros and cons that need to be taken into account, especially for beginning gardeners.
Advantages of greenhouses:
- earlier, almost a month, ripening of tomatoes;
- high yield;
- protection from adverse weather effects - frost, lack of heat, hail;
- the possibility of planting heat-loving and indeterminate species;
- protection from pests.
Tomatoes grown indoors usually have better quality and presentation due to their growth in favorable conditions.
The disadvantages of greenhouse cultivation include:
- additional costs for construction, heating, and maintenance of greenhouses;
- constant control over the temperature, since at temperatures above 30 ° there is a risk of slowing down the formation of the ovary and loss of tomatoes;
- the need for pollination activities;
- treatment and protection against fungal infections;
- combating condensation.
In cold regions, greenhouse cultivation is the only way to get a good harvest that ripens on the bush. The costs are always recouped by the yield and excellent taste of the fruit.
Deciding on a variety for greenhouses
Only an experienced gardener can understand the variety of varieties and hybrids. What you need to pay attention to when choosing seed:
- ripening periods;
- determinate and indeterminate species;
- productivity;
- hybrids - show good qualities of disease resistance.
Let us note the most popular types of tomatoes for greenhouse planting:
- early - Miracle of the Earth, Aurora F1, Sanka, Raspberry Surprise, Budenovka, President 2 F1;
- fruitful - De Barao, Black Prince, Ilyich, Honey Drop, Auria, Pink Pearl;
- large ones - Bull's Heart, Cardinal, Mazarin, Grandmother's Secret, King of the Giants, Volgograd;
- disease-resistant - Ural, Tatyana, De Barao, Dubok, Morozko, Tea Rose.
The ratings of favorite greenhouse varieties and hybrids are traditionally topped by De Barao, Bull's Heart, Eagle's Beak, and Golden Domes.
For planting, it is recommended to choose well-known and familiar varieties, as well as new hybrids.
Step-by-step technology for planting tomatoes
Preparation of the greenhouse for spring planting of tomatoes begins after harvesting the old tops, that is, in the fall. Remains of roots are removed from the ground and fallen leaves are collected. This is done especially carefully if the plants are sick.
The structure is washed with water from a hose, repaired, and metal parts are treated to remove rust. The wood is washed with antibacterial and antifungal agents. The top layer of soil is removed. Some of this work can be carried out in the spring, but treatment against fungal diseases should be carried out immediately after harvesting the tops so that the rot does not grow.
The treatment is carried out with a solution of copper sulfate and fumigation with sulfur bombs. The beds can be prepared in the fall.
Important: in the greenhouse it is necessary to have several vents for ventilation - in the side walls and on the ceiling.
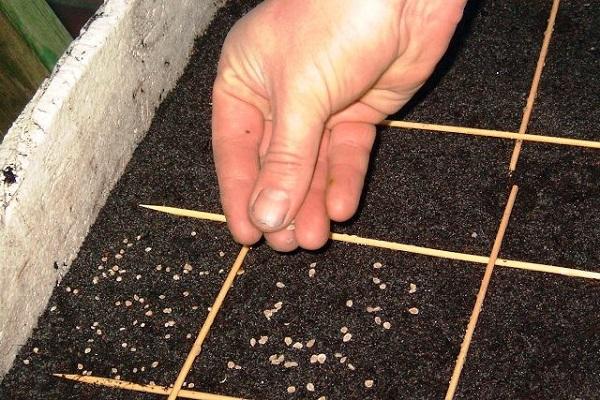
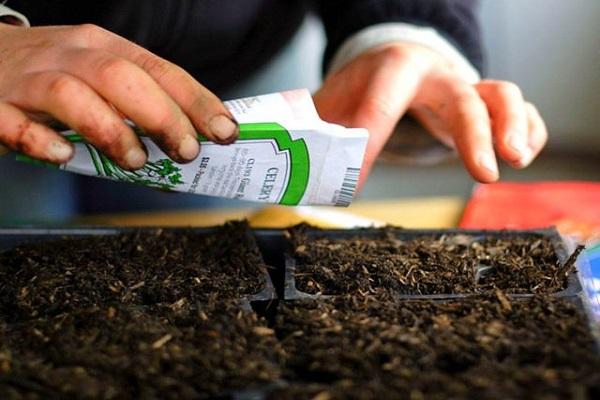
Sowing seeds
Seeds are sorted before planting, discarding small, twisted and chipped ones. Check germination by placing it in a glass with saline solution. Seeds that float within 5 minutes are discarded.
