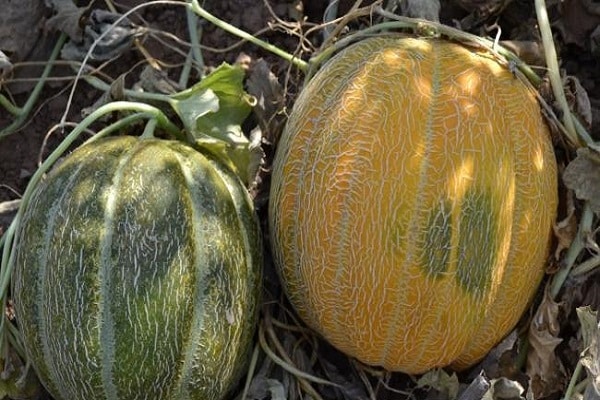
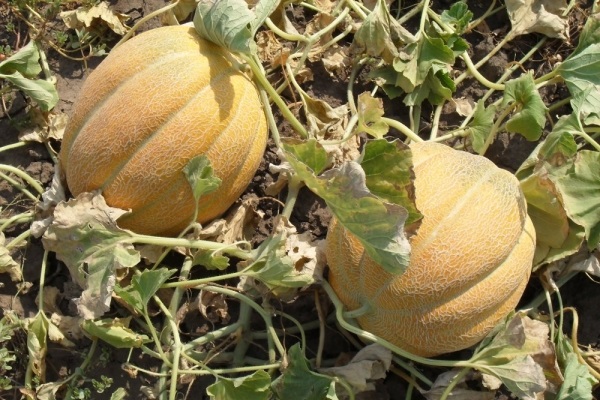
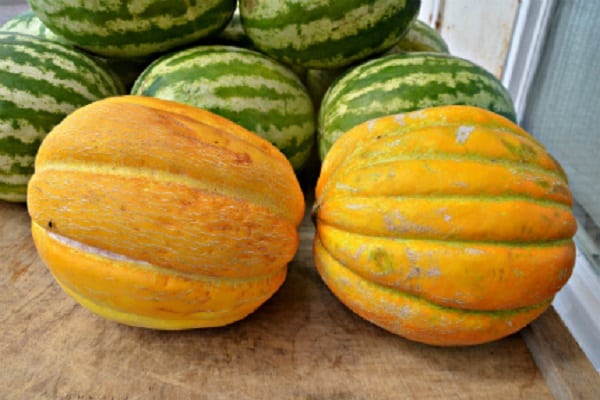
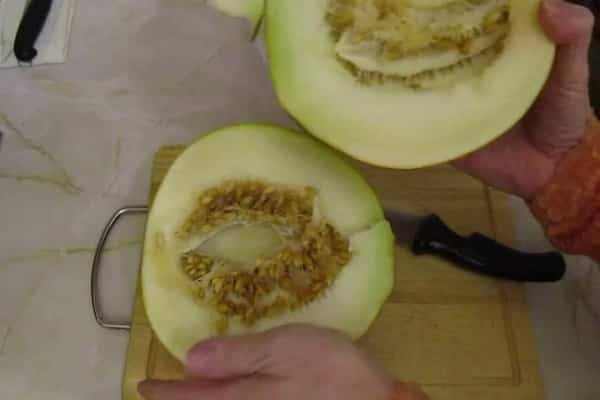
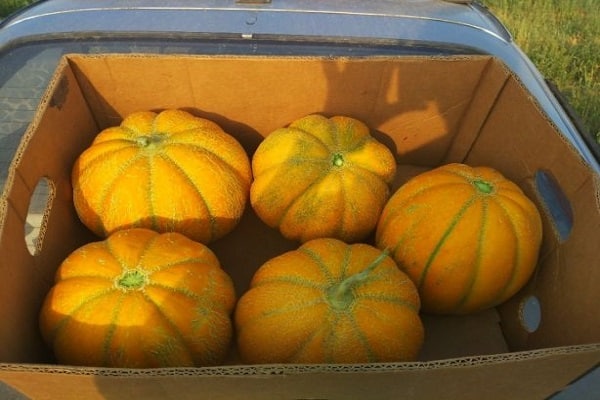
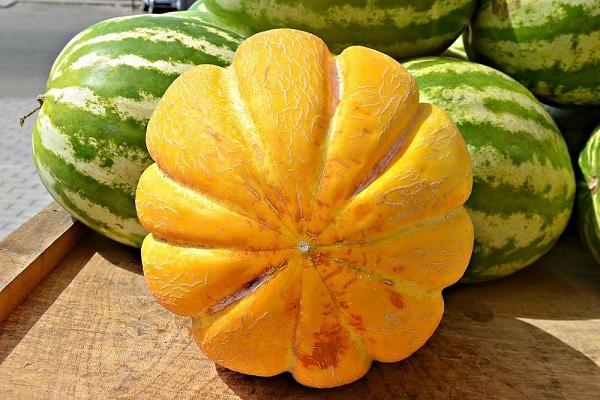
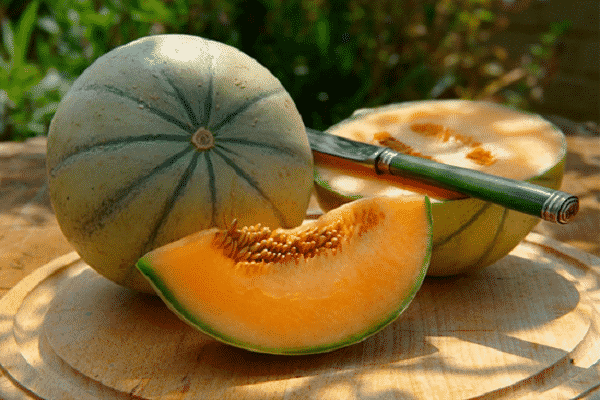
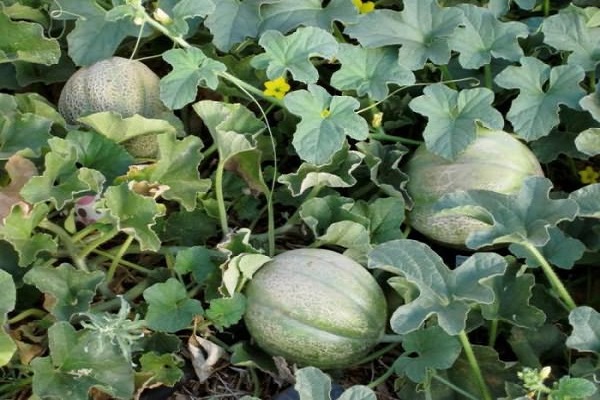
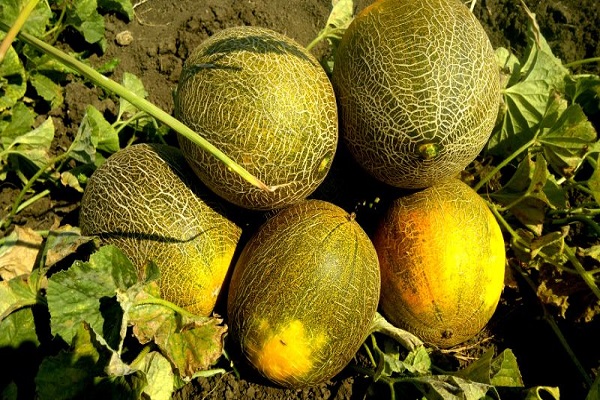
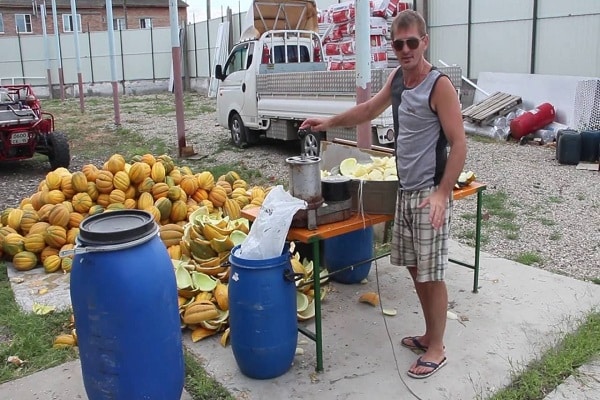
The Ethiopian melon received its name as a result of its resemblance to the fruits of the hot African continent. This means that the melon is both large and sweet. The variety was bred by Russian breeders, so it grows successfully in the country’s climate. The variety is popular among gardeners. It is grown everywhere in open ground.
