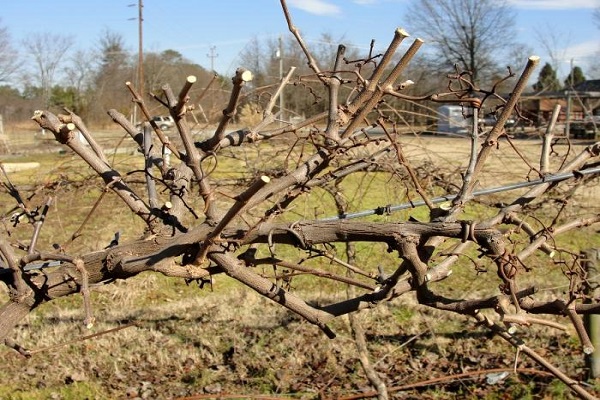
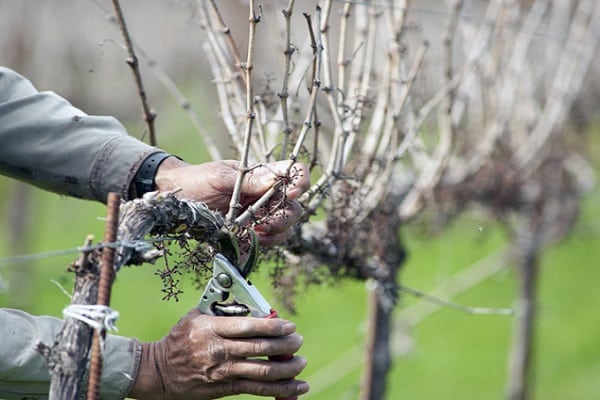
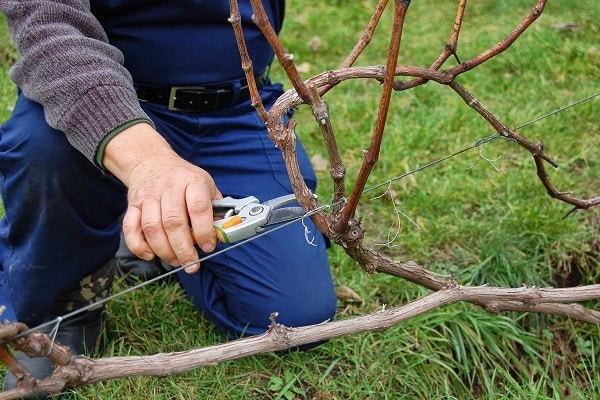
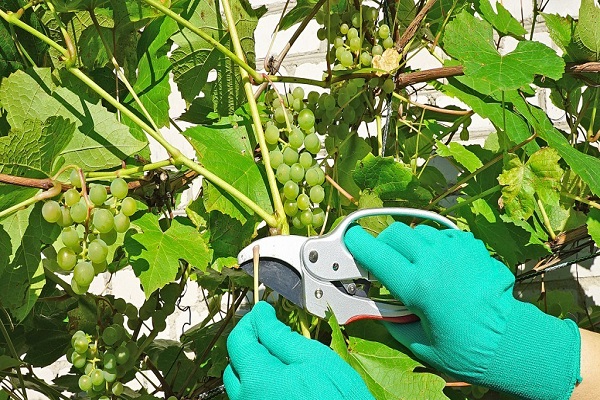
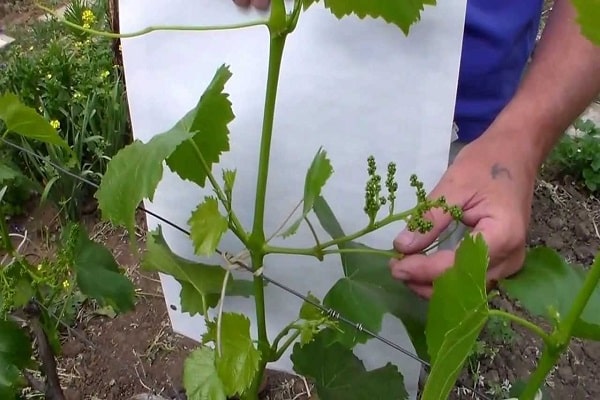
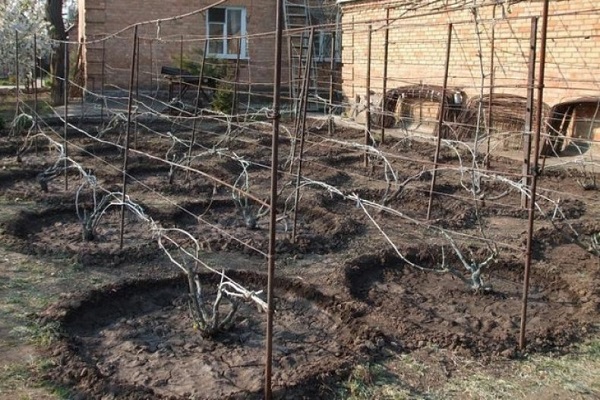
Growing a spreading vineyard and getting a good harvest from it is a difficult task even for an experienced gardener. In order for the vines to grow healthy and large, proper grape pruning and comprehensive care are required. Pruning bushes is one of the key points of care and is necessary to adjust the height of plants, give a decorative shape and active fruiting.
