There are many difficult aspects that require attention when raising newborn rabbits. If you do not know the most important rules for handling rabbits, you can lose the entire litter, and with it financial investments and labor costs. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to prepare for possible difficulties long before purchasing rabbits and obtain the necessary theoretical knowledge.
- Okrol
- What do newborn rabbits look like?
- Is it possible to pick up baby rabbits?
- Stages of growth and development of babies
- Newborn care
- Inspection of the offspring
- Problems with care
- Tips for rabbit breeders when refusing to feed
- Moving in with another female
- Force feeding
- Artificial feeding
- Separating and sorting baby rabbits
- Possible problems when raising young animals
- Newborn rabbits die
- The female scatters the cubs
- Baby rabbits squeak
- Babies leave the nest early
Okrol
In rabbits, pregnancy lasts up to a month. The approach of childbirth is indicated by a change in the female's behavior. She begins to prepare the nest, using various soft materials and plucking fluff from her chest and belly. She needs help by placing wooden boxes with straw or hay. During this period, the rabbit is especially timid, so you need to try to irritate and frighten her less. Birth most often occurs at night; the animal copes with the process on its own, biting the umbilical cord and licking newborn rabbits.
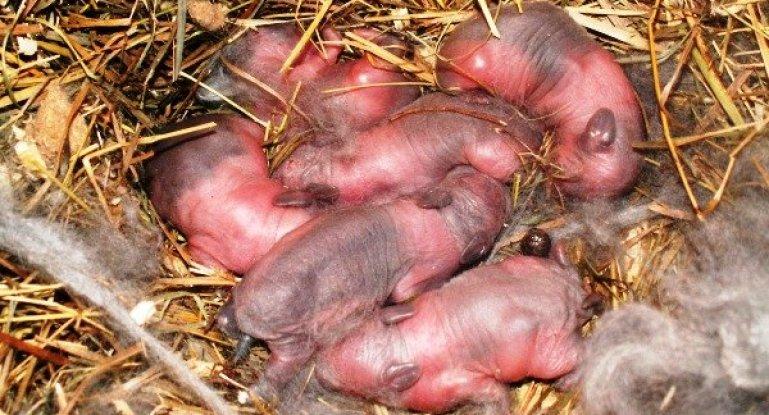
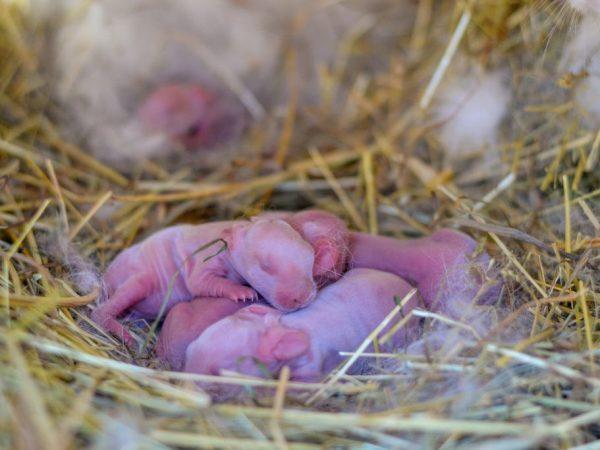
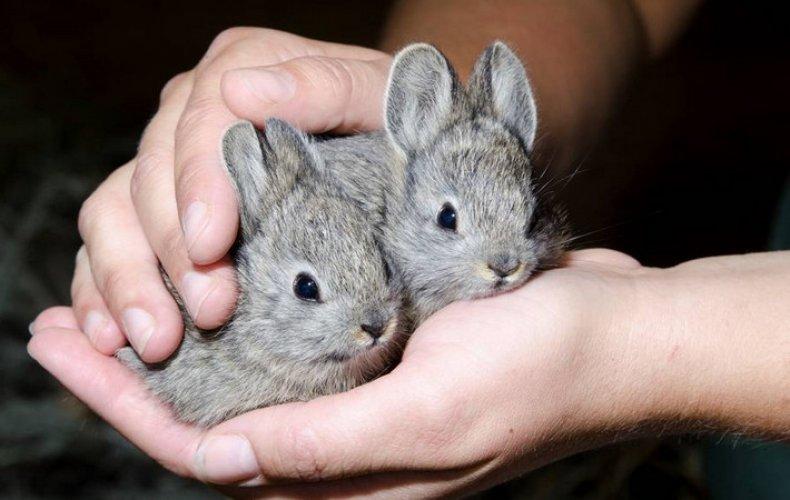
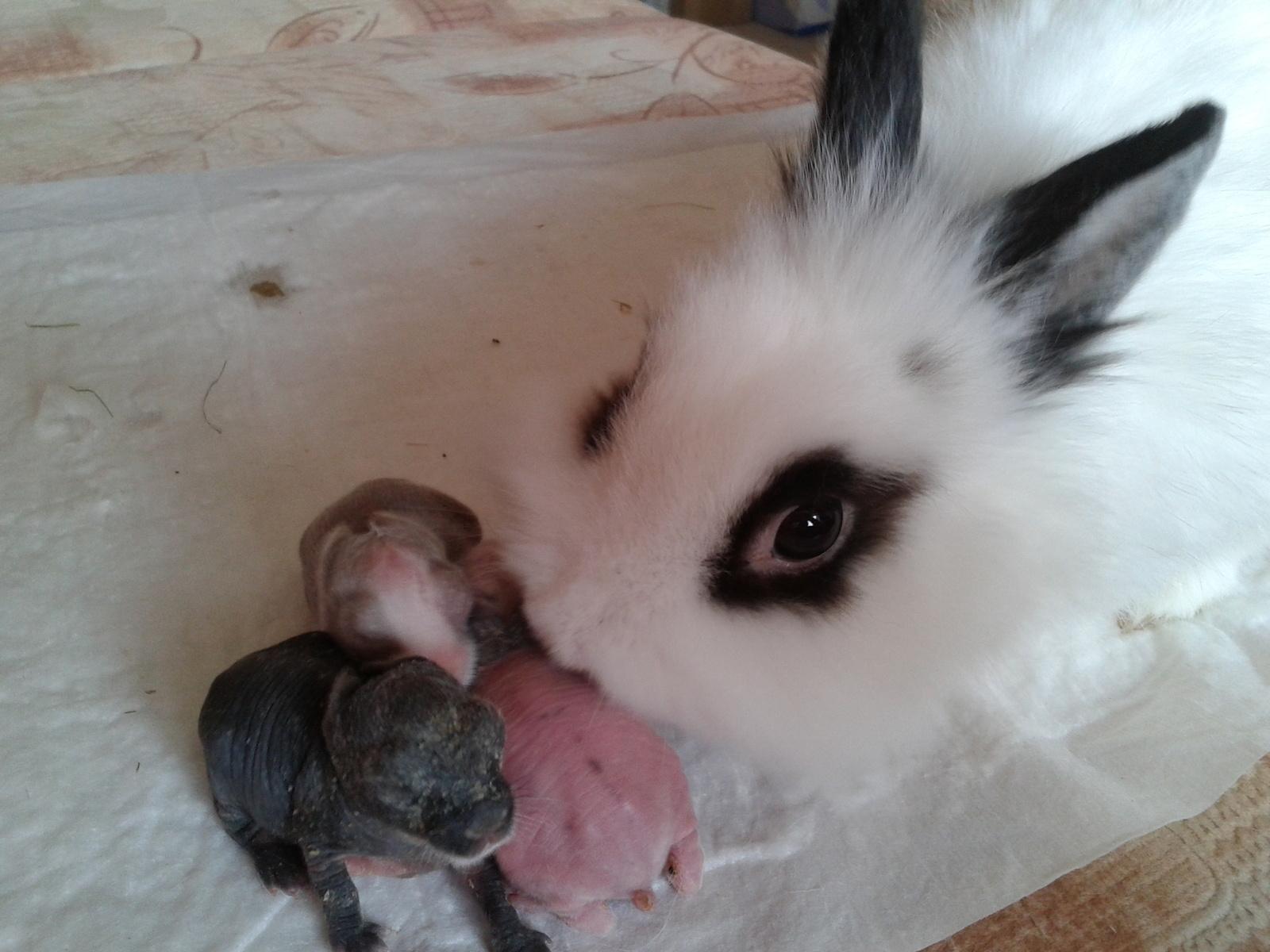
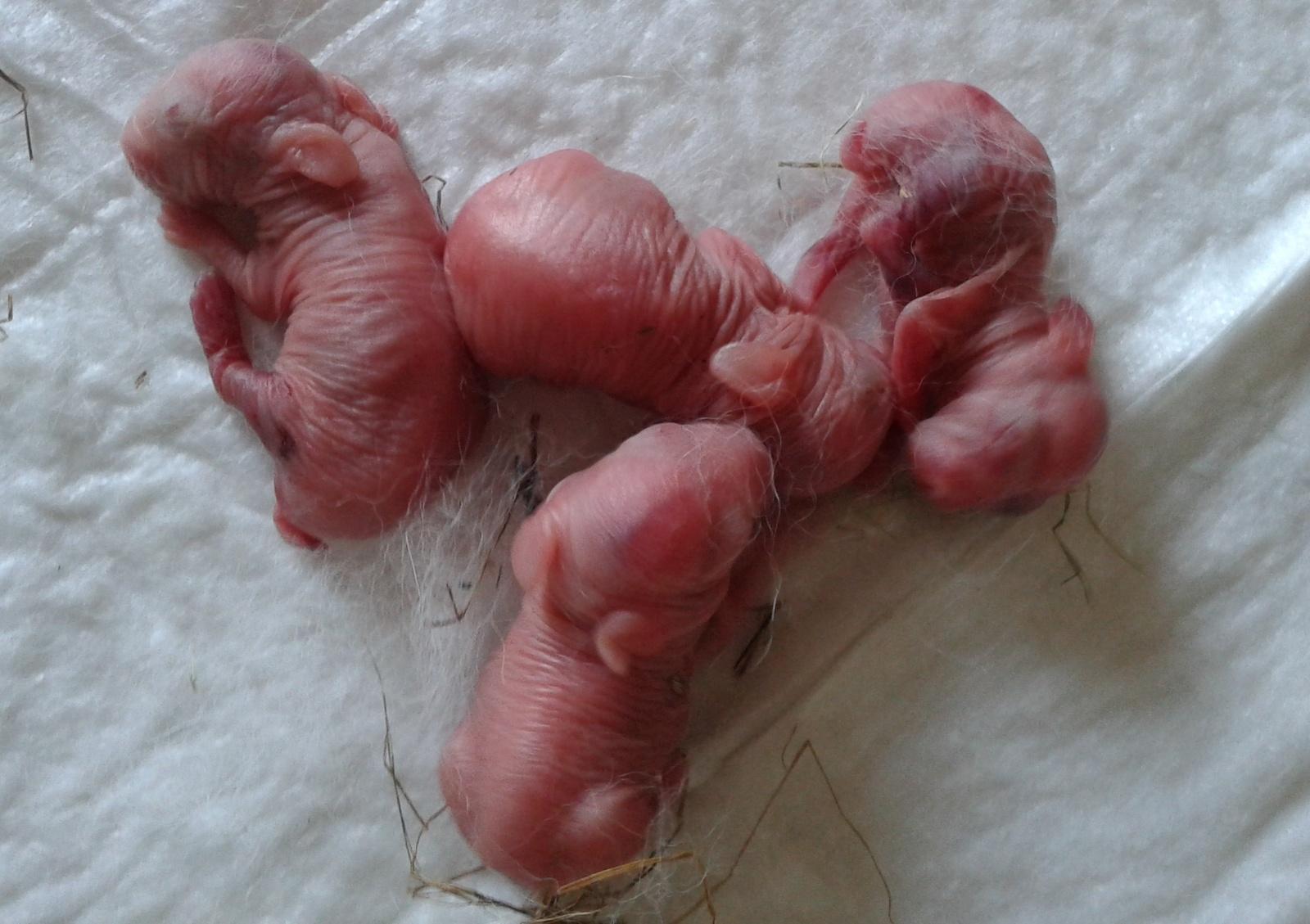
What do newborn rabbits look like?
