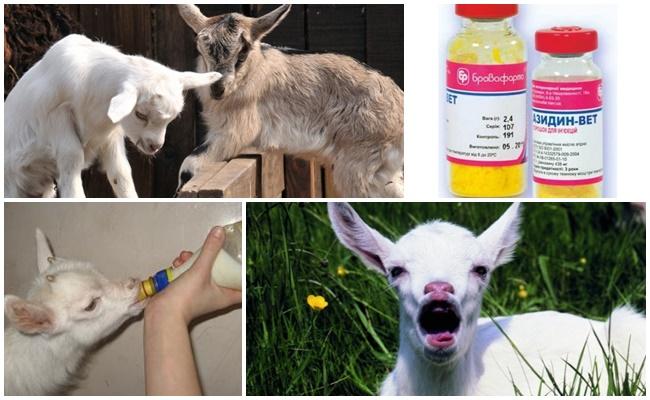
Treatment of adult goats and kids, of course, should be carried out by veterinarians. True, pet owners should know what diseases their pets can get. After all, it is important to recognize the disease in time and treat it at the initial stage. The cause of most diseases is improper maintenance and feeding of animals. There are diseases that affect goats through direct contact with carriers of the infection.
- Infectious diseases
- Smallpox
- foot and mouth disease
- Listeriosis
- Pasteurellosis
- Brucellosis
- Infectious pleuropneumonia
- Infectious mastitis
- Udder furunculosis
- Diseases of the genitals
- Trichophytosis
- Infectious stomatitis
- Footrot
- Non-communicable diseases of goats
- Arthritis and arthrosis
- Rickets
- Avitaminosis
- Injuries
- Mastitis (non-infectious nature)
- Cracked nipples
- Ketosis
- Poisoning
- Dyspepsia
- Gastroenteritis
- Acute rumen tympany
- Bronchitis
- Parasitic diseases
- Echinococcosis
- Fascioliasis
- Moniesiosis
- Piroplasmosis
- Eimeriosis
- Linognathosis
- What is the normal body temperature for a goat?
Infectious diseases
This category of diseases includes those caused by the penetration of various pathogens (viruses or bacteria) into the body of goats. Infection leads to disease only if the animal is weakened and does not have the necessary immunity. Such diseases are treated with medications, including antibiotics. Only preventive vaccinations, that is, vaccination at 3 months of age, save you from the most dangerous diseases.
Smallpox
This viral disease is transmitted through direct contact with animals infected with smallpox. Goats can also become infected on pasture, where an infected herd sometimes grazes, that is, through the grass. Smallpox can be identified by the characteristic reddish pockmarks that appear on the head, around the eyes and mouth, and on the genitals and udder of goats. The incubation period is only 1-2 weeks.
Animals suffer from smallpox in different ways. Some recover after 2-3 weeks, while others get sepsis (infection) and die. Only preventive vaccination can save you from smallpox. It is given to both adult and young goats. The main thing is that the animal is healthy.
foot and mouth disease
This is also a viral disease, which can be determined by looking into the goat’s mouth. A rash appears on the mucous membranes in the form of blisters, which over time burst and turn into ulcers. In animals with foot and mouth disease, redness is noticeable in the hooves, followed by areas of rotting. The cause of the disease is infection from sick animals.Foot and mouth disease in 9 cases out of 10 leads to the death of goats. Sick animals are usually sent to slaughter. Only vaccination can save goats from foot and mouth disease.
Listeriosis
This bacterial contagious disease cannot be ignored. Listeriosis affects the nervous system of goats. Animals lose coordination of movement, develop muscle tremors, convulsions, agitation, or, conversely, lethargy. Pregnant goats may experience miscarriages. Listeriosis is carried by rodents, and in the initial stage it is treated with antibiotics.
Pasteurellosis
This bacterial disease is characterized by multiple hemorrhages (red spots) on the mucous membranes and skin. Pasteurellosis is transmitted by sick animals and even through insect bites. Infected goats become lethargic, inactive, have no appetite, breathing is heavy and frequent, rhinitis and cough appear. The disease is treated with a special serum and antibiotics (penicillin and tetracycline). To prevent pasteurellosis, vaccination is recommended.
