Experts identify several reasons why potatoes may not grow well and what to do about it; they offer ways to solve problems. Unfavorable factors may include weather conditions, an incorrectly selected variety, or inappropriate soil composition. Vegetable growers often make mistakes in caring for vegetables. To correct the situation, you need to identify the cause in time and begin the fight to eliminate it.
- Causes
- Varieties
- No suitable variety
- Poor quality seeds for planting
- Simultaneous planting of several varieties
- Landing
- No crop rotation
- Depleted soil
- Deep landing
- Inappropriate landing method
- Height
- How long does it take for potatoes to sprout?
- Climate and planting dates
- Why did potatoes stop growing?
- What to do if potatoes don't sprout?
- Harvest
- Small fruits
- Rotten fruit
- Few ovaries and fruits
- Diseases and pests
- Fungal diseases of potatoes
- Viral diseases of potatoes
- Bacterial diseases of potatoes
- Late blight of potatoes
- Dry rot of potatoes
- Black potato leg
- Potato ring rot
- Medvedka
- Colorado beetle
Causes
There are several reasons why potatoes do not grow after planting, so knowing in advance about unfavorable factors can prevent the development of problems:
- Potato varieties are divided into three large groups according to the timing of root crop ripening: early, mid-ripening and late-ripening. Agronomists recommend planting varieties of different time groups.
- You cannot plant early and late potato varieties at the same time.
- Poor quality planting material.
- Failure to observe crop rotation, lack of timely fertilizing, improperly prepared land.
- Planting too deep can result in seedlings not appearing at all. The seed placement depth is approximately 8 cm.
Weather conditions play an important role. Heavy rains, return of frosts, low air temperatures or, conversely, hot days also cause poor plant development. Diseases and pests significantly reduce the quality and quantity of the crop.
Varieties
In order for root vegetables to grow large in size and with high taste, you need to choose the right variety. You need to take into account the climate, soil composition, and purpose of the crop.
According to the timing of crop ripening, they are distinguished:
- super early varieties that allow you to harvest after 40–45 days, so you can get two harvests per season;
- in early potatoes, the limits of fruit ripening are 50–60 days;
- The mid-early group of vegetable crops begins to ripen after 80 days;
- Root crops of mid-late varieties ripen after planting in 95–100 days;
- The late potato harvest can be harvested in 110–120 days.
Depending on the potato variety, the pulp can be white, yellow, purple, or red. The shape of potatoes can be round, oblong, cylindrical. In addition to these indicators, attention is paid to the main characteristics of the variety: yield, resistance to cold and drought, resistance to diseases and pests.
No suitable variety
Among the large number of varieties, there is a suitable variety that will adapt to climatic conditions, soil composition, and individual preferences.
For some, yield is extremely important, for others it is necessary for the potatoes to be boiled during cooking. You can find varieties that will thrive in sandy and clay soils and will tolerate drought and cold well.
Experts in vegetable growing recommend planting different varieties of potatoes, which will certainly allow you to harvest a good harvest of root crops.
Poor quality seeds for planting
Planting material is selected and carefully examined. Medium-sized potatoes (weight 80 g), without damage, stains or rot, are suitable for planting. Damaged seeds should not be left for propagation, otherwise there will be poor germination, low yield and a high risk of disease development.
The selected planting material is stored in a separate container. The room should be cool, about +2 degrees.
Tubers of any potato variety disinfected before planting. For this purpose, place the seeds in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 30 minutes; copper sulfate can be added to the composition.
Without germination, seedlings will appear slowly and the yield will be low.The most common method of germination is germination in the light. Planting material is distributed on the surface in one layer, the room temperature should be +8 degrees. Leave in this state until sprouts 1 cm long appear. Periodically turn the potatoes over.
Simultaneous planting of several varieties
It happens that a variety is selected in accordance with climatic conditions, planting rules are followed, but the vegetable does not grow. The reason may be that all varieties were planted on the same day. It is not right.
