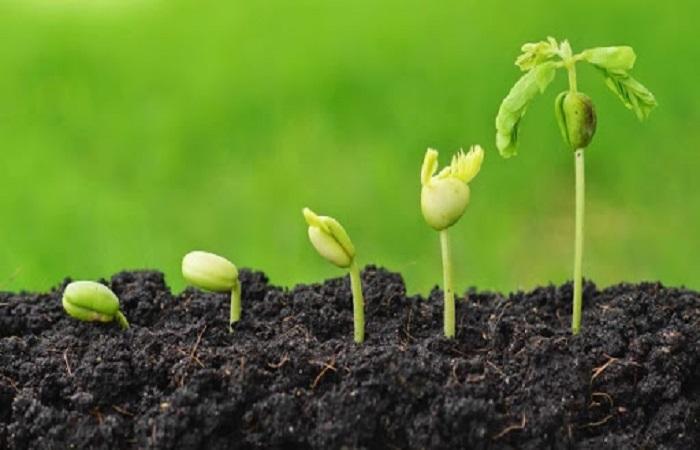
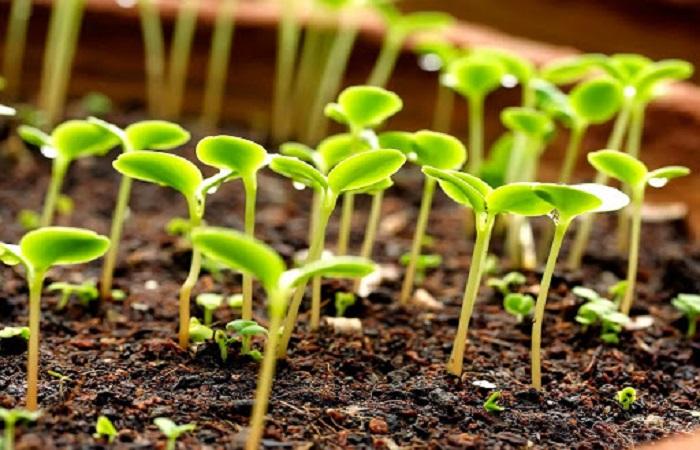
Soil fertility and plant health depend on the nutrient content of the soil. When there are enough of them, plants develop and bear fruit; when there are not enough of them, this impairs growth and fruiting. Let's consider what basic mineral elements are contained in the soil (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and microelements, in what forms, and how they are absorbed by the soil. How to regulate the nutrition of plants in the household.
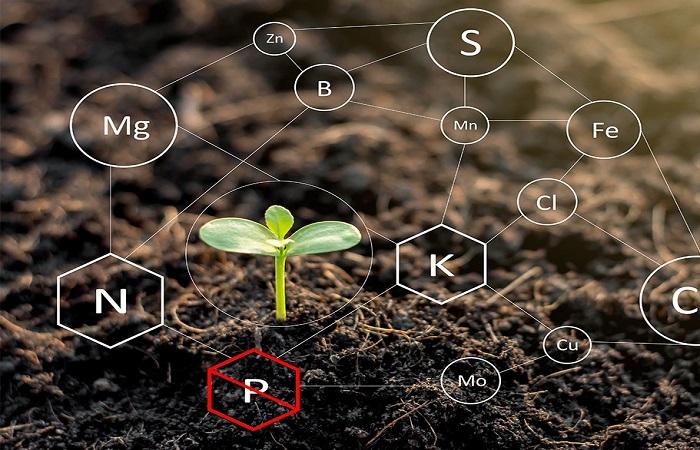
What nutrients are there in the soil?
The main ones are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium; these elements are present in any type of soil, but in different percentages. It also contains macroelements - sulfur, calcium, potassium, magnesium, and microelements, the content of which in small quantities is sufficient for plant growth.
Nitrogen
This element is necessary for plants at all stages of development, but it is especially needed at the beginning of growth. Nitrogen is part of proteins, chlorophyll, enzymes and other components of the plant body. Nitrogen is consumed by plants in 2 forms: nitrate and ammonium.
Ammonium
Nitrogen in this form is absorbed and retained under unfavorable conditions: soil acidity, waterlogging or dryness, deficiency of organic matter, cold soil. Ammonium nitrogen is better absorbed in acidic soils.
Nitrate
Nitrates move freely in the soil, are weakly fixed in it, and are easily washed down on light soils. They are the dominant form of nitrogen in warm, moist, breathable soil. Nitrates are contained in the soil solution; they easily move with the flow of water and are easily absorbed by the roots. Nitrates are better absorbed in neutral and alkaline soils.