Distinctive features of the melon variety
Melon crops came to our gardens from the hot regions of Central Asia. And the plant produces harvests of sweet fruits when the summer is hot and dry. The Ethiopian melon variety tolerates heat easily.The plant has powerful but short vines, so the bush looks compact.
According to the description, the Ethiopian melon has the following fruits:
- round shape;
- weighing from three to five kilograms;
- with a thick yellow peel, painted with a grid pattern;
- as if divided by stripes into slices;
- with white flesh;
- juicy, with the taste of honey.
A feature of the Ethiopian vegetation is self-pollination, since on the shoots male flowers are adjacent to female ones.
The advantage of the melon variety is the following characteristic of the plant:
- You can get fruits from melon 80 days after the first shoots appear.
- There is no need to pollinate the plant.
- Compact bushes of the Ethiopian variety are grown in a small area of the garden.
- One plant produces up to 5–6 fruits per season.
- It is worth growing the variety even in areas with a temperate climate - it has time to ripen.
If favorable conditions are created for the plant and protected from fungal infections, then it will reward you with sweet, juicy fruits.
Growing Ethiopian Melon
For melons and melons, a planting site is chosen in the fall. The area should be well heated by the sun. The soil for melon is not swampy, loose. River sand and wood ash are added to heavy clay soil. Depleted soils are enriched with humus or peat. Fertilizers include complexes containing potassium and phosphorus. After digging, leave the beds under melons for the winter.
In areas with a warm climate, melons are immediately sown in open ground; in cold climates, the seedling method of cultivation is adopted.
We grow seedlings
After rejecting the seeds, they are kept in a solution of boric acid and zinc sulfate for twelve hours. For disinfection, it is recommended to place a bag of seeds in a one percent solution of potassium permanganate for half an hour.It is better to harden the seed material by alternately immersing it in warm water for a day, then in cold water. The hardening procedure is carried out three times.
In the first half of April, containers are prepared by filling them with nutritious, air- and moisture-permeable soil. It is better to choose a peat pot or glass for each plant. Then it will be more convenient to transplant the seedlings into the beds.
By mid-May, 3–4 leaves will appear on the seedlings. If the soil in the garden has warmed up to 10–15 degrees, then it’s time to transfer the seedlings to open ground.
Planting in open ground
For cultivating melons, the square-cluster planting method is used. A distance of 50–70 centimeters is established between the nests. River sand is added to the holes in advance, which helps increase the looseness of the soil and improve heating. If grown by seeds, then plant them to a depth of 3–5 centimeters. Seedlings are buried at the level of the lower leaves. The first three days do not water the sprouts, giving them time to get stronger.
To increase the yield of melons, it is recommended to plant corn or sunflowers next to the plant. Such rocker plantings will protect the Ethiopian melon from the cold wind and save it from low temperatures.
Care instructions
Timely care of the Ethiopian melon consists of:
- thinning plantings;
- pinning lashes;
- row spacing processing.
Plant breakthrough is to leave up to 3-4 seedlings in the nest.
As soon as the fruits begin to set, the lashes are pinned to the ground with wooden hooks or the shoots are sprinkled with earth. Then the formation of additional roots will begin. To make the procedure effective, make a hole and place a leaf petiole there, then sprinkle soil on top of the lashes.
To speed up ripening, bushes are formed by pinching the main stem above the fourth leaf.After all, almost no female flowers are formed on this shoot.
Loosening of row spacing is carried out first to a depth of ten centimeters, then to seven. During the summer period, the procedure is carried out three times.
As for fertilizing, the Ethiopian variety needs:
- the first - with a solution of bird droppings in a ratio of 1:15 when 4-5 true leaves appear;
- the second after 2–3 weeks with a mineral complex of 50 grams of superphosphate, 20 grams of potassium salt and ammonium nitrate per bucket of water;
- the third - after a two-week break with mineral fertilizers.
Half a liter of nutrient solution is poured onto the well.
Water Ethiopian melons regularly, monitoring the growing season of the plant. The plant does not need excess moisture - the fruits and shoots will begin to rot. But a lack of water will affect the number of ovaries, and therefore the harvest.
Increase the frequency of watering during fruit set, and reduce it before the flowers appear and during the ripening period.
Diseases and pests of melon
The Ethiopian variety is good for everyone, but growing melons is associated with diseases and pests that attack the plant during the development period.
Fungal infections have to be dealt with:
- black leg;
- olive spot;
- powdery mildew.