Early-ripening potatoes are planted first in the spring, as they are not afraid of cold weather. Varieties with average fruit ripening boundaries begin to be planted when the air temperature warms up to +13 degrees. Late varieties are planted last, when the temperature reaches +21 degrees.
The method for planting different potato seeds may look like this. Furrows are made on the prepared plot of land, into which early varieties are planted in turn, then mid-early and late varieties.
Landing
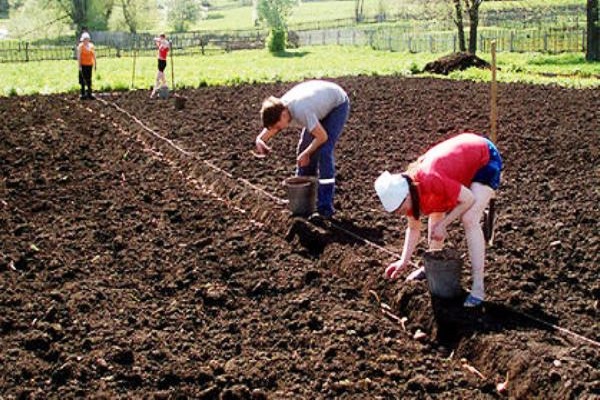
One of the main reasons why potatoes do not grow in the garden is poor soil. The vegetable develops best in light, fertile soil with good aeration.
Land with high acidity is absolutely not suitable. It is not advisable to choose an area where groundwater flows too close to the surface. The tubers will be small and have low taste.
The soil is prepared in advance before planting potatoes. In the fall, the site is dug up to a depth of 30 cm and fertilizers are applied. Rotted manure and humus, superphosphate and potassium nitrate are best suited. If the soil is highly acidic, add dolomite flour or wood ash.
No crop rotation
Every year, the soil gives up a lot of nutrients to the plants and, as a result, becomes depleted, so it is not recommended to plant potatoes in the same place for several years in a row. In addition, bacteria and pests accumulate in the soil.
The best neighbors for potatoes are corn, sorrel, and onions. Good predecessors are cabbage, cucumber, beets, and rye. Potatoes develop poorly after crops such as sunflowers, eggplants and tomatoes.
Depleted soil
Over 3–4 years of constant potato cultivation in the same area, the soil is depleted, so fertilization is required.
In the fall, humus, superphosphate, and potassium sulfate are added. If the soil is acidic, then liming is carried out. It is useful to fertilize any soil with wood ash. It contains many microelements (phosphorus, potassium, calcium). For 10 sq. m requires 8 kg of wood ash.
During spring plowing, it is recommended to add superphosphate, compost, and manure infusion, burying the components to a depth of 12 cm. Fresh manure should not be added. It reduces the taste of potatoes and the fruits become watery. In addition, the risk of infection with fungal diseases increases.
It is recommended to apply nitrogen fertilizers during the spring preparation of the soil for planting, as well as before the first hilling potatoes.
During the entire growing season, it is useful to carry out root and foliar feeding. The main components of solutions can be bird droppings, cow manure, urea, and herbs.
Deep landing
If potatoes are planted too deeply, seedlings will appear slowly and later than usual. This happens due to poor supply of heat and oxygen from the surface of the earth. The sprouts will be weak and the yield will decrease.
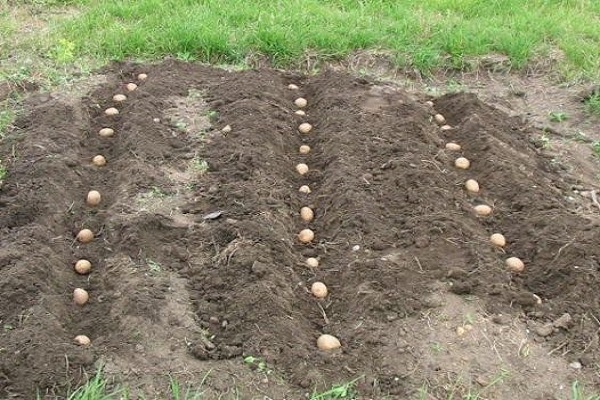
You can plant potatoes in a hole with a depth of 5 to 11 cm. The lighter the soil, the deeper the seeding depth. The optimal depth of the hole is considered to be 8 cm. At the same time, it is useful to fertilize the soil. During planting, a mixture of humus, wood ash and superphosphate is placed in each hole.