Brucellosis
This disease is also called Maltese fever. Usually brucellosis in goats is asymptomatic. In bucks, the testes become slightly swollen, and in females, nodular thickenings form on the udder. Brucellosis leads to involuntary miscarriages and the appearance of polyarthritis. The disease is contagious and is transmitted through the milk and meat of infected animals and through direct contact. There is no cure for brucellosis, but there is a vaccine against it, but only healthy kids can be vaccinated.
Infectious pleuropneumonia
This is a contagious disease that is transmitted from sick animals through airborne droplets. Sick goats start coughing, they develop mucus from the nose, noticeable lethargy, depression, and a sharp increase in temperature. Pleuropneumonia often leads to the death of goats. She is treated with Novarsenol. You can get a preventive vaccination against pleuropneumonia.
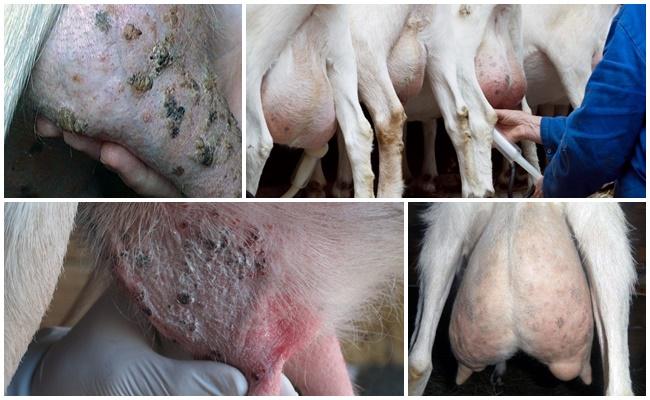
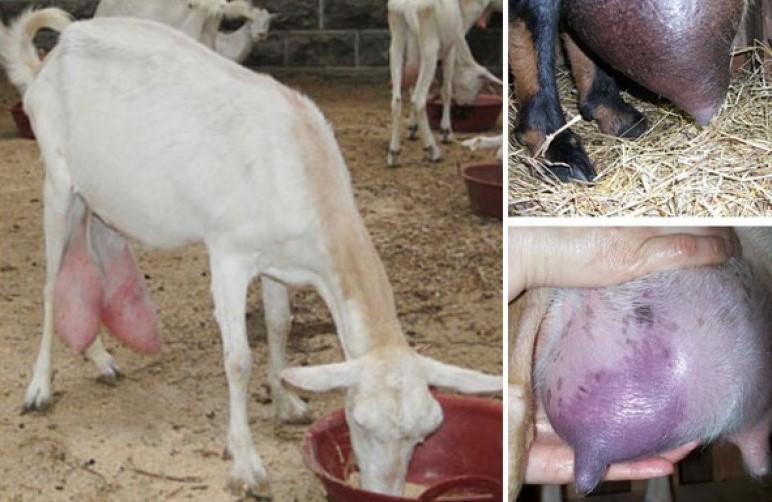
Infectious mastitis
This disease is characterized by serious (gangrenous) inflammation of the udder. The causative agent is staphylococcus. The infection enters the udder through damaged skin and leads to the appearance of extensive red spots and inflammation. In the early stages, mastitis is treated with antibiotics (Bicillin) and sulfonamide drugs. For gangrene and abscesses, surgery is needed.
Causes of mastitis: dirty bedding, dampness, drafts, cold, poor feeding, udder injuries.
Udder furunculosis
The causative agents of this disease are staphylococci and streptococci. Large boils appear on the udder of sick goats, and then they fester. Extensive skin lesions lead to a deterioration in the condition of animals and a decrease in milk production. Furunculosis is treated with streptocide, and the skin is wiped with antiseptics, boils are lubricated with iodine and ichthyol ointment. The disease occurs when the animal is poorly fed and kept without bedding (on concrete) or on dirty straw.