Newborn rabbits are born naked, blind and deaf. At first, they are completely dependent on the female, but do not need her constant presence. Beginner rabbit breeders are concerned about the fact that the female rabbit may not be in the nest, but this is normal behavior for these animals.
Three days after birth, fluff begins to grow on the baby rabbit’s body. Newborn rabbits begin to see after 10 days, and the fluff is gradually replaced by normal hair characteristic of the breed.
Is it possible to pick up baby rabbits?
It is believed that newborns should not be touched because the mother may abandon the offspring. But this is not entirely true. You should not touch it with bare hands, without special need and too often. After birth, this must be done, especially during the first birth. This way, dead or weak rabbits are identified that can still be saved.
The inspection is carried out with gloves, quickly, but without sudden movements, noise and fuss, so as not to frighten the nervous mother, otherwise she may abandon the nest.As a last resort, you can thoroughly wash your hands with unscented soap, because the rabbit may leave offspring precisely because of the extraneous aroma or because of the stress caused by the invasion.
Stages of growth and development of babies
Rabbits grow and mature quickly. 15-20 days after birth, their mass increases 10 times. The development of newborn rabbits by day is as follows:
- From birth and during the first 10-12 days, the rabbits are helpless, blind, deaf, feed on their mother's milk and depend on her care.
- After 3 days, fluff begins to grow on the animal’s body, which gradually turns into full-fledged fur.
- After a week, rabbits develop hearing.
- After 10-14 days, the rabbits gain the ability to see.
- They begin to feed on their own at 16-20 days of age. Very “early” rabbits, striving for independence after 16 days, should receive softer food as their first food, for example, grated carrots.
- After 3 weeks, the vast majority of rabbits begin to feed on their own.
- Mature rabbits can be transferred from the queen cell.
Babies need to be closely monitored because they are prone to illness, and female rabbits may refuse to feed.
Newborn care
In order to successfully raise newborn rabbits, owners need to know the basic rules for handling them.
Inspection of the offspring
After birth, it is necessary to examine the baby rabbits. There can be many newborns in the litter, but for normal rearing you need to leave no more than 8 babies per female. Upon inspection, you need to immediately remove the dead ones, and start caring for the weakened rabbits. “Excess” rabbits can be placed with another female who has given birth, or you can try to feed them artificially.
Problems with care
The main condition for success, especially during the first birth, is the complete absence of stress and anxiety for the animals. Otherwise, the female may abandon her offspring or even kill her children. This can also happen if there are too many rabbits in the litter, if weak offspring are left in the nest, or if the female is frequently disturbed.
There is a situation when the offspring is in danger of trouble due to the fact that the female is in heat after giving birth. To avoid unpleasant incidents, the female rabbit is placed next to the male. After fertilization, the female calms down, but she and the newborn rabbits need to be constantly monitored, as she may stop feeding them.
If the baby happened in winter, you need to take care of heating, and also add cotton wool to the nest if there is little fluff in it. The rabbit should eat plentifully and variedly; she is given only warm and clean water.
Tips for rabbit breeders when refusing to feed
If the female refuses to feed the rabbits, you need to make sure that the reasons for this are not the following problems:
- Lack of milk or poor quality, as well as lack of lactation.
- Sore, painful nipples.
- Hormonal changes in the female body.
- Stressful situation.
You need to try to eliminate the reasons for refusal to feed, and if this does not help, start feeding the rabbits in other ways.
Moving in with another female
If there is another female rabbit on the farm who has recently given birth to offspring, you can place the young rabbits who are left without the support of their mother with her. To do this, the new rabbit is distracted, for example, with food, and the baby rabbits are carefully placed in the nest. Hands must be clean or gloved. If there are a lot of rabbits, it is better to distribute them over several nests.
Force feeding
If the female refuses to feed the offspring, but she has milk and it is of good quality, force feeding is used. To do this, one person holds the rabbit lying on her side, the second places the baby rabbits on the nipples. When they are full, they will become round and can be taken away from their mother.