Inappropriate landing method
There are many ways to plant potatoes. When choosing, you first need to consider the composition of the soil. The most popular planting method is the smooth method. In previously prepared furrows, depressions are made into which planting material is placed and covered with earth.
Other known methods of planting vegetables are the following.
- If the soil is light or sandy, the trench option is suitable. Dig trenches 13 cm deep at a distance of 73 cm. In the fall, rotted manure, sawdust or straw are placed in the prepared trenches. Over the winter they will decompose and warm the soil. In spring, potatoes are placed in trenches at intervals of 40 cm. With this method, planting can be started two weeks earlier.
- If the soil is heavy and wet, then a ridge planting method would be ideal. The height of the embankment can be more than 15 cm.
During the entire growing season, it is recommended to carry out three waterings: two weeks after planting, during flowering and three weeks before harvesting. An important aspect of crop care is hilling and weeding. Hilling is carried out immediately after the first shoots appear, and a second time before flowering begins.
Height
Potatoes have five growth periods:
- Germination of tubers and appearance of first shoots.
- The appearance of a green stem with the first leaves.
- The formation of buds and the beginning of the flowering period.
- Active flowering and cessation of tops growth.
- Drying of the tops and final formation of root crops.
At any of these stages, potato growth may stop. The cause is improper care, return of frost, rainy or dry weather, pest invasion, and infection.
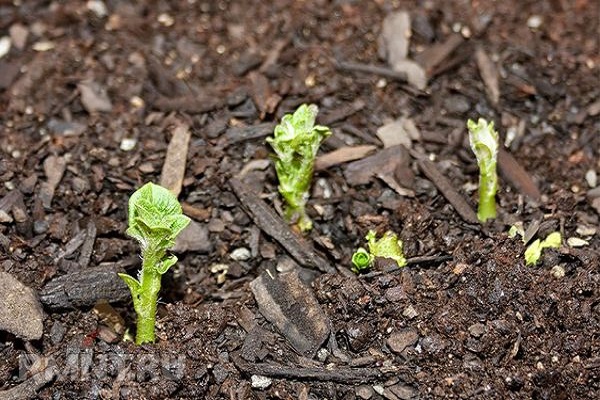
How long does it take for potatoes to sprout?
The first young seedlings, subject to warm weather, begin to appear after 23 days. If the weather stays at +20 degrees for a long time, then the first shoots appear already on the 16th day. The time of emergence of seedlings is delayed due to cold weather.
Need to plant potatoes into heated soil (+10 degrees) and shallowly, into the top layer of soil, it is best to pre-germinate the planting material.
Shoots may appear unevenly due to different depths of seed placement, different sizes of tubers, and when choosing potato varieties with different ripening periods.
Climate and planting dates
The time for planting potatoes is determined by certain criteria: air temperature, soil moisture level (too wet soil leads to rotting of the planting material rather than germination), and the selected variety.
Sometimes potato bushes do not develop due to non-compliance with planting dates. Most often, planting work begins in early May, but it is better to focus on weather conditions.
The soil should warm up to 8–10 degrees to a depth of 10 cm. By this time, the risk of frost returning is minimal. In regions with different climatic conditions, the soil does not warm up at the same time.
Why did potatoes stop growing?
The growth of tubers and above-ground parts of a vegetable crop can stop due to bad weather, poor care, lack of nutritional components, and also as a result of pest attacks.Potatoes stop growing in hot weather without regular watering.
What to do if potatoes don't sprout?
