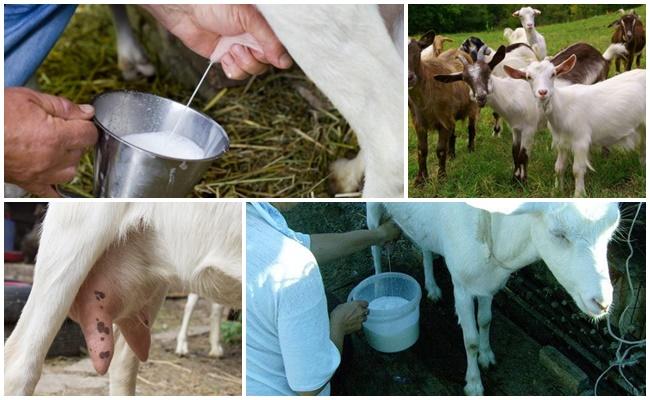
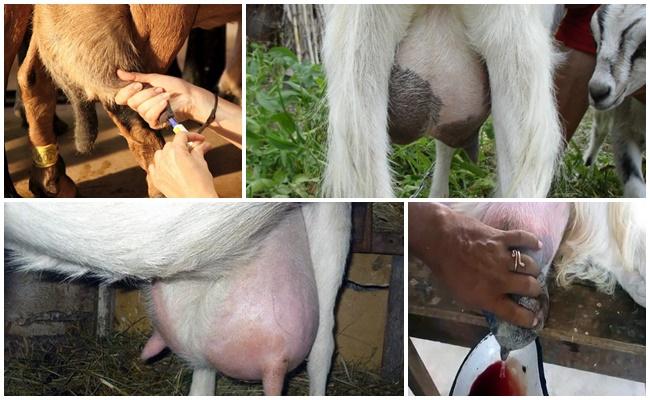
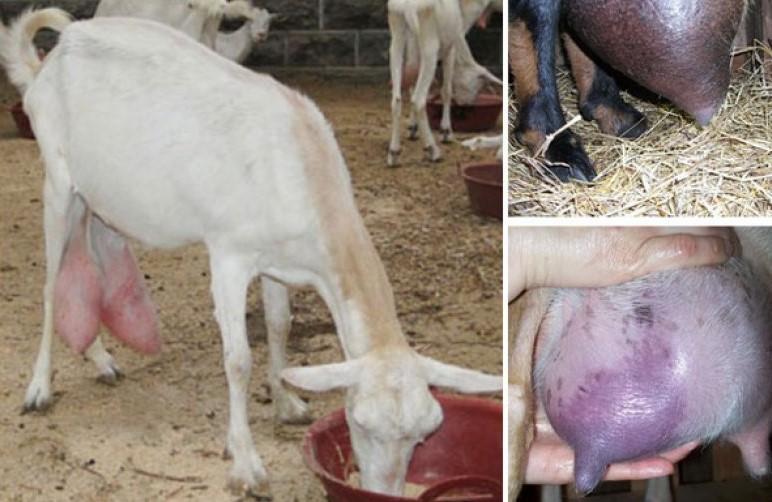
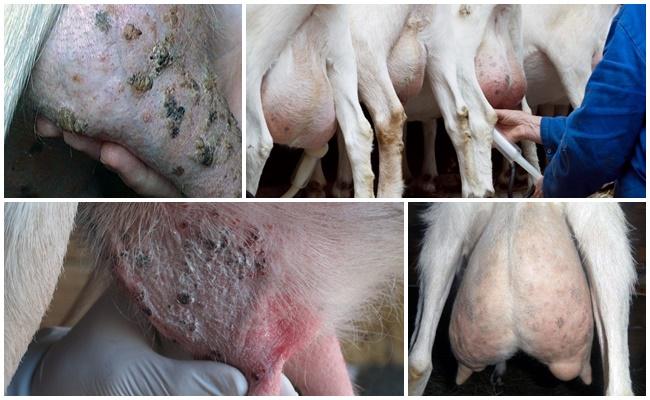
Any cattle breeder at least once in his life is faced with diseases of his pets. As a rule, illnesses are caused by improper diet and keeping of animals. But there are also more serious problems that increase the risk of developing serious diseases. If during milking a goat produces bloody milk, there can be many reasons for this problem. How to recognize each of them and provide timely assistance to your beloved and valuable pet?