- Why prune grapes? Advantages and disadvantages
- Timing of pruning according to growing area
- Common Schemes
- Features of bush formation
- In the first year
- In the second year
- In the third year
- Reshaping old bushes
- Pruning grapes and forming fruit units in spring
- Features and technologies of summer pruning
- Pinching
- Removing stepchildren
- Lightening
- Coinage
- Rules for pruning vines in autumn
- Post-procedure care
Why prune grapes? Advantages and disadvantages
Without constant care, the grapes grow long vines and cling to various supports, including neighboring trees.. The branches reach towards the sun's rays and accumulate nutritional components in order to form fruits by autumn for subsequent reproduction. The main benefits of pruning a plant are as follows:
- In a thickened state, the bushes will bear small berries, and pruning promotes the active growth of large fruits.
- When growing established plantings, it is more convenient to harvest using improvised means.
- Pruned bushes have the ability to recover and produce new healthy branches when old ones are removed.
In addition to the obvious advantages, there are several disadvantages to removing old branches. The main problem is that incorrectly chosen timing leads to fragility and breaking off of the bushes. Due to improper formation of the crown, the bush intensively develops shoots, resulting in a reduction in yield.
Timing of pruning according to growing area
The period during which bushes should be formed by pruning depends on the growing area. In areas with a cold climate and the risk of return frosts, bushes need to be formed 2 times a year - in autumn and winter.
In the middle zone, it is enough to carry out the procedure only with the onset of spring. Based on the swollen areas, it will be possible to visually identify living buds and remove dead ones.
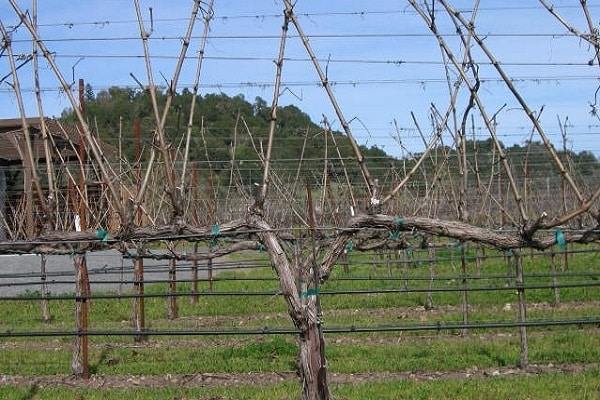
Common Schemes
There are several types of formation of grape bushes. Conventionally, all schemes are divided into 2 categories - covering and non-covering.Covering ones include fan and cordon ones; the non-covering group includes arbors and standard ones, used for pruning frost-resistant varieties.
For beginner gardeners, fan pruning is recommended as it is the most convenient method. In the first year of life of the plantings, it is necessary to grow a large shoot and trim it in the fall, leaving 2 eyes from the ground level. Over the next year, grown annual shoots are pruned into short and long ones. In the spring of the third year, sleeves are created, growing 2 vines on each of them.
To avoid mistakes and avoid regrowth of bushes, it is recommended to perform pruning according to schematic drawings.
Among more experienced gardeners, the Kurdyumov pruning method is in demand. The process of leaving during the first two years does not differ from the fan method. Starting from the third year, in the spring they tie the vine in a horizontal position and wait for the growth of annual shoots. After the autumn harvest, the vine with spent shoots is cut off to form a new one.
Features of bush formation
When pruning grapes, it is necessary to take into account a number of features. At different periods of a plant’s life, the nuances of crown formation and the location of fruiting vines depend.