If potato seedlings have not appeared by the expected, calculated date, then measures need to be taken:
- First of all, make sure that the potatoes are not planted too deep. All you have to do is dig up a few tubers and take a look. If this is the case, then germination will take 7–10 days.
- If the weather is warm and dry, watering will help speed up seed germination.
- It is worse if the sprouts do not appear due to rotting tubers or damage by pests. In this case, all planting material is dug up and burned, and the land area must be treated with fungicides.
In an infected area, it is better to plant another crop that is immune to potato diseases. In another area, you can plant early varieties of potatoes and have time to reap a rich harvest.
Harvest
Growing potatoes is not difficult, but some unfavorable conditions can reduce productivity:
- too cold or hot weather;
- dense planting;
- lack of moisture, especially during flowering;
- lack of air in the soil;
- excess or lack of nutritional components;
- lack of light.
The yield may decrease, and the tubers lose their taste and external qualities or are not completely formed.
Small fruits
A small potato harvest can occur due to many unfavorable factors:
- A common cause is a fungal disease - late blight. When bushes are damaged, the tubers do not rot, but only stop growing.
- An excess of nitrogen leads to active development of green mass. All nutritional components go up, root crops develop poorly.
- High air temperature. If the heat occurs during a period of active growth of root crops, then their growth stops.Even if the temperature drops soon, the tubers will be small.
- Lack of moisture also causes small harvests.
Regular watering in hot weather, compliance with the dosage when applying fertilizers, preventive treatments against diseases and pests will help to reap a large and tasty harvest.
Rotten fruit
The potato crop may rot. The cause is wet, rainy weather, too densely planted bushes, fungal or bacterial infections.
If dry and yellow tops appear among the green potato bushes, some kind of disease is most likely developing. Rotting of potatoes can be caused by: late blight, fusarium, blackleg, ring rot. Diseased bushes are dug up and burned.
Another reason for tuber rotting during growth is an excess of nitrogen in the soil. Voids form inside the tubers, and the pulp begins to rot. Next year you need to reduce the application of nitrogen and increase potassium.
Few ovaries and fruits
Few ovaries and fruits are formed due to hot weather and dry air. In this case, the ovaries fall off. The bushes look lethargic, emaciated, there are few tubers and they are small. In this case, you need to water the area with water and treat it with Zircon.
If the stem is straight, the leaves are green, the bush overall looks healthy, and there are no ovaries, then this will not affect the quality and quantity of the harvest. You also need to know that not all varieties are able to bloom.
Diseases and pests
Diseases and pests can significantly worsen the condition of the bushes and reduce yields. The vegetable slows down in growth and stops developing. The disease can be provoked by viruses, bacteria and fungi that penetrate the plant through leaves, roots, and damage.
Fungal diseases of potatoes
Fungal spores are spread by wind, insects, and water. Under favorable conditions (cold weather and high humidity), fungi begin to actively multiply, spreading over large areas.
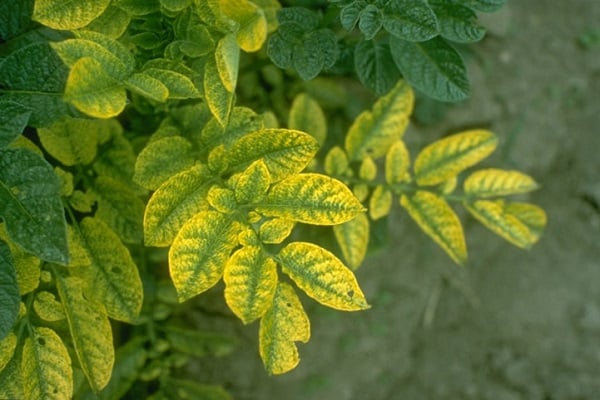
Viral diseases of potatoes
The most common viral disease is mosaic, which has three types. The reason is a decrease in the plant’s immunity due to improper watering, lack of nutrients in the soil, and damage to the bushes by pests.