Phosphorus
The second irreplaceable component, which is necessary for the normal course of photosynthetic and energy processes, for the formation and development of growth points, and cell differentiation. Phosphorus stimulates fruit ripening and makes plants resistant to adverse factors.
Potassium
The element improves the quality of fruits and enables plants to resist diseases. Potassium is involved in the activation of enzymes, retains water in cells, which helps plants tolerate drought and cold snaps.
Sulfur
The element participates in the formation of proteins, chlorophyll, fats, some vitamins, amino acids, enzymes, and increases their content in plants. Visually, sulfur deficiency is expressed by symptoms similar to nitrogen starvation: yellowing of leaves, thinning and elongation of young shoots, and stunted plant growth. Chlorosis begins to appear on young leaves because sulfur cannot move up the plant from lower leaves.
Calcium
The element is involved in regulating water and acid balance, creates conditions for proper development of roots, and increases the solubility of substances in the soil. Potassium helps plants absorb nutrients and affects the availability of certain mineral elements.
Magnesium
The element is present in chlorophyll, participates in the synthesis of amino acids and the assembly of proteins, the transformation of organic acids, and the construction of cell walls. Magnesium is a component of energy metabolism.
With a deficiency of this element, the synthesis of compounds with nitrogen, for example, chlorophyll, is inhibited and inhibited. Deficiency leads to a decrease in phosphorus levels and a decrease in its digestibility. With a deficiency of the element, root growth is suppressed, which leads to a decrease in the absorption of nutritional components entering the plants from the soil solution. This is especially noticeable during drought. Under unfavorable conditions, magnesium moves from leaves to flowers and fruits; its deficiency can be determined by the leaves.
Microelements
They are no less important for plant development than the basic elements, although they are required in smaller quantities. The role of microelements in plant life:
- Iron is necessary for the production of chlorophyll. Fixes atmospheric nitrogen, participates in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, hormones, affects the movement of plastic substances, cell growth and division.
- Copper is involved in the formation of carbohydrates, vitamin C, proteins, and fats. Increases cold and drought resistance, improves the growth of fruits and seeds, accelerates the supply of nitrogen and magnesium to plants.
- Zinc increases the content of carbohydrates and proteins, vitamins, activates growth hormones, enhances root growth, and increases resistance to drought and cold.
- Manganese activates auxin and some enzymes, reduces the nitrate content in fruits, but increases the content of ascorbic acid.
- Boron affects the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates, enhances pollination of flowers, prevents the ovary from falling off, prevents rotting of root crops, and enhances the outflow of nutrients into fruits.
- Molybdenum has a positive effect on nitrogen metabolism and protein synthesis, and reduces the amount of nitrates. Participates in the synthesis of nucleic acids, chlorophyll, enhances photosynthesis.
- Cobalt enhances nitrogen fixation, is part of cyanocobalamin, and increases the content of carotenoids and chlorophyll. Participates in nitrogen metabolism, protein and nucleic acid synthesis. Retains moisture in plants, especially during drought.
- Chromium activates enzymes, enhances immunity and immunity to stress.
- Selenium increases crop resistance to diseases and stress.
As you can see, the soil of gardens and vegetable gardens should contain these elements in sufficient quantities.
Absorption processes
Soil has mechanical, physical and chemical absorption abilities. Mechanical – the ability to retain particles larger than soil pores. This allows silty and colloidal particles to remain in the soil. Physical absorption is the ability to change the concentration of molecules of various compounds upon contact with a soil solution.
Regulating plant nutrition
An effective method of regulating the nutrition of cultivated crops is the application of organic and mineral fertilizers when preparing beds or during the growing process. Feeding can regulate the balance of mineral elements, increase the content of those that are missing, and reduce the amount of others if they are in excess. Fertilizer application must be carried out in precise dosage and at a certain time.
Neutralizing acidity makes elements more available for absorption by plants. Other processing methods: adding sand to clay soils, clay to sandy soils, which improves their mechanical composition.
An important point in the normal organization of nutrition is the irrigation regime, since mineral elements are in the soil solution, which must flow freely to the roots. In arid soil, the supply of mineral elements is difficult, even if they are present in sufficient quantities.
Any soil is saturated with nutrients, but in different quantities.They enter plants through the roots and are used by them to build cells and form substances specific to a given plant type. To get a good harvest, the soil must contain all the minerals and substances necessary for the crop. The easiest way to regulate their content is with fertilizers, but it is also necessary to carry out agricultural practices that improve soil characteristics: warming, ability to pass air and moisture and retain important components.