The soil is a constant source of nutrition for all plants, which draw out the mineral elements contained in it with their roots. Let's consider what chemical composition the soil has, the nutritional value of arable land, and the gross content of elements. The percentage content and importance of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for crops, the content and effect of microelements on plant growth.
Chemical composition of soils
The presence of chemical elements contained in the soil is influenced by the composition of the geospheres that took and are taking part in its formation: lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere.
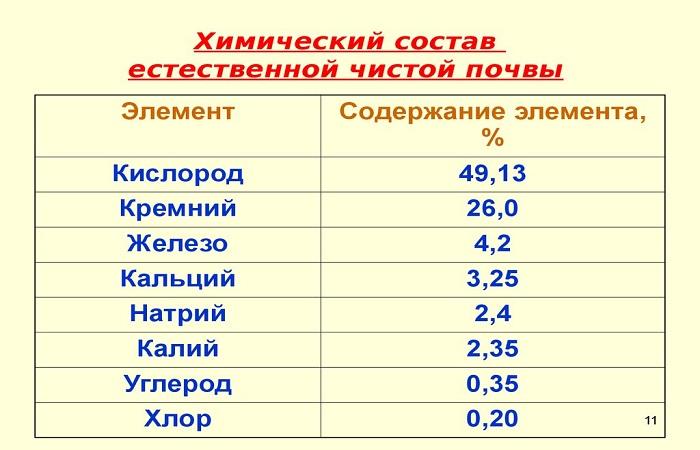
Almost all chemical elements can be found in soil, but most of them are found in small quantities. Only 15 are of great importance: C, N, O and H, which create organic matter, non-metals S, P, Si and Cl and metals Na, K, Ca, Mg, AI, Fe and Mn. The quantitative content of elements is different: oxygen and silicon predominate, followed by aluminum and iron, calcium, sodium, magnesium and potassium. They occupy 99% of the mineral volume of the soil, all others - 1%. The soil contains 20 times more carbon and 10 times more nitrogen compared to the lithosphere, which is associated with the activity of soil bacteria.
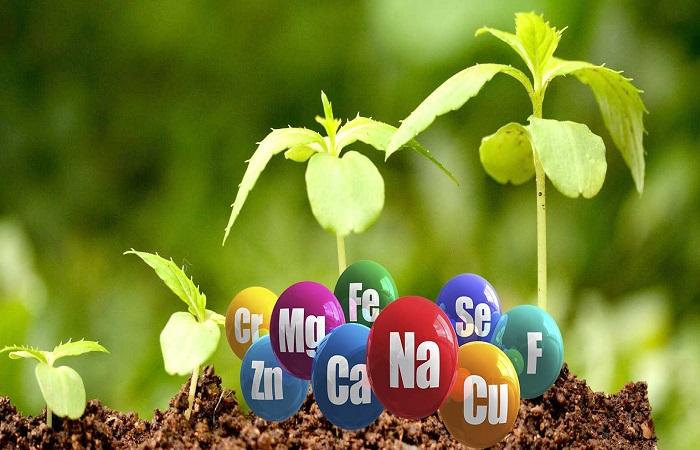
All elements, except nitrogen and oxygen, make up the ash part of organic matter, which is formed from chemical components concentrated in the soil. The life of vegetation depends on the presence and quantity of available forms of elements in the earth. They absorb, for the most part, N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, Si, which is why they are called macroelements; B, Mn, Mo, Cu, Zn, Co, F, consumed in smaller amounts - microelements. Of these, N, P, S, Fe, Mg are involved in the construction of proteins, K, Cu, Mn, Na - regulate the functioning of cells and serve for the formation of various plant tissues.
Arable land
The chemical composition of agricultural land depends on the type of soil and mechanical composition. The main elements form different mobility and compounds, which determine the ability to migrate, accessibility to plants and soil acidity.The compounds differ in structure, composition, resistance to weathering, and solubility. In soils they can be contained in the following forms: primary and secondary minerals, organomineral compounds, organic, absorbed forms, soil solutions and its gaseous part, living matter (bacteria, algae, fungi, microfauna).
Plants and soil microorganisms consume elements dissolved in the soil solution, are in an exchangeable state and are part of quickly dissolved organic matter.
Gross element content
The gross content of elements in the mineral part of the soil is determined as the content of oxides, expressed as a percentage. This indicator gives an idea of what elements the soil consists of, which ones predominate in it, and how they are distributed along the profile. Based on the gross content, it is possible to determine the origin of the soil, the processes that formed the horizons, and predict the level of fertility of such soil.
In almost all types of soils, the main component is silicon oxides, they occupy 60-70%. Aluminum occupies, on average, 15-20%, iron content varies from 0.5-1% to 20-50%. Oxides of potassium, magnesium, calcium and sodium occupy 5-6%, oxides of other elements together make up 1%.
Nitrogen content
Found in humus, it is part of organomineral substances and is the main component of plant nutrition. Nitrogen is bound to organic matter in the soil and is available to roots in ammonium, nitrate and nitrite forms. Stimulates the growth of green parts, most important in the initial stages of plant development.
Phosphorus in soils
It is part of the organic matter of soil, contained in it in the form of salts of phosphoric acid in combination with iron, aluminum and calcium.From organic matter, phosphorus passes into a form accessible to plants during the process of mineralization after the processing of organic residues by microorganisms. Phosphorus is extremely necessary for plants and, above all, for the normal development of roots and improving the quality of fruits.
More about potassium
The third main nutrient element is included in the composition of primary and secondary minerals, and therefore is not readily available to crops. In the soil solution, potassium is in the form of simple salts, on the surface of colloids - in an exchangeable state. From the soil solution, potassium easily enters plant cells through the roots. Vegetables, root vegetables, potatoes, tobacco, and cultivated herbs love potassium.
Microelements
They are found in the soil in small quantities, but they are also important for normal plant growth and development. Their number is determined by how much is contained in the breed. Microelements are found in humus, as part of primary and secondary minerals.
20 mineral elements are considered necessary for plants, each of them is responsible for the physiological processes occurring in plants and becomes a building material for their tissues. If any element is missing, plants develop worse and slow down, they get sick more often, do not tolerate cold and heat well, and their yields are sharply reduced. The same thing is observed with an excess of nutrients.The content of elements must be balanced; fertilizers should not be neglected, nor should the recommended dosage be exceeded, so as not to overfeed the plants.