Ketosis is a metabolic disease in goats. The disease occurs if you feed animals with protein feed and do not give them food rich in carbohydrates. The desire of some goat breeders to quickly fatten the animal leads to violations. Obesity is no less harmful to goats than to humans. The main food of these animals should remain fresh grass and sun-dried meadow hay.
Description of the disease
Ketosis is a condition that develops as a result of impaired protein-carbohydrate metabolism.Goats affected by this disease are diagnosed with indigestion, low milk yield, and a depressed state, and spontaneous abortions (miscarriages) occur in pregnant females.
With ketosis, an increased content of ketone bodies in the blood is observed, and this pathology can be detected by the sharp acetone smell of milk and urine. The disease directly depends on the conditions of keeping and feeding of domestic animals. Goats get sick if they eat only concentrates and protein feeds, but little grass or hay.
Ketosis is carbohydrate starvation that occurs as a result of dietary errors. Goats receive too much protein food (grain, meal, cake, legumes) and not enough juicy meadow grass, sun-dried hay and sweet root vegetables (carrots, sugar beets). The disease at the initial stage is treated with one nutritional adjustment.
Causes of ketosis
This dangerous disease occurs in goats if they are not fed correctly. You should always remember that the basis of the animal’s diet should be hay and fresh grass. Livestock breeders, wanting to improve the menu of their goats with protein food (grain, meal, cake), do not receive high milk yields, but sick animals. Prolonged fasting or too long a break between feedings can also lead to illness.
Main causes of ketosis:
- lack of herbs high in carbohydrates and vitamins in the diet (clover, fescue, timothy);
- excess protein (protein) food (grain, cake, legumes);
- deficiency of sweet root vegetables (carrots, sugar beets);
- feeding with oilseeds (rapeseed, field cabbage, mustard);
- low-quality feed;
- prolonged fasting;
- stress.
Ketosis occurs more often in fatty goats. Well-fed animals may develop this disease in the future.A long-term lack of healthy feed (fresh grass and hay) and feeding goats concentrates (grains) and protein-rich crops.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
Ketosis in domestic goats can be detected by the signs characteristic of this disease. It is always important to remember that healthy animals are active, calm and have a good appetite. If goats refuse to eat, are overexcited or, conversely, drowsy, then there is reason to suspect they have some kind of disease. It is difficult to determine the disease on your own. However, it is worth examining the animal, and if alarming signs are detected, it is recommended to consult a veterinarian.
Symptoms of ketosis:
- skin, milk, feces and urine smell of acetone;
- lack of appetite;
- tachycardia, shortness of breath;
- digestive problems (constipation, diarrhea, intestinal atony);
- overexcitation turning into a depressed state.
Signs of a severe stage of the disease:
- weakness, drowsiness;
- weakening of muscle tone;
- reduction in milk yield;
- exhaustion of the nervous system;
- noticeable enlargement of the liver (the right side is larger than the left);
- spontaneous abortions;
- postpartum complications;
- mastitis.
A sick animal, depending on the severity of the disease, may exhibit certain signs. Ketosis at the initial stage is determined by the acetone smell of milk and urine. Before treating a goat, you need to show it to a doctor and do laboratory tests. Ketosis symptoms are very similar to poisoning.
Diagnostic rules
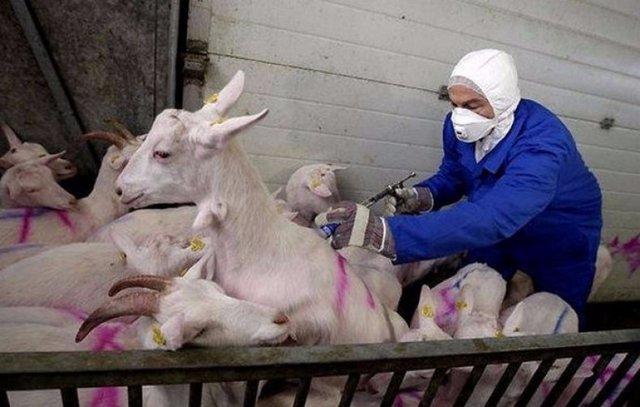
The disease is determined based on the clinical picture and laboratory data. If you notice symptoms similar to those of ketosis, you should take your goat to a veterinarian. Blood, urine and milk should be sent to the veterinary laboratory for analysis (to determine the content of ketone bodies).