The leaves of the plant curl, change color, and light, brown spots appear. Over time, the stem becomes damaged, and the leaves become completely yellow, dry and begin to fall off.
Bacterial diseases of potatoes
A bacterial infection may appear throughout the growing season. Most often, the source of infection is seed material. Particularly dangerous are rots that affect tubers, making them unfit for food.
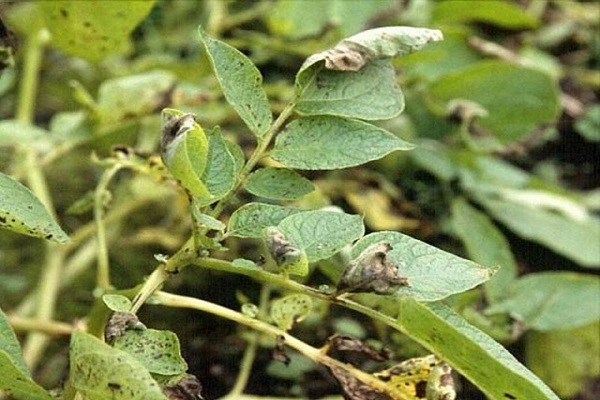
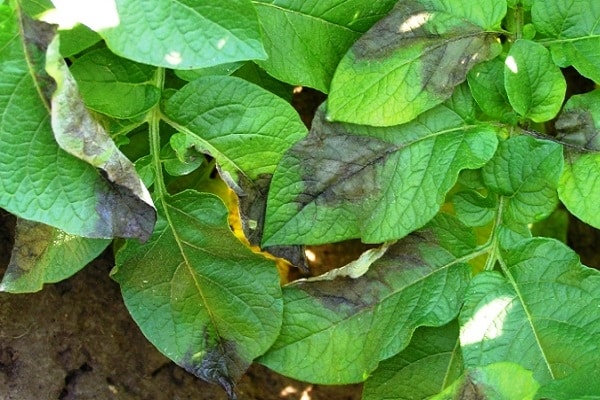
Late blight of potatoes
The first sign of late blight is the appearance of brown spots on the top of the leaves. The inner half of the leaf plate is covered with a white coating. If you do not start treatment, then within a month all potato plantings will be infected with the disease. The leaves turn brown and the tubers are also affected. Over time, the tops become thinner, rot, wither and dry out. For a month, every week it is recommended to treat the bushes with Bordeaux mixture.
Dry rot of potatoes
Dry rot or fusarium refers to a fungal disease that affects the above-ground part of the plant during growth. It develops on tubers most often during storage. Spread begins in dry, hot weather.
With fusarium blight, the leaves change color. Their edges become brownish-purple, and the top begins to lighten. Gradually, the leaves wither, the stem darkens, and brown spots covered with a white-gray coating appear on the fruits.
