Before buying rabbits, you need to decide for what purpose you plan to breed them: to obtain fur or meat. The breed chosen must be suitable for the purpose. If an ornamental pet living at home does not require large expenses, then for industrial breeding of rabbits you will have to spend a lot on arranging a rabbitry, food, vaccination, care and hygiene products, as well as spend a lot of time and effort.
- Choosing a breed for breeding
- For meat
- For skins
- For meat and fur
- What to consider when purchasing
- Methods of content
- Cells
- Aviaries
- Pits
- Sheds
- Mini farms
- Nuances of care
- Features of the diet for feeding
- Mating, pregnancy and childbirth
- Raising young animals
- Methods for slaughtering rabbits
- Rabbit diseases: symptoms and their treatment
- Mistakes of inexperienced farmers
Choosing a breed for breeding
Meat rabbit farming predominates; breeding rabbits for fur is not common. Rabbit meat is tasty, nutritious, easily digestible, and suitable for dietary nutrition. Fur clothes and hats are sewn from the skins, and hoods and shoes are trimmed.
For meat
The most popular breeds for breeding for meat are:
- California rabbit;
- New Zealand (red and white);
- French ram;
- Flanders
Data types of rabbits They are characterized by rapid weight gain; breeding does not require large amounts of feed. By 4-6 months, the young individual weighs about 5 kg.
For skins
The following breeds are selected for breeding for skins:
- silver rabbit;
- Viennese blue;
- black-brown;
- Soviet chinchilla;
- Russian ermine.
For meat and fur
Breeds of rabbits popular for breeding for both fur and meat:
- butterfly;
- giant (white and gray);
- chinchilla.
What to consider when purchasing
To successfully start a business from scratch, you should know what criteria to use to choose rabbits for breeding:
- the coat is smooth, shiny, without tangles or bald patches;
- the body is flexible, the muscles are developed;
- the back is elongated, without sagging;
- the ears are covered with short fur on the outside and light pink on the inside;
- ear cartilages unbroken;
- the bite is correct, the upper jaw protrudes above the lower jaw;