Violation of containment conditions
In order to raise healthy dairy goats that produce large yields of healthy and tasty milk, first of all, you need to take care of the living conditions.
- In the room where animals are located there should not be high humidity, which contributes to the spread of fungal, viral and bactericidal infections.
- A thick layer of straw is laid on the floor.
- If animals lie on stone or concrete surfaces, the risk of hypothermia and udder inflammation increases.
- Inflammatory processes have a destructive effect on small vessels in the mammary gland, so after milking a red sediment appears in the milk.
Important! In winter, the room with the goats is heated and ventilated daily.
Milk stagnation
Incorrect milking technique and unfavorable housing conditions increase the risk of milk stagnation in goats. In this case, the goat also gives milk with bloody clots and sediments. If the inflammatory process is not detected in time, over time it will develop into a serious disease - mastitis.
Stagnation occurs due to improper milking, when a small amount of liquid remains in the udder.
Signs of stagnation:
- milk acquires a watery consistency;
- flakes appear in the product;
- pronounced swelling of the udder;
- the skin of the udder becomes hot, red spots appear;
- touching the mammary gland causes anxiety in the animal;
- a pinkish or red tint appears in the milking product;
- a sharp decrease in the activity and appetite of the animal.
This problem can be eliminated with daily udder massage. If the inflammation develops into mastitis, serious drug treatment is prescribed.
Non-compliance with milking rules
Incorrect milking technique and violation of hygiene requirements often lead to inflammatory processes in the goat's udder.
The milk remaining in the udder stagnates and provokes the development of the disease. Also, pathogenic microbes can enter through microcracks in the nipples. As a result, small vessels are damaged and the valuable drink turns pink.
Wrong diet
A reddish sediment in milk also appears when animals are given an improper diet.
- A large amount of vegetables and fresh herbs cause disruption of the digestive processes in goats, which contributes to the development of harmful microorganisms.
- Poor quality hay weakens the vascular system of animals, which leads to milk turning pink.
- Also, do not use feed contaminated with fungi and mold to feed goats.
During periods of prolonged drought, it is not recommended to turn livestock out to pasture. Green shoots that are beneficial to animals dry out, and only poisonous plants can boast of drought resistance.
You cannot make hay in fields where buttercup or milkweed grows. The ingestion of these plants into the body of animals also contributes to the coloration of milk in a reddish color.
Inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs
Often, a pinkish sediment in the milk appears after the goat lambs, accompanied by complications. As a result of prolonged separation of the placenta or latent endometritis, inflammation of the udder occurs, developing into mastitis. In such cases, drug treatment is used. Also, after lambing, the mammary gland is rebuilt to feeding kids. The vessels and tissues of the udder cannot withstand the increased load and are torn, which causes blood to get into the milk.
Signs of inflammatory processes after lambing of a goat:
- a pink tint to the milk appeared immediately after the kids were born;
- a sharp increase in the amount of milk;
- greatly enlarged udder;
- redness and inflammation of the breast.
Most often, this problem occurs with young animals bearing offspring for the first time.
Injuries
In the process of life, animals can receive udder injuries. In pastures, goats scratch themselves on thorns and sharp edges of grass. In the resulting wounds, an inflammatory process occurs, leading to the development of stagnation or mastitis.
Goats are active animals, and udder injuries can occur while jumping or playing with each other.
Signs of injuries and wounds on the udder:
- the appearance of blood clots during milking;
- the animal shows anxiety when touching the udder;
- reddish sediment in the product after milking.
To treat such injuries, use a solution of furatsilin, which is used to wash the udder and nipples of the pet.
Reference! On large farms, livestock are carefully inspected for injuries and damage after daily grazing in meadows and fields.
Complication after drug treatment
Inflammation of the udder can also occur after long-term drug treatment with antibiotics. The drugs help destroy beneficial microflora in the body of goats, weaken the walls of blood vessels and reduce blood clotting. This increases the risk of injury, scratches and abrasions.
Long-term treatment also weakens the animal’s immune system. As a result, there is an increased risk of developing fungal, viral and bacterial infections that weaken the goat's vascular system.And weak blood vessels provoke local bleeding, which turns the milk red or pink.