Flour obtained from cereal grains is the most important product of its processing. Flour for baking bread and bakery products is usually obtained from soft wheat. The quality of flour affects the quality of products made from it. It is determined by different methods. Let's consider the meaning of the falling number of wheat, what it is, the calculation technology, how the indicator affects the quality of future bread.
What is the falling number of wheat
One of the main criteria for the baking quality of flour is autolytic activity, which is determined by the intensity of the processes occurring during the production of dough and baking products from it. This is the ability of flour to form substances under the influence of enzymes or when the flour mixture is heated.
Determination of autolytic activity by falling number is based on the viscosity level of the water-flour mixture when heated in a boiling bath for 1 minute. For wheat grain, the falling frequency value should be 250 seconds.
The falling number is an indicator of the activity of alpha-amylase, an enzyme in the grain of wheat, barley, rye, triticale and in products obtained from them.
Computing technology
Activation of the alpha-amylase enzyme occurs during grain germination. Protein breaks down starch into sugars. At the same time, the quality of the raw materials decreases, and products from them are of poor quality: small in size, dry and quickly become stale.
The higher the enzyme activity, the more intense the destruction of starch will occur, in this case the indicators will be low. The unit of measurement for the characteristic is usually considered to be a second.
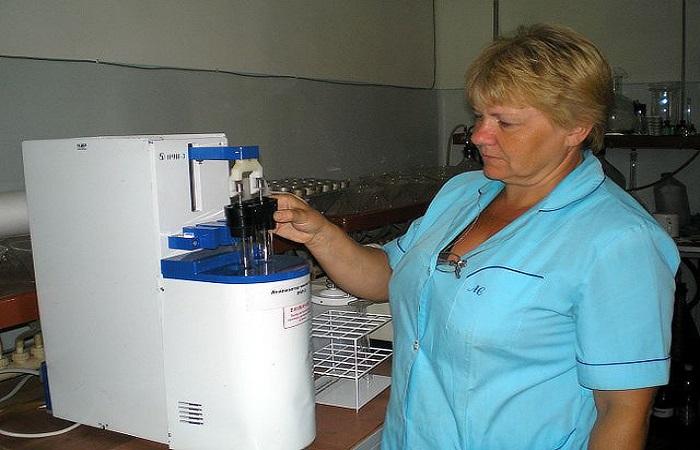
The falling number is measured by the Hagberg-Perten method, which is based on the gelatinization of ground grain or flour in a test tube, which is heated in a boiling bath, and determining the rate of enzyme activity.
Preparation
Enzyme activity is measured using a colorimetric method. To carry out the analysis, you will need special instruments (colorimeter and stopwatch) and solutions of calcium chloride, iodine and a buffer solution. As well as special equipment in the form of a centrifuge, a laboratory mill and a sieve, and measuring instruments, scales and a pH meter.
Mixing
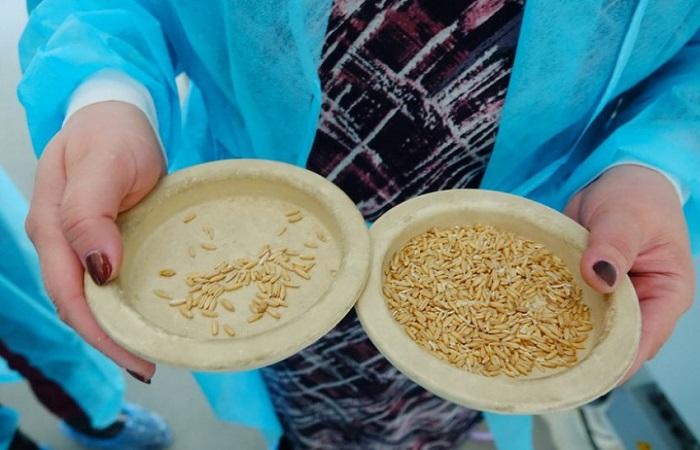
Flour is poured into test tubes, 25 ml of distilled water is poured into them, the temperature of which should be 20 °C. The test tubes are sealed with stoppers. The contents are mixed by shaking until it becomes homogeneous.
Analysis
The water bath in the device is heated to boiling. Test tubes without stoppers are placed in the device and the stirring rods are lowered into them. After 5 seconds, the device begins to move the tubes vertically at a frequency of 2 Hz. The mixture begins to thicken, swell, gelatinize, and the process of enzyme activation and starch breakdown begins.
After a minute, the stirring rods should move down the tubes. The drop time is affected by the degree of resistance of the water-flour mixture.
What determines the reliability of the result?
There may be errors at each measurement stage. They arise due to flour not meeting the standard requirements (coarse or, conversely, fine), incorrect humidity, high or low sample temperature. Corrections are made by insufficiently accurate scales, non-compliance with the mixing time, and insufficient temperature of the water bath.
The influence of falling number on bread quality
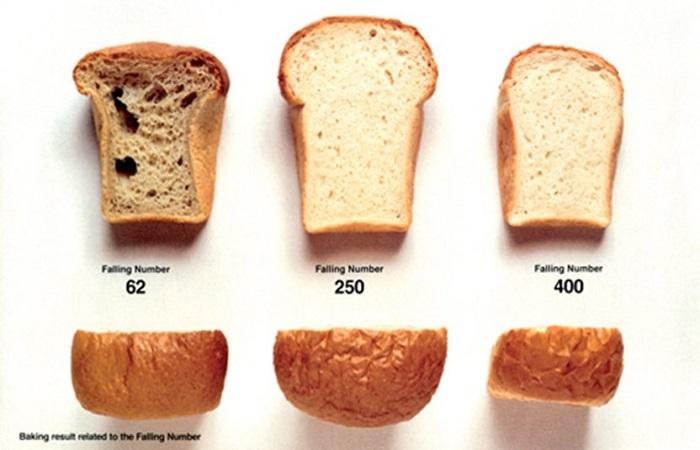
Good quality flour has average performance. Both low and too high indicate its poor quality.
Low performance
A low number indicates that the flour is made from sprouted grains. It is in germinating wheat that the amount of enzyme increases, the dough from it spreads, the bread crumb becomes inelastic, sticky, with rough, uneven porosity.Poor product quality negatively affects the volume and taste of bread. Raw materials with low performance are not recommended for processing.
High quality indicators
They indicate low enzyme activity in flour, which is necessary for the normal fermentation process and the acquisition of plasticity and elasticity by the dough. High performance flour is obtained from grain that has been dried at high temperatures. The dough does not rise well from it, the volume of the finished product decreases, the bread turns out to be insipid, with a weak odor, and pale in color.
The falling number of flour is an indicator that is used to characterize the quality of grain and flour obtained from it. The standard for grade 2 wheat flour is 160 seconds, for other grades – 185 seconds.