Diseases of the genitals
Males and females have diseases of the reproductive organs. These diseases lead to decreased productivity and reproductive functions. Males suffer from orchitis (inflammation of the testes). This disease occurs due to injury and infection of tissues, is characterized by swelling of the scrotum, and in severe cases is treated with antibiotics and sulfonamides.
Females suffer from their own diseases (vestibulitis, vulvitis, vaginitis), that is, inflammation of the vagina with the release of liquid and cloudy exudate. Treatment includes the introduction of antimicrobial emulsions and ointments into the vagina.
Trichophytosis
This is ringworm, that is, a contagious fungal disease when bald areas covered with crusts and scales appear on the skin. Fungi can be found in the soil and are carried by rodents and sick animals. Trichophytosis is treated with fungicidal agents, and vaccination is carried out as a preventive measure.
Infectious stomatitis
This is a viral disease that is characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa and increased salivation, the appearance of blisters and ulcers in the mouth. Cause of stomatitis: rough and low-quality feed. Sometimes pimples in the mouth appear due to infection with foot and mouth disease. Ordinary stomatitis is treated with streptocide powders, rinsing the mouth with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, soda or chamomile.
Footrot
The disease is caused by bacteria found in pasture that attack the hoof epithelium. Inflammation and purulent discharge appear in the interhoof gap, the goat limps, and its temperature rises. During treatment, the hooves are washed, baths are given, and the animal itself is given antibiotic injections (“Nitox 200”).
Non-communicable diseases of goats
Pets are sensitive to living conditions and to feed. Goats can catch colds if they are kept in the cold. In case of malnutrition, poor nutrients, vitamins and minerals, their immunity decreases, problems with metabolism or stomach appear.
Arthritis and arthrosis
These are joint diseases. The development of diseases can be prevented by feeding goats legumes and giving vitamin D. Arthritis and arthrosis are difficult and cannot always be treated. The most characteristic signs of the disease: changes in the shape of the joints, pain, swelling, lameness. A sick animal lies down most of the time, breathes frequently, and its temperature rises.Patients are prescribed chongroprotectors, steroids and NSAIDs.
Rickets
Reason: lack of vitamin D, unsanitary conditions, feeding sour and spoiled food. This is a disease of young goats born from weakened uteruses and not receiving enough sunlight. Sick animals move little, eat poorly, and are stunted in growth and development. For treatment, injections of vitamin D and other vitamins and minerals are prescribed, as well as improved feeding and walking in the fresh air.
Avitaminosis
The disease occurs when there is a deficiency of vitamins in feed. Animals weaken, become lethargic, lose their appetite, and in severe cases, convulsions are observed in goats or miscarriages in females. During treatment, the goats are given better living conditions and food, and are also prescribed pharmaceutical vitamins and minerals. In winter, as a prevention of vitamin deficiency, it is recommended to give spruce and pine branches, vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, beets).
Injuries
These active animals often get injured while grazing. There are various types of injuries: udder, teat, hooves, limbs. The affected area must be disinfected with an antiseptic. If there is bleeding, it must be stopped with a tight bandage. For limb fractures, a splint is applied. The injured hoof is treated with a disinfectant solution and bandaged.
Mastitis (non-infectious nature)
If a goat gets mastitis after lambing, it means it was milked too late or an infection got into the udder, for example, due to trauma to the nipples and dirty bedding. During treatment, the udder is massaged and lubricated with ichthyol ointment or a drug based on novocaine, milk is given, and if a bacterial infection is detected, Mastiet Forte is prescribed.
Cracked nipples
This problem occurs when milking is improper, dairy goats are kept on rough bedding, or as a result of milk feeding of kids. Cracks in the nipples are treated with antiseptics. The udder can be washed with warm boiled water and wiped dry. Before each milking, it is recommended to lubricate the teats with grease or Vaseline.
Ketosis
A metabolic disease that occurs when there is an excess of grain mixtures in the diet. Characteristic symptoms: acetone smell of urine or milk. Ketosis is treated by adjusting the diet, enriching the diet with vegetables, and sweetened water. In winter, they give spruce or pine branches and pharmacy vitamins.