Soak in a solution of Fitosporin, prepared according to the instructions. It is also useful to soak the seeds in a growth stimulator.
The time for planting seeds depends on the growing season of the variety and the temperature characteristics of the region. Basic rules for sowing dates:
- end of February - for late varieties and warm regions;
- early-mid March - mid-season species for the Middle Zone;
- end of March - the earliest varieties and hybrids.
Sow tomatoes in containers about 15 centimeters high, deepening them by 1-1.5 centimeters. For planting, use special soil for seedlings or prepare the soil mixture yourself. The distance between seeds is 2-3 centimeters.
It is the gardener’s choice to germinate pre-seed material or press with dry seeds. Note that when planting, sprouts often break; maximum care and working with tweezers are required.
Germination of seedlings
After planting, the containers are transferred to a lighted place with a temperature of 20-22 °. Immediately or after 3-5 days, cover with a transparent film to obtain a greenhouse effect with good moisture and maintaining a constant temperature.
We adhere to the following rules when growing:
- Until the leaves begin to grow (the third and beyond), watering is not needed - light moistening with a spray bottle;
- in low light conditions - use electric fluorescent lamps;
- rotate the drawers for uniform illumination;
- dive into separate containers when 2 true leaves appear (usually 2 weeks after germination).
When transplanting into an individual pot, it is important not to touch the seedling, take more soil so as not to expose the roots. In the future, the containers need to be turned with the other side towards the light so that the seedlings do not bend and develop evenly.
Hardening helps to grow high-quality seedlings. It begins with a gradual decrease in room temperature and ventilation with cold street air.10 days before transfer to the greenhouse, containers with plants are taken out to the veranda or loggia with a temperature of at least 12 °.
Transplanting into a greenhouse
Stationary greenhouses are prepared in the fall, washing the walls and disinfecting them. It is important to remember that tomatoes are not planted in one place for two years in a row; they can be alternated with cucumbers.
When to transplant
Seedlings are transplanted into unheated greenhouses when the danger of frost has passed and consistently warm weather has established. This usually happens in the first ten days of May.
By this time, the seedlings should have the following characteristics:
- seedling height – 15 centimeters for low-growing varieties, 30 centimeters – for tall ones;
- more than 8 leaves per bush;
- the stem at the bottom is wide and dense;
- there are 1-2 ovaries with buds, but without fruits.
The ground inside the greenhouse should warm up to 12-15 °. To transfer seedlings to the greenhouse, choose evening or a cloudy day.
Preparing the ground
The initial stage of soil preparation is to remove the top layer by 20 centimeters. Next, well-rotted manure is introduced, which is covered with new soil on top. The soil composition requirements for tomatoes are high. When preparing the beds, it is also necessary to add sand and peat.
To loosen the soil, earthworms are buried in the ground; you can also buy and water future beds with a bacterial cocktail. Thanks to the vital activity of bacteria, the properties of the soil will improve, and it will be easier for tomatoes to absorb nutrients.
We apply fertilizers
An important factor in soil composition is acidity. For tomatoes, the norm is a neutral composition with a pH of 6-7 units. If there is a deficiency, add lime in a volume of 0.5 kilograms per square meter.
It is also recommended to add potassium sulfate and superphosphate, based on the composition of the soil and recommendations for fertilization.
To disinfect and warm the soil, the soil is spilled with a warm (60 °) solution of potassium permanganate (1 gram per 10 liters of water) and covered with film.