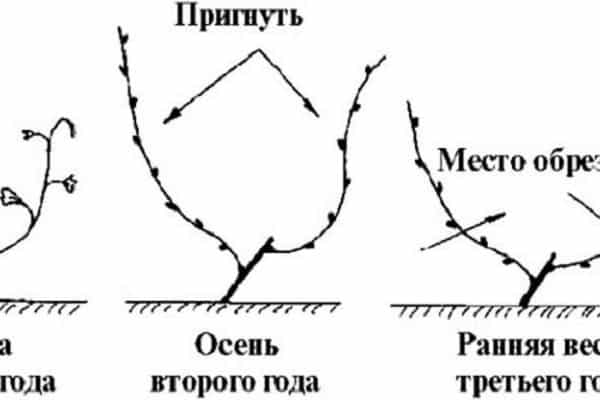
In the first year
During the first year after planting grape seedlings Constant care is required as the plant is in its development stage. With the onset of spring, 2 lower buds are left on the central trunk, and all the rest are removed. Young shoots are grown from the remaining buds and fixed in opposite directions.
With the onset of autumn comes the need to trim the shoots. You should wait until the leaves fall and only then start pruning so that the grapes do not leak juice.It is recommended to shorten the shoots to different lengths, leaving 2-4 buds. On the eve of winter, the grapevine is covered to protect it from frost.
In the second year
When the grape bushes take root and the threat of severe cold passes, it is necessary to remove the covering material and tie the fruiting vine to a support, pointing the tops in different directions. The stems grown from the buds are directed upward or with a slight slope to the side from the central part of the bush.
In autumn, the long sleeve on the bushes is shortened, getting rid of unnecessary shoots. Then the vertically growing stems located closer to the center are cut off, leaving the 2 best buds for their further development. For the winter, the vine is removed from its support and covered until the onset of spring warming.
In the third year
In the third and each subsequent year of bush growth, the care process is carried out according to the same scheme. In the spring, after the risk of cold weather returning has disappeared, the covering material is removed and oblong arrows are tied in a horizontal direction, pointing the ends in opposite directions.
During the hot period, stems are formed from each bud, which are cut to 10-15 cm in early August. Due to this, the quality and quantity of the harvest increases. To prevent an excessive mass of shoots from forming on the vine, it is not recommended to carry out chasing before August.
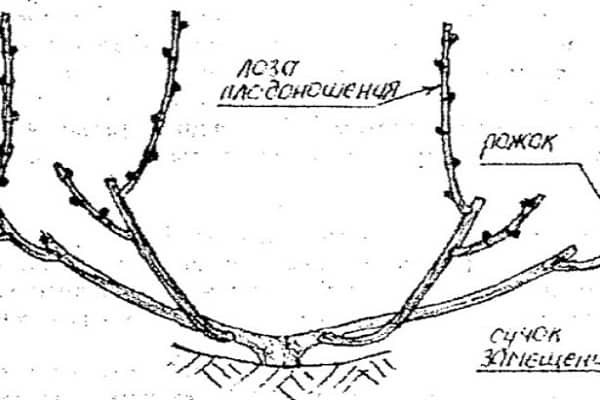
In the fall, it is enough to cut off the fruit-bearing shoots with part of the sleeve so that a link with two shoots remains on each side. In the future, pruning is carried out in the same way as in the previous year.
Reshaping old bushes
To restore fruiting and give old bushes a decorative appearance, you can resort to reshaping.To give shape to young bushes, in which the bulk of the branches are located near the ground, the immature vines are removed and half the branches are trimmed. The remaining vines will be needed for the fall harvest.
If the branches grow significantly above the soil level, then at the beginning of spring the bushes are heavily pruned in order to get a harvest this year. After the grapes are harvested, the trunk is removed, and new bushes are created from the newly formed shoots.
Pruning grapes and forming fruit units in spring
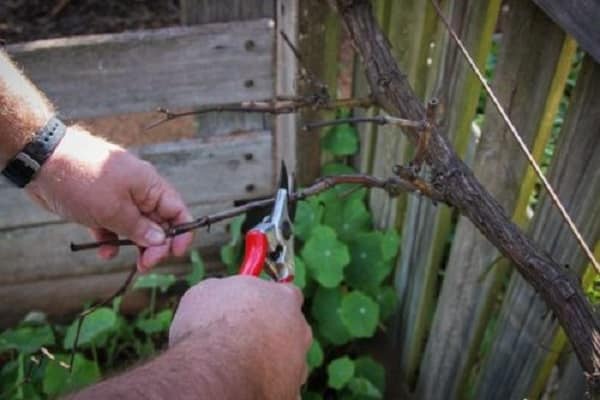
Regardless of the chosen formation scheme, in the spring it is necessary to remove frozen, rotten and broken branches. Also, large shoots with a thickness of more than 11 mm and too fragile - up to 5 mm in diameter - must be pruned. Before the onset of the hot season, the shoots should not be very long, so it is enough to leave no more than 15 eyes. As a rule, when forming a fruit unit and pruning, 1-2 nodes are left on each shoot.