- eyes are clean, no redness or discharge;
- the nose is clean, cool and moist to the touch;
- the rabbit does not panic when a person approaches and behaves adequately;
- the area around the anus is clean, the fur is not stained with dried feces;
- the belly is soft, no lumps can be felt;
- the genitals are clean, without discharge, the skin is pink.
To have healthy and purebred rabbits, you should purchase from an experienced farmer who cares about his reputation.
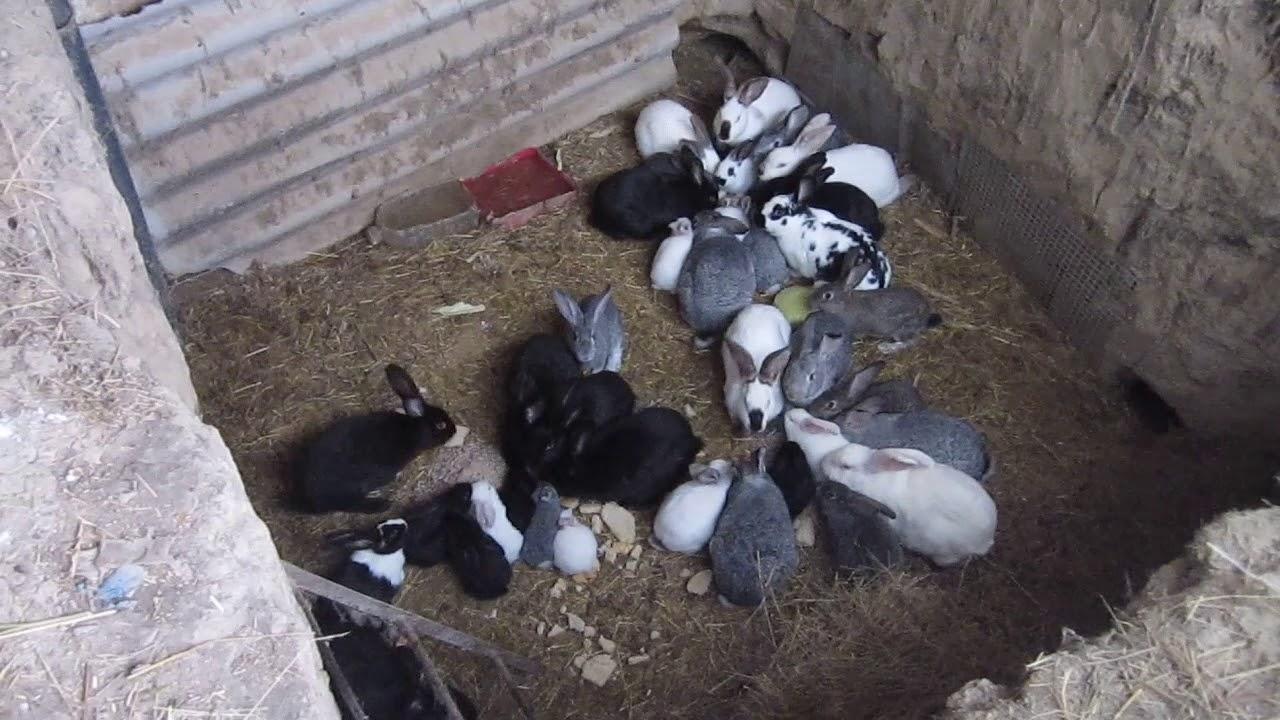
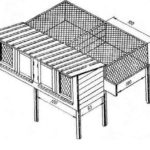
Methods of content
Industrial breeding of rabbits requires not only a lot of money and labor, but also a large space: a farm, a summer cottage. Pets are kept in closed rabbitries or in open cages, pits, and enclosures.
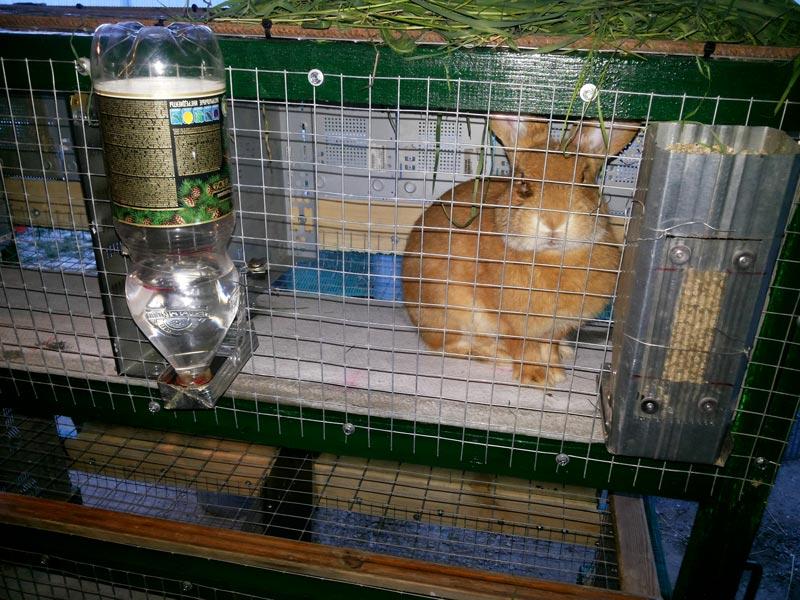
Cells
Cage equipment is the most convenient and common option of all possible methods of keeping rabbits. Its advantages:
- the ability to accurately dose feed;
- ease of monitoring the condition of individuals;
- exclusion of uncontrolled reproduction;
- ease of breeding, care, disinfection, vaccination.
It is convenient to keep cages in a barn, a specially built rabbitry, and even in a private house if there are few rabbits. The structures can be made portable to allow animals to be taken outside into the yard during the warmer months.
Rules for making cages at home for beginning farmers:
- The optimal cage size per individual is 1 m2.
- The cage should be divided into two sections: open and house.
- A queen cell is placed in the cage of a pregnant rabbit - a box for baby rabbits measuring 50x30x25 cm, the diameter of the hole should be 18-20 cm.
- Partitions and doors make it convenient to clean and disinfect cells.
- The back and side walls of the cage are wooden, the front is mesh.
- The bottom is wooden or plastic, but not made of metal mesh, otherwise the rabbits will cut their paw pads.
- A removable tray for urine and feces is installed under the floor of the cage.
Aviaries
To keep rabbits in conditions close to natural, enclosures are built.
Advantages of breeding in such conditions:
- rabbit activity;
- ensuring strong immunity;
- low maintenance costs.
