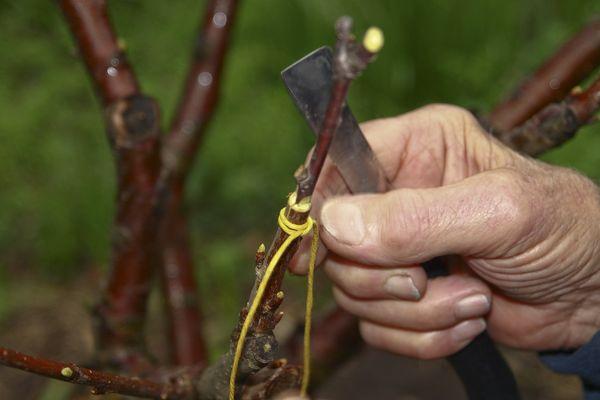
One of the ways to propagate sea buckthorn is grafting. A male cutting is grafted onto a female tree, which eliminates the need to grow different trees nearby. When wondering how you can graft female sea buckthorn onto male one, you will need to understand all the nuances of the procedure in order to avoid mistakes.
Benefits of sea buckthorn grafting
Grafting a berry crop allows you to increase productivity and grow different types of sea buckthorn on a tree. Reproduction is based on feeding the young shoot with nutritional components through the roots.
The advantages of sea buckthorn grafting include the following:
- the possibility of obtaining a harvest of a new variety without planting a separate tree;
- reduction of the ripening period;
- saving space in a summer cottage;
- replacing a variety you don’t like with another variety using a viable powerful rootstock;
- growing varieties that are not adapted to the climate in the growing region.
Required Tools
The correctness of the procedure for grafting a cutting to a planting largely depends on the devices used for grafting.
To plant sea buckthorn you will need:
- A garden knife used to form cuttings and clean the cut area on the trunk.
- A budding knife with a concave blade used to push apart the bark.
- A cutting knife with a straight blade for making oblique or straight cuts.
- Grafting pruner with different attachments.
All of the listed tools should be well sharpened, as this will simplify the work process. Also, to propagate sea buckthorn, you may need plastic film to fix the new cutting on the tree.
Dates
Sea buckthorn grafting is carried out in stages, and the exact timing depends on weather conditions. Young and strong shoots about two years old are cut from sea buckthorn in late November - early December. Then the cuttings are stored at low temperatures, and with the onset of spring, a rootstock is made.
After a warm winter, when there is no chance of young branches freezing, it is possible to select cuttings for propagation at the end of March or early April. Selected cuttings are wrapped in plastic wrap to prevent drying, and then placed in the refrigerator or placed in a cool room.
The recommended time for grafting occurs at the beginning of the spreading of the integumentary bud scales of the rootstock used, which most often occurs towards the end of April.
How to graft sea buckthorn?
There are several methods of grafting sea buckthorn, which differ in the nuances of their implementation. It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the different options and features of their implementation in order to choose the appropriate method.
For the bark
The bark grafting method should be used for older plantings, when the diameter of the rootstock exceeds the diameter of the cutting. It is important to consider that the diameter of the rootstock branch must exceed the thickness of the scion.
The vaccination procedure is as follows:
- In the fall, cuttings are selected and prepared in advance. A young shoot with 2-3 formed buds is best suited.
- At the end of the cutting, leave a cut at an angle of 45 degrees.
- The rootstock is trimmed so that it meets the cut on the scion. The depth of the cuts should be identical.
- Using a budding knife, lift the bark on the rootstock and place the shoot in the split. On either side, the rootstock and scion are combined along the educational tissue.
- The grafting area is wrapped with plastic film or special grafting tape. The upper part of the cutting is treated with garden varnish.
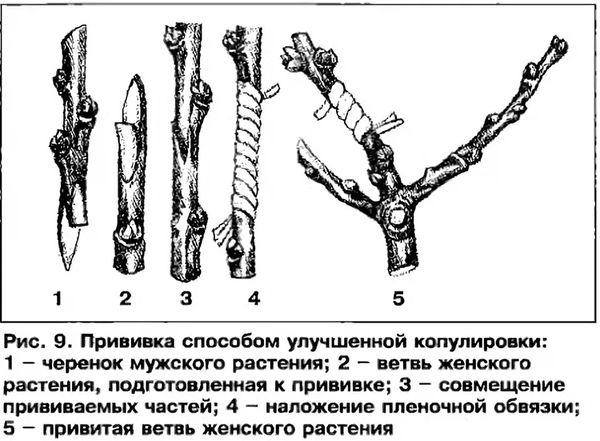
Copulation
The copulation method is suitable for immature seedlings and mature plants. The main requirement for copulation is the same diameter of the scion and rootstock. Before performing the procedure, it is necessary to prepare the rootstock. If the grafting is carried out on a young seedling, then the sea buckthorn trunk is shortened a couple of centimeters above the root collar.
Then the most powerful and healthy shoot is selected, and the rest are cut off. Within 3-4 months the shoot is grown.In order for the cutting to actively thicken, the lateral stepsons are cut off at a distance of 15 cm from the lower base. When the rootstock grows, they begin direct propagation.
The process includes the following steps:
- An incision up to 3 cm deep is made on the rootstock. An identical cut is left on the cutting under the bud located below.
- Stepping back a third from the end of the cuts, a tongue is formed, the length of which should not reach the cut. To form the tongue, a sharpened knife is placed perpendicular to the cut and pressure is applied, moving the blade to the right and down.
- The cuts formed on the rootstock and scion are joined to each other.
- The junction of the cutting is wrapped with plastic film. Wind the material in a clockwise direction. If gaps form, they can be filled with garden pitch.
Care after vaccination
Features of caring for berry crops depend on the chosen grafting method. After copulation, the result can be seen within 10-15 days. If the cutting takes root on the plant, shoots will grow on it. In the case when the buds on the cuttings bloom, but do not continue to develop and dry out, this means that the shoot has not taken root.
On each correctly established cutting, several shoots are formed. When they grow up to 10 cm in length, you need to select the most developed one, and pinch the tops of all the others.
After grafting onto the bark, when the growth of the cuttings stops, the stepsons growing from the bottom are shortened. The growth under the rootstock is removed so that it does not absorb nutritional components and does not reduce the immunity of young seedlings. To ensure the direction of juices to the place of the rootstock, it is allowed to leave buds under it.At the same time, shoots will form from them that need to be pinched.
The rest of the sea buckthorn care is carried out in the standard mode. For the development and fruiting of trees, it is necessary to water, loosen the soil, and carry out protective spraying to combat diseases and pests.
Spreading the gardener's mistake
When grafting sea buckthorn, many novice gardeners often make common mistakes. By familiarizing yourself with possible errors and using the right technology, you will be able to prevent a number of problems.
When performing the procedure, you need to know the following nuances:
- The cutting should be grafted not into a small branch, which will dry out after fruiting, but into a large branch growing on the sunny side. This way the new cuttings will not wither away.
- When copulating, the optimal size of the scion is 5-10 cm. On shorter or excessively long branches, the rootstock may not take root.
- Despite the plasticity of berry crops under external influences, cuttings and further actions must be made in a short period of time. Otherwise, you can harm the plant.
It is important to store cuttings in suitable conditions to ensure rapid and proper fusion.