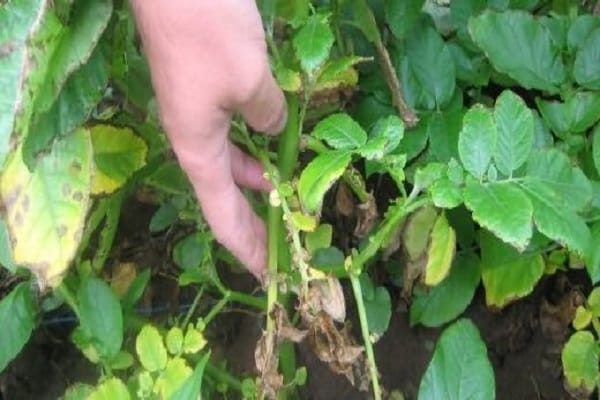
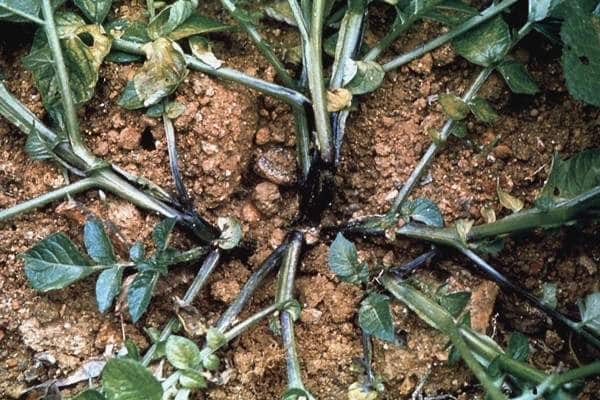
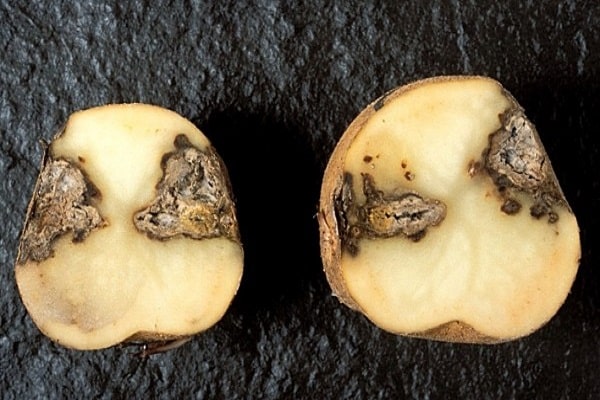
Black potato leg
Black leg can destroy the entire potato crop. The stem and roots begin to rot, the leaves curl and become stiff. The tubers become soft and have an unpleasant odor. Rot can develop both from inside the fruit and from the outside. A preventive measure is the treatment of seed material with special preparations.
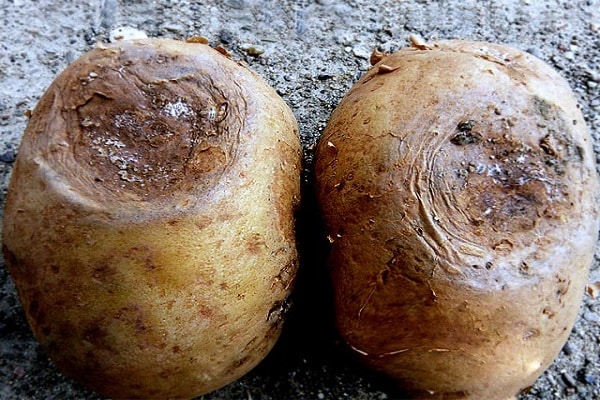
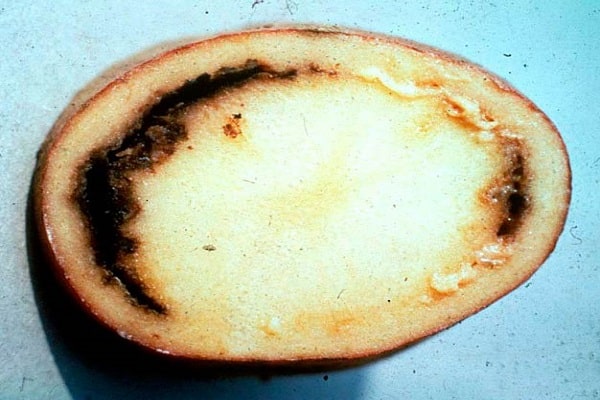
Potato ring rot
A common bacterial infection is ring rot. It is difficult to notice the disease at the initial stage. When the leaves and tops begin to fade, the plant is already infected from the inside.
In the veins of the leaves, the juice becomes yellow-brown, which indicates the process of decay. Putrefactive rings and spots are visible not only on the surface of the tubers, but also inside, when cut. The damaged part of the potato becomes filled with an oily liquid, which turns brown over time.