Blackleg fungus destroys seedlings and young shoots. Pathogenic microorganisms are activated when there is a lot of moisture in the soil and stagnation of water. And sudden temperature changes contribute to the spread of spores. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to treat the seeds in a solution of Fitosporin or potassium permanganate.
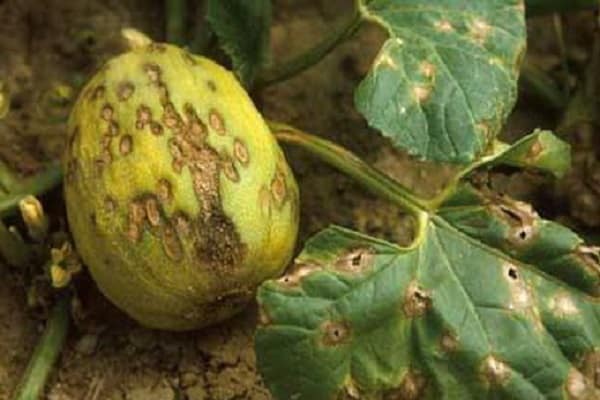
Olive-colored spots with an oily structure on the leaves indicate the development of a fungal disease. They fight pathology by treating with fungicidal preparations and Bordeaux mixture.
White coating on the leaves is a sign of powdery mildew.Timely measures taken will help get rid of the infection. To do this, pollination with sulfur powder or treatment with a strong solution of potassium permanganate is used. Fungicidal agents will also help: Fundazol, Topaz.
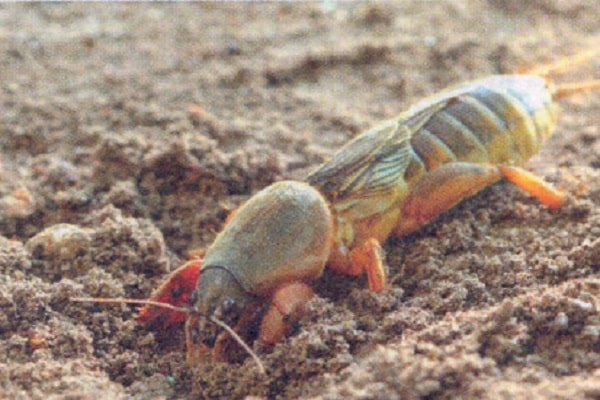
Among the pests that affect the beds melon fly. Its larvae penetrate the pulp and cause the fruits to rot. To destroy the pest larvae, plow up the areas after harvesting ripened melons, and treat the bushes with Rapira twice during the summer.
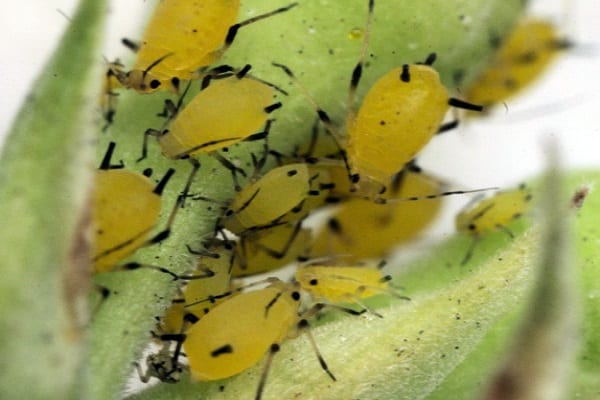
The larvae of the cutting armyworm can cause damage by damaging the roots and stems of the plant. They destroy adult insects and larvae using insecticides such as Decis. Spider mites can be easily recognized by the threads with which they entangle the leaves of the plant. Pest colonies are destroyed by treatment with Fitoverm.
For prevention melon diseases and pests The Ethiopians deep-plow the area in the fall and regularly loosen the rows. And after collecting the fruits, they burn the remaining vegetation, digging up the ground.
What do vegetable growers say about the Ethiopian variety?
Positive reviews about the Ethiopian melon indicate that the product is popular among gardeners. The honey taste of ripe fruits, which reach a weight of five kilograms, is noted. To obtain specimens of large mass, careful care of the plant is necessary. Lazy gardeners will not grow large fruits.
Gardeners note many positive qualities in melon varieties Ethiopian. The fruits ripen in August. They are large, with a thick yellow skin, and the flesh is white and juicy.
Fans of the variety believe that it is easy to grow. The main thing is to protect the melon from diseases and create favorable conditions for growth.