The enclosure fence is buried 60 cm into the ground, its height above ground level should be 1.5 m. A space of at least 1 m is required for one individual2. The fence is made of mesh, boards, slate plates. A canopy is installed over the enclosure to protect from precipitation and sun.
Pits
The pit breeding option is chosen by farmers who breed rabbits for meat. Raising rabbits for their fur in this manner is unacceptable. Pits are made both in the country and in urban areas. The main thing is a low groundwater level and soil without stones.
To breed 20 rabbits, dig a hole 2x2x1 m. The floor can be left empty, or it can be covered with a net or boards, under which you can make a slope for waste (or place a pallet). If the floor is left empty, it is lined with straw, which must be replaced regularly.
This method of breeding rabbits is convenient, but there are several significant disadvantages:
- inability to control reproduction;
- the appearance of offspring with anomalies due to inbreeding;
- gradual feralization of rabbits;
- frequent fights between males.
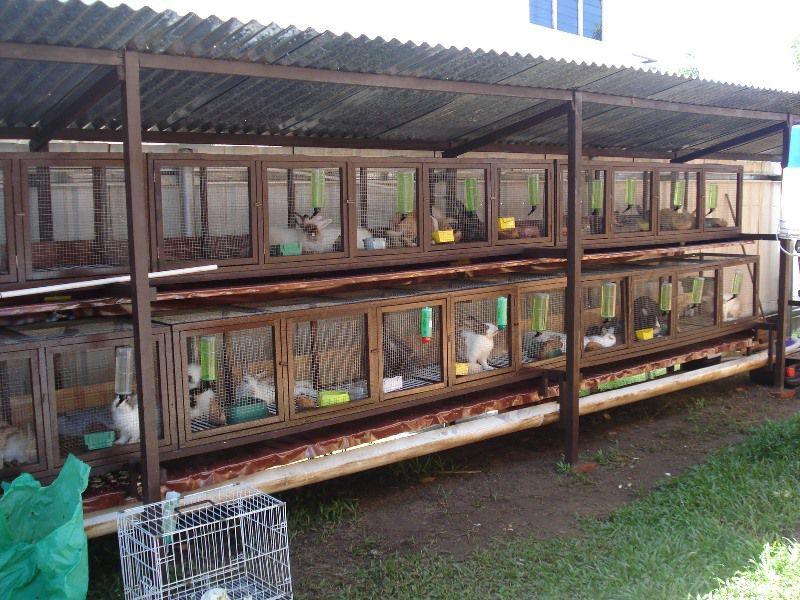
Sheds
It is convenient to raise rabbits in sheds - long sheds in which non-portable cages are placed in rows in several tiers. This method of breeding significantly saves space, making it possible to raise a large number of individuals at the same time. In warm months, the shads are not heated; in winter, the heating system must be turned on.
Mini farms
Academician Igor Nikolaevich Mikhailov developed designs that are convenient on farms where large livestock are planned to be raised. Spacious cages are installed in 2-3 tiers, accommodating 20-25 individuals. Cell design:
- pitched roof;
- mesh floor for exit of feces and urine;
- outer pipe for gas exchange;
- insulated northern wall;
- south wall opening for ventilation.
To simplify the care of rabbits in cages, automatic feed and water supply and waste removal systems are installed.
Nuances of care
Rabbits are sensitive to environmental conditions, get sick if the farmer does not want to care for them properly, or ignores hygiene rules. It is necessary to clean the rabbitry 2 times a week, change the bedding in the cage, disinfect equipment, wash drinkers and feeders daily, change water, remove rotten food and feces. It is better to use straw or sawdust as bedding.
Rabbits should be kept in a room where the temperature is from +18 to +20 °C, air humidity is about 50%, there is good ventilation, but there are no drafts.
In the summer months, sunlight is sufficient, and if the weather is clear, a shading canopy is used. In winter, the installation of additional lighting sources is required.
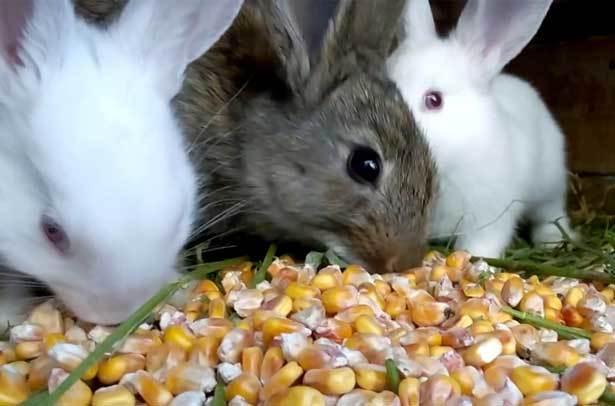
Features of the diet for feeding
To raise healthy rabbits, you need to properly prepare a diet for them. It should be balanced and varied, including:
- hay;
- grass;
- vegetables, roots, twigs;
- compound feed;
- grain food.