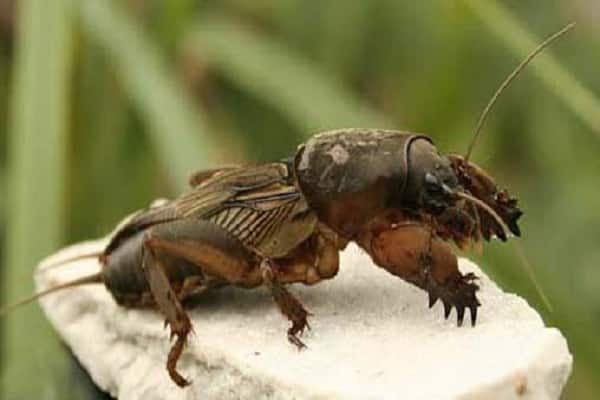
Medvedka
Adult insects (up to 6 cm in length) and mole cricket larvae cause significant damage in vegetable beds. They damage the roots and stems of potato bushes and gnaw through root crops. In the fight against mole crickets, folk methods and chemicals are used (Prestige, Aktara, Masterpiece).
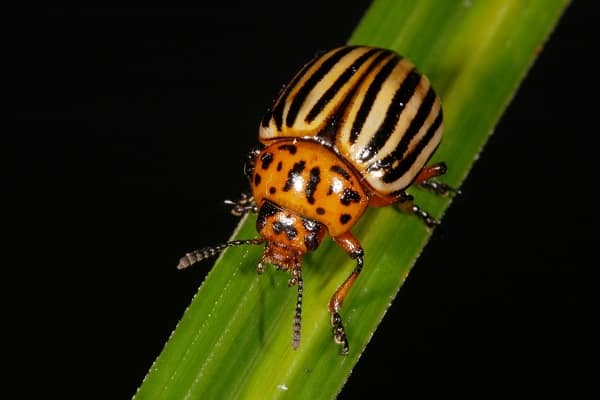
Colorado beetle
The Colorado potato beetle feeds on the leaves of nightshade crops, but prefers potatoes most of all. Eats leaf petioles, but does not touch flowers, stems and roots. If measures are not taken, the plant will stop developing and the tubers will be small.
For the Colorado potato beetle, remedies such as Confidor, Regent, and Commander are used.Weeds should not be allowed to appear, crop rotation must be observed, it is important to plant planting material on time and remove all plant debris from the site after harvesting.
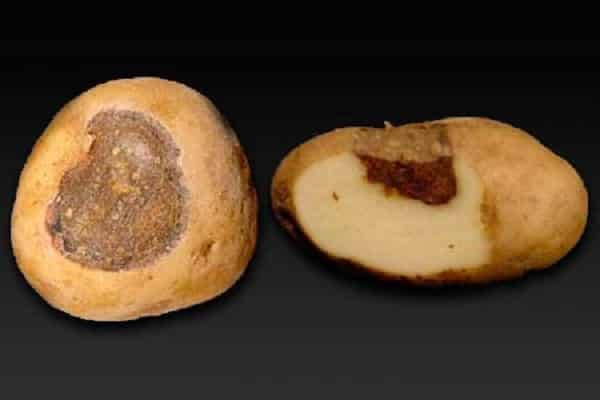













































Thank you for an excellent article. Important issues were revealed to me.
I plant several buckets of medium-sized potatoes and harvest 2 buckets of peas. What I didn’t do. I changed the planting method, changed the honeycomb material, fertilized the soil with humus, manure, mineral fertilizers, and watered it. There are no diseases or pests, but the reason is simply a mystery. Thank you.
Thank you very much for your feedback.
As for “peas,” there may be several reasons. Perhaps you still lack the necessary minerals. Or try changing the landing site. It is believed that potatoes are best nourished by nitroammophoska. Try it.It is also recommended to use a mixture of 1 part nitrogen, 2 parts potassium and 1 part phosphorus. The total weight is 25 grams, it is diluted in 10 liters of water.