Poisoning
If the goat does not eat anything, lies and moans, it has stomach problems, it means it has been poisoned. Reasons: eating poisonous plants, low-quality feed, consuming toxic substances, pesticides, medications. Treatment depends on the activity of the poison. Poisoning is treated by gastric lavage and enema. Animals are given adsorbents (activated carbon) and diuretics.
Prevention includes feed control. It is especially important to monitor the nutrition of small goats, whose body may not be able to cope even with poisonous plants (buttercups, sweet clover).
Dyspepsia
This is a digestive disorder in newborn goats. The pathology occurs as a consequence of poor nutrition of pregnant females who give birth to weak cubs. The kids are blaspheming, do not eat anything, lie on the floor. Young animals are prescribed the introduction of solutions of bicarbonate and sodium chloride, antibiotics, and sulfonamides.
Gastroenteritis
This is a disease that occurs when eating spoiled or moldy feed. Sick goats lose appetite and develop diarrhea.To treat gastroenteritis, laxatives and antiseptics (Salol) are prescribed.
Acute rumen tympany
This disease is the result of improper feeding. If a goat eats a lot of legumes or soap plants, wet grass, or drinks large amounts of water, then it may experience bloating due to the accumulation of gases in it. Symptoms: refusal to eat, depressed state. The goat stops belching and sometimes its head shakes. Tympany is treated by pulling the tongue out of the mouth or releasing gas using a rubber probe.
Bronchitis
Inflammation of the bronchi causes hypothermia and poor feeding. The disease is recognized by a strong or weak cough. Bronchitis is treated with medications (antibiotics, sulfonamides, aminophylline).
Parasitic diseases
Animals such as goats graze in the meadow, that is, they eat from the ground, eat unwashed vegetables, and they also come into contact with various pets (chickens, dogs, cats). They can be protected from worms and fleas only through preventive measures, that is, vaccination (Ivomec, Dectomax and other macrocyclic lactones).
Echinococcosis
This disease usually affects dogs. Echinococcosis is caused by Echinococcus larvae. Parasites can live in the intestines, lungs, spleen, kidneys, liver and even the heart. The disease is asymptomatic. Only vaccination helps protect against echinococcosis.
Fascioliasis
The disease occurs when infected with trematodes of the genus Fasciola. This parasite lives in the liver. Sick goats don't eat well, weaken, the mucous membranes of the eyes become yellowish. Fascioliasis is treated with anthelmintics (Hexichol, Acemidophen).
Moniesiosis
The disease in domestic animals is caused by ribbon-shaped moniesia, living in the small intestine. Infected goats lose their appetite, develop diarrhea, and fragments of parasites are visible in their feces. Anthelmintics (Fenasal) are used in treatment.
Piroplasmosis
This is a seasonal disease transmitted by ixodid ticks. Parasites settle in blood cells and destroy red blood cells. Sick animals become weaker and their temperature rises. If the goat is not treated, it may die. For treatment, Flavacridine and Azidine are used.
Eimeriosis
These are protozoan coccidia that live in the epithelial cells of the small intestine. Infected goats eat poorly, lose weight, diarrhea, and develop a fever. For treatment, “Clopidol”, “Pharmcoccid”, “Norsulfazol”, “Monensin”, “Khimkoccid” are prescribed.
Linognathosis
This is a disease caused by lice. Sick goats rub against trees and walls, lose weight, and experience itching and dermatitis. During treatment, Deltanol and Baymek are prescribed.
What is the normal body temperature for a goat?
The normal body temperature of an adult goat is 38.5-40.5 degrees. You can measure it using a special device - a thermometer with a long end, which is inserted into the animal's anus. If the temperature is low (36-37 degrees), then most likely this is a symptom of poisoning or metabolic diseases. Too high (41-42 degrees) indicates an infectious, inflammatory nature of the disease. In addition, a goat infected with an infection has a sweaty neck, increased heart rate and breathing, and colder ears and feet. Average, that is, normal temperature is a sign of good health.