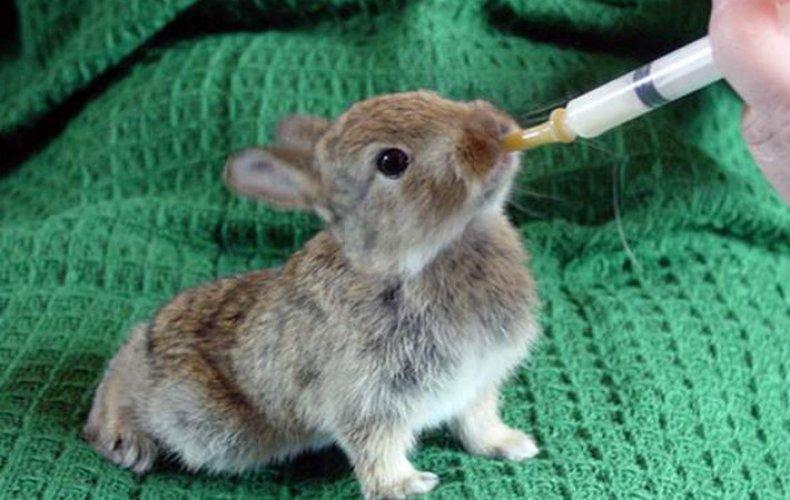
Artificial feeding
If the female dies, gets sick, does not have milk, or behaves aggressively towards the offspring, the rabbits will have to be fed artificially. Specialized mixtures or formulations based on goat's milk are used (cow's milk is not recommended).
Newborn rabbits are fed from a syringe or pipette. The daily dose starts with 5 milliliters of milk, gradually doubling. After 14 days, you can give pureed vegetable puree, monitoring the reactions of the baby’s body.
Separating and sorting baby rabbits
When breeding rabbits, the following weaning periods are used:
- On day 28. Used if the female has an accident with the rabbit after giving birth. You should not abuse this method, as it greatly weakens the rabbit, and the rabbits are not yet ready for independent life.
- For 35-40 days. You need to make sure that the rabbits do not start to overeat.
- In 40-45 days. The optimal time for weaning from the mother.
- 56-60 days. This period is called broiler jigging, because the young animals go to slaughter immediately or after 10-20 days of intensive fattening.
It is advisable to sort the rabbits during jigging, first separating the strongest and strongest ones. The reduction in “mouths” leads to the fact that weakened and small rabbits begin to grow rapidly and are compared in weight and size with the previously placed brothers and sisters.Grown-up rabbits are sorted by sex.
Possible problems when raising young animals
Frequent problems with newborn rabbits arise during the first birth, but even in an experienced female, the rabbits may die.
Newborn rabbits die
There is a strong belief that a mother rabbit can kill her own newborn rabbits. This happens, but very rarely. Most often, bite marks on the bodies indicate the inexperience of the mother, who tried to help the offspring be born or bit off the umbilical cord.
If infection is present, newborn rabbits can die very quickly. This will require veterinary intervention.
The female scatters the cubs
There may be several reasons for this:
- Inexperienced mother.
- Lack of maternal instinct.
- Sexual hunting.
- It's too cold in the nest.
- Weakened or sick offspring.
- Mastitis or other breast problems.
- The baby rabbit accidentally falls out of the nest.
- Human interference, noise, stress, bright light.
To preserve the offspring, you need to carefully monitor the behavior and actions of the mother.
Baby rabbits squeak
There are two reasons for this: hunger and cold. Well-fed and warm newborn rabbits behave quietly and calmly.
Babies leave the nest early
Most often this happens due to malnutrition. The female may have little milk or it is not nutritious enough, so the young tend to find food outside the nest. The baby rabbits need to be weighed and, if they are found to be underweight for their age, the rabbit’s diet needs to be improved and/or supplementary feeding should be started.
Despite the fact that the rabbits have begun to feed on their own, it is still too early to separate them from their mother. This can be done in 40-45 days.
Newborn rabbits are weak and defenseless, so owners will have to put in a lot of effort to preserve and raise their offspring. But if this is successful, the number of rabbits will begin to grow exponentially, as will the material well-being of their owners.