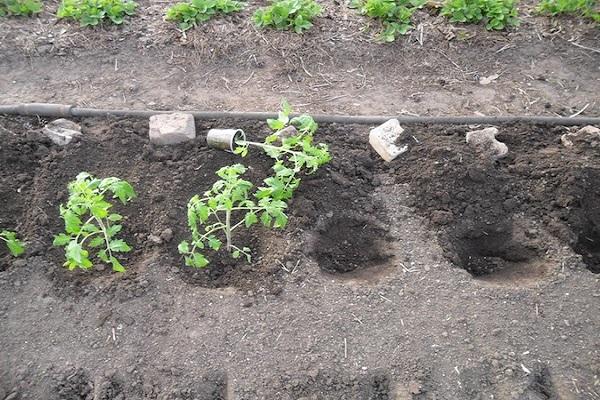
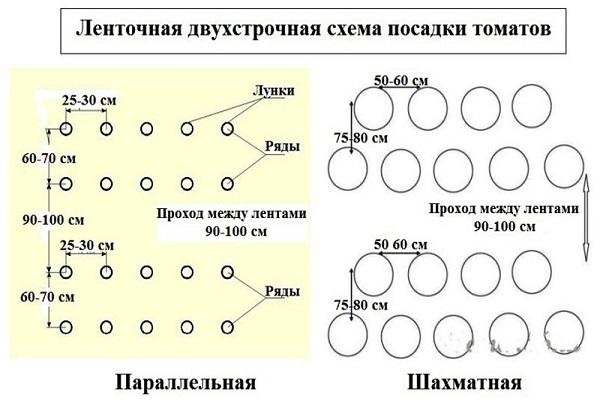
Tomato planting scheme
Tomatoes are planted in beds arranged longitudinally. The number of beds is determined by the width of the greenhouse. The width of the bed is selected according to the varieties being planted, usually 60-90 centimeters. Large branched bushes need more space, and the passages are also made wider.
Modern methods of tomato agricultural technology recommend the following planting schemes:
- Checkerboard pattern for tall branched tomatoes. The distance is 60-70 centimeters, between the beds for passage – 70-80 centimeters.
- Fast maturing varieties with several stems are planted in a checkerboard pattern. The distance is 35-40 centimeters between neighbors, between rows – 55-60 centimeters.
- Standard species, as well as determinate ones, with one stem - in rows with a distance of 45-50 centimeters. Between the holes - 30-35 centimeters.
It is important to remember that an excess of tomatoes in the greenhouse will not lead to an increase in yield.
Important: thickening interferes with ventilation, provokes the accumulation of moisture, the development and rapid spread of fungal diseases.
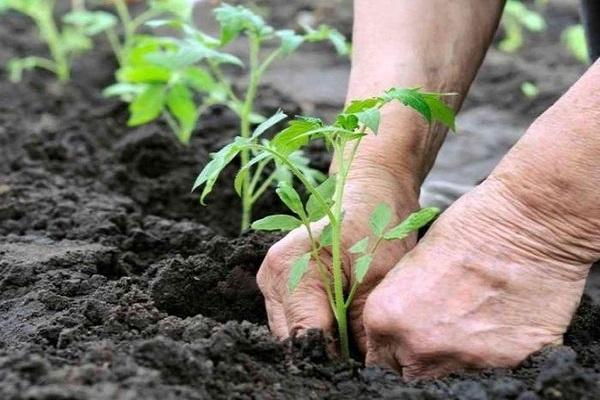
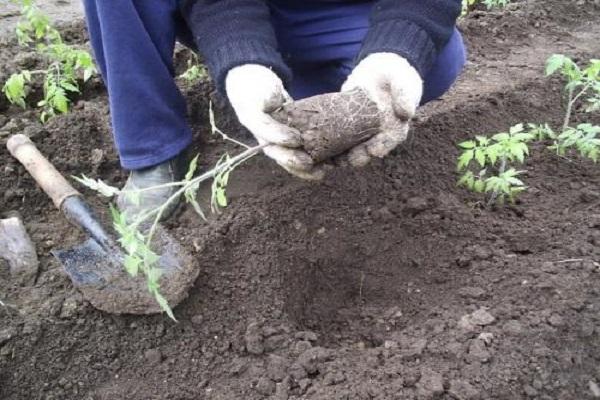
Planting seedlings in the beds
Seedlings in peat pots are placed directly into the holes; in other cases, the seedlings with a lump of earth are carefully removed and placed vertically so that the foliage does not touch the soil.
If the tomatoes are overgrown, it is not recommended to place the stem in the hole. Dig a hole to the depth required for vertical standing, covering only the root system with soil and leaving part of the stem exposed. The hole is completely filled in after 10-14 days, when the stem becomes coarse.
Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse
Growing tomatoes in a greenhouse helps with knowing the basic rules of care, which include watering, fertilizing and pruning.It is also necessary to monitor the appearance of pests and diseases in tomato bushes.