A sick goat should be examined by a doctor, determine the condition of the organs, and measure the temperature. The final diagnosis is made based on laboratory data. If goats have high levels of ketone bodies and low levels of sugar, protein, white blood cells and hemoglobin, then the animal is in ketosis and urgently needs to be treated.
How to properly treat ketosis in goats
This disease is often confused with poisoning. Laboratory testing of blood, urine and milk helps to make a diagnosis. If ketosis is detected, animals are transferred to a special diet. The disease is treated with medications and the introduction of carbohydrate-rich foods into the diet. Protein foods are completely excluded from the diet.
Treatment with medications
Goats are treated with medications given to them orally or through injections. Animals are prescribed "Katozal". This is a drug that stimulates metabolism. It is not recommended for pregnant females to inject it. The doctor may prescribe intravenous glucose, subcutaneous insulin, hydrocortisone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, sodium lactate, Sharabrin liquid, choline chloride, vitamins A and E, sodium propionate.
Goats are given sweet water in the morning (half a glass of sugar per half bucket). During the day, pharmaceutical vitamins and minerals are added to drinking water. In the evenings, give a solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per 1 liter of water) to alkalize the body. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Diet adjustments
The acid-base balance can be normalized by adjusting the goats’ diet.In order to increase the sugar content, animals need to be given carbohydrate-rich foods (carrots, sugar beets, potatoes). The diet should contain fresh grass and hay, cut during flowering and heading, as well as dried in the sun. There are many carbohydrates in such plants: red and pink clover, fescue, meadow timothy, cocksfoot.
In parallel with the increase in the amount of grass, hay and sweet vegetables in the diet, goats are no longer given grain, meal, silage, oilseed grass and legumes. In mild forms of ketosis, one dietary adjustment is enough to completely cure the animal. In severe cases, goats are treated with medication. If the problem is ignored, the animal may die.
Possible consequences of the disease
Ketosis is a disease that can be cured in its early stages with just one dietary adjustment. The diet is enriched with sweet vegetables, the amount of fresh grass and hay is increased, and protein feeds and concentrates are completely excluded. The disease is simply impossible not to notice - milk and urine begin to smell like acetone.
If you ignore warning signs and do not change the goats' diet in time, complications can be serious.
A sick animal's milk yield decreases, complications arise during pregnancy and childbirth, and miscarriages occur. In severe cases, toxicosis, convulsions, and muscle tremors appear. A prolonged form can lead to coma and even death.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. Preventing ketosis is by feeding goats fresh grasses rich in carbohydrates, quality sun-dried hay and sweet vegetables. Grain, cake, meal, legumes and oilseeds are given only in winter, but in minimal quantities.Animal nutrition should contain pharmaceutical vitamin and mineral preparations. Goats need to be given fresh water twice a day.
Animals should graze in the meadow in warm sunny weather, eat fresh herbs, and in the rain it is better for them to stay in the barn. Goats need to exercise a lot and cannot be kept indoors all year round. In summer, goats must be taken out to pasture. The main food in summer is fresh meadow grass.
In winter, it is recommended to keep animals in a barn, where the temperature is not lower than 15 degrees Celsius. In a cold room they stop producing milk. The main diet in winter is hay (up to 4 kg per day). In winter, it is imperative to give goats pharmaceutical preparations with calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D. Coniferous and pine branches are recommended as feeding. Grain feed should be present in minimal quantities (it causes ketosis). Every day in winter you need to give finely chopped beets, carrots, pumpkin (up to 1.5 kg per day).