During the spring period, it is necessary to take into account a number of features when caring for grapes. In particular:
- It is always allowed to shorten the vine only on one side;
- pruning shears for cutting branches and leaves must be sharp;
- shoots should be trimmed in the direction from the eye;
- During the shaping process, the fruit shoot must be left above the replacement knot.
Features and technologies of summer pruning
After the start of flowering and spring processing of grapes it is necessary to continue caring for the plantings. With the onset of heat in June, fatty shoots, which form from the old parts of the vine, begin to grow intensively. With proper summer pruning, the following results can be achieved:
- A sufficient number of shoots will be formed on each plant, taking into account the size of the bush.
- The grapes will be protected from diseases and attacks by harmful insects.
- The ovaries will have access to ultraviolet rays and free passage of air.
- Nutrient components are redirected from parasitic shoots to green brushes.
Summer formation of bushes should be carried out in early June, when newly grown shoots reach a length of 15-20 cm. In August, shoots are more difficult to remove, which causes difficulties for inexperienced gardeners.
Pinching
Shoots growing on grape bushes require constant care. Pinching to remove them is carried out daily. Since the structure of the vines is similar to vines, the tendrils serve as clamps. If the bushes are tied to special supports, then the tendrils can be plucked off completely.
Pinching is done manually before active flowering. It is necessary to tear off the upper elements of young branches so that the remaining parts of the shoot reach a length of about 10 cm. As a result of pinching, the strength of the plant is restored in future inflorescences. The procedure has a beneficial effect on the number of clusters formed and the quality of the harvest.
Removing stepchildren
After waiting until the flowering period is over, you should begin removing the stepsons. The elements are small processes that form in places located between the leaf and the stem of the branch. If you do not remove the shoots, they will begin to grow rapidly, and the bush will become thickened, which will prevent the passage of sunlight to the grapes. In addition, there will be a risk of developing infectious diseases, due to which the fruits will lose their taste characteristics and become sour.
It is not recommended to remove the stepsons to the base, since after a couple of days a new shoot will form in the same place. Experienced gardeners pinch off part of the shoot, leaving 2 cm.The procedure must be performed weekly.
Lightening
The procedure for lightening plants involves pruning aimed at thinning foliage. This ensures sufficient air flow to the grapes during the period of active ripening of the bunches. It is recommended to immediately destroy the branches cut off during lightening, as they may contain pests that can move onto the plants and cause an infection.
Excessively dense bushes are also subject to thinning, even if brushes have already formed on them. The procedure may slightly reduce the amount of ripening grapes, but its quality will increase significantly. During lightening, 3-5 bunches should be left on powerful branches, and only one bunch on weaker branches.
Coinage
As a result of chasing bushes, the upper elements of growing shoots with leaves are removed. The purpose of minting is to stop development for several weeks and redistribute nutritional components between all parts of the grape plantings.
By chasing each vine, they save about 15 developed and unaffected leaves, which can provide the bushes with nutrients in sufficient quantities. Short pruning of the vine does not allow for normal saturation of the bunches with nutrition, which provokes a reduction in yield.
Rules for pruning vines in autumn
During the autumn preparation of grape vines for winter, it is necessary to perform two-stage pruning. At the first stage, dried leaves and inflorescences are removed. After this, it remains to wait until the foliage completely falls and the nutritional components transfer to the main trunk.During this period, the thickest shoots are shortened to form a replacement knot during berry ripening.
At the second stage of pruning, crowns are formed according to a non-covering pattern. Every second shoot is shortened, leaving 3 buds on each of them. If there are other shoots growing on the trunk, they are also removed, leaving 5-6 buds.
Post-procedure care
After pruning the bushes, it is necessary to continue comprehensive care for them.. The main stages of care are watering and fertilizing. Watering helps plantings recover after cover is removed. To treat the soil, it is recommended to mix a solution of 20 g of superphosphate, 3 g of boric acid, 10 g of potassium, 1 g of iodine and 2 g of sulfuric acid. Water the soil evenly and abundantly.
Grape bushes should be fed with fertilizers from the fungicidal and insecticidal categories. Such fertilizing ensures intensive growth and development of green spaces, repels pests and prevents the occurrence of infectious diseases. Even in the absence of obvious signs of plant damage, fertilizing can be used for preventive purposes to ensure the ripening of a good harvest.