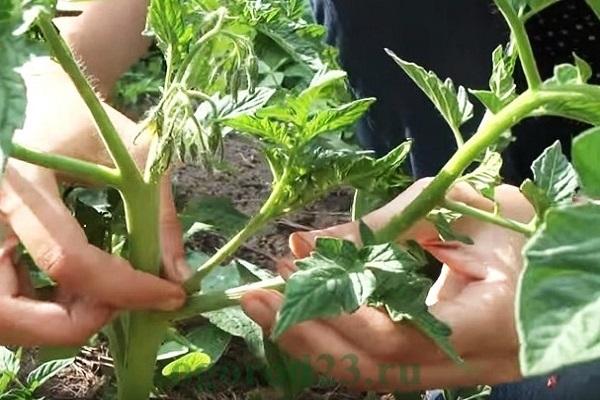
Growing tomato bushes
Removing excess shoots growing from the leaf axils frees up the bush, provides air access, and does not take away the plant's strength for the excess green part.
Stepchildren are broken off at a size of 5-8 centimeters, simply with fingers or cut with pruning shears. The best time for stepsoning is morning. To prevent a sprout from appearing in the same place again, when removing it, leave 2 centimeters of the stem.
Regularity of irrigation
Choosing the right watering regime helps speed up the growth and formation of the ovary. For the first 7-8 days, young seedlings are not watered. In the future, the following irrigation rates are recommended:
- young seedlings - 3 liters per bush after 3-5 days;
- during flowering and the beginning of fruiting - 5 liters per plant once a week.
The best way to supply water is by drip. The water cannot be cold; the temperature must correspond to the soil temperature. The best time is morning and evening, preferably morning. Water is poured under the root without soaking the green part.
To prevent excess water from turning into condensation on the walls of the greenhouse, the soil after watering is covered with organic mulch, which will later become fertilizer.
Drip irrigation systems help to distribute water evenly without excess, while applying fertilizers.
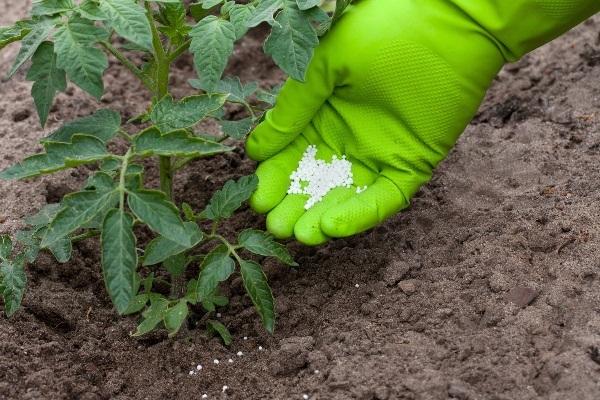
How and what to feed seedlings and adult bushes
Tomatoes are fertilized 3-4 times during the period of growth and fruiting. Most summer residents try to use organic fertilizers, diluting manure in each feeding.
Feeding times:
- 2 weeks after planting - nitrophoska (NPK complex), mullein. Consumption – a tablespoon of nitrophoska, 500 grams of manure per 10 liters. The norm is a liter per root.
- After 10 days. Potassium sulfate (1 teaspoon), manure. 5 liters per square meter.
- After 2 weeks - superphosphate (1 spoon), ash (2 spoons) per 10 liters. 5-7 liters per square meter.
When the tomatoes begin to ripen en masse, gardeners use sodium humate and superphosphate for additional plant support.
Garter and bush formation
The most hardworking summer residents have two trellises along the bed at different heights, to which the bushes are tied as they grow. The seedlings are attached 1-2 weeks after planting to the lower trellis, and as the bushes grow, they are transferred to the upper one. It is especially important to have 2 levels for tall bushes with large fruits and high yields.
Gardeners also recommend removing the lower leaves from the bushes. Rot often develops on foliage below the ovary. All other leaves with traces of disease and damage are also cut off.
Treatment against pests and diseases
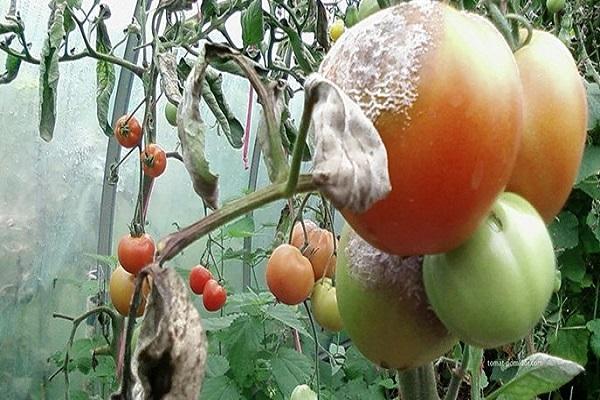
Having planted tomatoes in a greenhouse, you need to constantly monitor the condition of the bushes and ovaries in order to notice diseases and pests in time.
