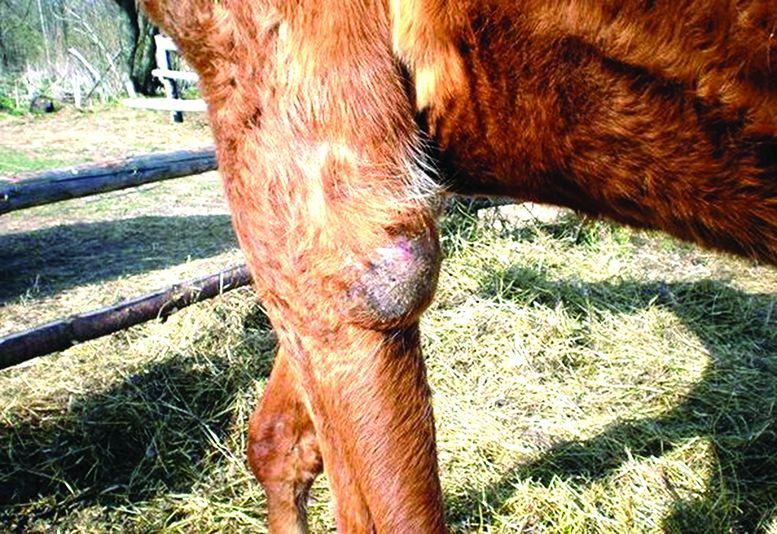
The development of brucellosis in goats is considered a very dangerous condition. It poses a threat not only to livestock itself, but also to people. This is an infectious-allergic pathology caused by zoonotic bacteria. They often cause damage to small livestock, and goats are no exception. The pathology usually becomes chronic. In this case, the genital organs are affected. The disease can also affect the musculoskeletal system.
The main causes of the disease
Goats get brucellosis due to infection with Brucellus melitensis and other types of bacteria. The routes of infection by microorganisms are varied. However, most often this occurs through mucous membranes or wounds on the skin. At the same time, no manifestations are visible on their surface.
Infected goats spread pathogens. They spread bacteria with various liquids and feces, which subsequently enter the body. A key feature of brucellosis is the high risk of affecting individuals of other species. At the same time, the disease poses a danger to people.
Signs and symptoms
The incubation period of the pathology can last from 1 week to 1 month. With a hidden course of infection, it reaches 2-3 months. Today the disease is classified according to its forms:
- Acute – duration is 1.5 months.
- Subacute – lasts up to 4 months.
- Chronic – lasts more than 4 months.
- Residual – complications persist after recovery.
Acute brucellosis is characterized by rapid or gradual development. Typically, primary symptoms appear in older individuals. In this case, pain, sleep disturbances, and weakness appear. These signs indicate inflammation in the joints. However, they are not always present and can be almost invisible.
Abortion is considered the main symptom and source of infection in goats. The infection subsequently spreads through milk and urine. Little by little, the entire body and places of care become infected. During abortions, fluid with a large number of bacteria is released. In this case, infection of 60-80% of individuals is observed.
Abortion usually occurs at 3-5 months. A few days before this, the genitals swell and a colorless liquid with a distinct odor is released. After an abortion, the following symptoms occur:
- retention of placenta;
- development of endometritis;
- the appearance of purulent mucous discharge - sometimes it contains fibrinous elements;
- increase in temperature - observed in acute cases;
- a strong decrease in milk yield;
- weight loss;
- acceleration of erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- leukocytosis;
- violation of the reproductive cycle - observed with damage to the ovaries and fallopian tube;
- infertility;
- damage to joints and inflammation in them.
Diagnosis of the disease
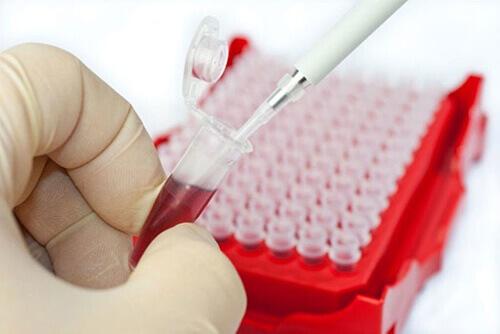
The main diagnostic method is serological testing. It is recommended to carry it out in accordance with a specific plan. In this case, it is worth taking samples from goats for 4 months. When goating, a blood test is required. However, it is recommended to do it 1 month after birth. Otherwise, the results will be unreliable.
The following parameters are determined in the laboratory:
- rose bengal test;
- agglutination reaction;
- type of reaction to a related compliment.
If the first study has no effect and the parameter is 25-50 international units per milliliter, a repeat diagnosis is performed. It is carried out after 2-4 weeks. If a repeat study shows the same result, the diagnosis is confirmed.
If the first test reveals an antibody level of more than 100 international units per milliliter, there is no need to confirm brucellosis.
How to properly treat brucellosis in goats
The disease is almost untreatable. Therefore, the farmer’s attention should be directed to purchasing goats from healthy farms. They need to be checked for brucellosis twice a year. If a disease is detected on the farm, veterinary and sanitary measures are carried out.People who have come into contact with infected animals should also be systematically examined.
Sick goats should be immediately isolated. It is recommended to follow all the veterinarian’s prescriptions. At the same time, people should maintain personal hygiene. Consumption of raw milk and unprocessed animal products is strictly prohibited.
Possible consequences
The pathology is practically untreatable and can lead to negative consequences. The disease can cause significant economic harm, as it leads to mass abortions, barrenness, and culling of productive animals. The appearance of brucellosis on a farm provokes the loss of valuable producers and the costs of carrying out anti-epizootic measures. In addition, infected animals pose a danger to people.
How to prevent infection
The farmer is responsible for the health of the goats. To avoid the development of brucellosis, it is recommended to strictly adhere to sanitary standards for the maintenance, operation, and care of animals.
To prevent such problems, you should follow these rules:
- When purchasing goats, inspect and register the animals. This is especially true when purchasing goats from unverified suppliers. This also needs to be done when purchasing animals from sellers who cooperate with areas of minor spread of brucellosis.
- Request documents for the goat from the seller.
- Quarantine the goat. Its minimum duration should be 2 weeks. However, experts recommend isolating the new animal from the rest of the livestock for 1 month. Then take repeated samples.
- You cannot import animals from areas where many cases of brucellosis have been recorded.The same applies to the import of soil, manure, feed and other similar products.
- The condition of animals must be constantly monitored by veterinary authorities. It is important to monitor the life processes of animals and provide them with optimal conditions in order to minimize risks.
- It is important to comply with veterinary and zoohygienic standards when keeping goats and performing various procedures.
- Immediately report deaths, pathologies, and abortions of goats to the veterinary authorities.
To avoid problems, it is recommended to vaccinate in a timely manner. This applies to the herd and staff. When pathology is detected, it is important to provide the animals for slaughter. To do this, as a rule, a double diagnosis is carried out. In case of obstruction in the work of veterinarians or concealment of the fact of illness, the farmer is fined.
The slaughter of goats suffering from brucellosis can only be carried out in special sanitary slaughterhouses.
Even if a single case of illness is detected, quarantine is usually declared. During this period, animals are prohibited from contacting the outside world. It is also prohibited to bring other individuals onto the farm territory. It is forbidden to remove goat waste outside the yard.
Brucellosis is a serious pathology that occurs in goats. It can lead to dangerous consequences for the entire livestock and is practically untreatable. Therefore, all efforts of the farmer should be aimed at preventing the disease.