Diseased leaves and fruits are immediately removed; if the bush is significantly affected, it must be dug up and burned. More often than others, fungal diseases develop, which are provoked by excess moisture and poor ventilation. In this case, the greenhouse is dried by opening the doors and windows in dry weather.
Late blight is the most common greenhouse disease. It will be necessary to treat all plants with Fitosporin or analogues, remove all excess leaves and cover the soil with mulch.
For root rot, water the soil well with Alirin-B, Trichocin or Glyocladin. These are biological substances that produce natural antibiotics.
Important: for greenhouses it is better to choose varieties with increased resistance to diseases and carry out preventive treatments of the soil and plants with Fitosporin-M.
Nuances of caring for tomatoes
Greenhouses should be located in well-lit areas with an east-west orientation. With a lack of sunlight, tomatoes grow poorly and drop their ovaries. It is recommended to maintain the humidity in the greenhouse no higher than 65%, otherwise fungal diseases will develop.
You need to constantly care for tomatoes, providing timely ventilation, fertilizing, and following the recommended watering schedule.
To pollinate, tomato trusses are gently shaken during flowering to ensure the movement of pollen. It is useful to open greenhouses; to attract bees and other insects, put out fragrant flowers, jam, honey or compote.
In the winter greenhouse
In winter greenhouses with good heating, tomatoes are planted a month earlier (in April), using early tomato varieties that are resistant to fungal and viral diseases. In film greenhouses, a second layer is added to provide insulation.
When growing in a greenhouse, you should follow the same rules of agricultural technology as in greenhouse conditions. They are made in the southern high parts of the garden with low groundwater.
In order for tomatoes to grow well, they are illuminated for up to 16-18 hours a day, providing a temperature of 20-25 °, at night - not lower than 15 °.
Growing tomatoes in winter requires stationary greenhouses, a special regime and appropriate knowledge of agricultural technology.
In an unheated greenhouse
Greenhouses without heating help maintain the desired temperature for tomatoes during cold spells, protect against frost and excess rainfall.They create favorable conditions for constant growth and allow tomatoes to be grown until they ripen on the bush, which is important for cold regions.
The first harvest is harvested much earlier than in open ground, at the end of June, beginning of July.
The secrets to growing a good harvest are choosing the right varieties and proper care, focused on greenhouse conditions.
How to achieve a good harvest in greenhouse conditions
Growing tomatoes in greenhouses requires compliance with certain conditions that help increase yield:
- In hot weather, doors and windows should be open. If the greenhouse is film, the bottom edge needs to be folded back. High temperatures prevent the ovary from forming; at low temperatures, growth slows down.
- Ventilation is required. Tomatoes are not afraid of drafts; you can use fans to increase air movement.
- Compliance with watering and fertilizing regimes.
- Mulching the soil and wiping the walls to remove condensation. Humidity 60-65%.
- Temperature range – 22-25° during the day, up to 15° at night.
- Protection from pests and diseases, removal of affected leaves and plants.
- Helping tomatoes with pollination.
The right choice of varieties will provide you with delicious tomatoes for the whole season and will allow you to make winter preparations.
Harvesting tomatoes
When harvesting, observe the following rules:
- the stalks are left on the bush;
- It is better to remove milky ripe (brown) tomatoes so that other ovaries grow faster;
- In spring, tomatoes are harvested every 2-3 days (planted in winter), in summer – daily;
- For seeds, tomatoes are kept on the bush until fully ripe.
Note that if the temperature drops to 7-8 °, the tomatoes are completely harvested; they will not be able to grow or ripen.
For ripening, green tomatoes are placed in a dark room with a temperature of 15-20 °.The container with tomatoes should be ventilated, the number of layers should be 1-3. Red tomatoes accelerate the ripening of green ones, and with their help they slow down or increase the ripening time of the bulk.
Growing tomatoes in greenhouses helps most summer residents get tasty, juicy fruits. Breeders are constantly developing new varieties and hybrids that are more resistant to diseases and produce a stable yield in greenhouse conditions. Each summer resident gains his own experience in the process of work, finds the best ways to solve problems that arise when growing heat-loving tomatoes.