Overfeeding rabbits is unacceptable. It leads to obesity, due to which animals become less active and produce few offspring. During the cold period, rabbits are given more root vegetables and vegetables (zucchini, carrots, pumpkin, fodder beets, boiled potatoes) and silage. Hay and succulent plant foods should make up 30% of the diet, and mixed feed and grain feed – 70%.
You should not feed rabbits:
- legumes;
- nuts;
- raw potatoes and food beets;
- cabbage;
- pasta and bakery products;
- sweets;
- meat and sausages;
- waste from the master's table.
Mating, pregnancy and childbirth
In rabbits, reproduction occurs outside of the seasons. Thanks to their high fertility, it is possible to breed a large population in a short time. In summer, a female rabbit's estrus lasts 8-9 days, in winter – 5-6. Individuals are distributed so that a male covers 8 females.
A female rabbit can mate 5 times during the year and produce up to 40 cubs. There are 6-12 rabbits in a litter. A couple of days after giving birth, the female is ready for new breeding. Females that have reached 5 months of age and 7-month-old males should be bred. The female is placed in a cage with the male for 10-15 minutes.
Pregnancy lasts 28-30 days. A pregnant individual becomes aggressive and does not allow herself to be touched. The rabbit is carefully looked after, protected from stress, and the daily portion of food is increased. Before giving birth, the female rabbit builds a nest from straw and fluff torn from her breast. There is no need to help the female during childbirth.
Raising young animals
Rabbits are born blind and naked, begin to see after 10 days, and are covered with fur after a month. From the 3rd week of life, baby teeth begin to change to permanent ones.
A young individual weighs:
- 50-60 g immediately after birth;
- 80-120 g after 2 days;
- 2-3 kg after 3-4 months.
The rabbits should not be touched until they are covered with fur, otherwise a nervous rabbit may destroy them. After 50-60 days from birth, the offspring are separated from the mother. Young rabbits should be raised in the same conditions as mature rabbits. The cage should have plenty of space to keep your pet active.
Methods for slaughtering rabbits
When bred for meat, rabbits are slaughtered at 4 months of age. To obtain fur, the slaughter period is delayed to 6-7 months. There are several methods of slaughter:
- mechanical (the most common);
- electrical discharge;
- French (vascular rupture);
- using an automatic pin;
- embolism (introduction of air bubbles into a blood vessel);
- neck twisting.
In the mechanical method of slaughtering meat or fur, a heavy object is struck forcefully on the forehead, back of the head, or nose of the animal, which is suspended upside down. The carcass is hooked onto a spreader, the skin is torn off, gutted, and the blood is bled out.
Rabbit diseases: symptoms and their treatment
Rabbits are susceptible to many infectious and non-infectious diseases, of which the most common are:
- Pneumomycosis is a fungal pulmonary disease accompanied by sneezing, difficulty breathing, and yellowing of the mucous membranes. Associated with poor hygiene. There is no treatment, sick individuals are killed, the cells are treated with formaldehyde.
- Myxomatosis is a fatal viral disease manifested by nodular formations on the head and in the genital-anal area. For prevention, animals are vaccinated.
- Hemorrhagic viral disease is another incurable disease. Therefore, we must not forget about timely vaccination.
- Scabies, manifested by peeling skin. The affected body is lubricated with turpentine. The cage is disinfected.
- Bronchitis appears from temperature fluctuations and drafts. Suitable medications are Brovaseptol, Tromexin, Brovafom.
- Helminthiasis occurs due to poor hygiene. The drug “Naftamon” is used for treatment.
- Conjunctivitis occurs due to eye injuries or retinol deficiency in the rabbit's body.
- Mastitis in a nursing rabbit is manifested by hardening and redness of the nipples, and the appearance of ulcers. The disease is serious and should be dealt with by a veterinarian.
To prevent a possible epidemic, the purchased rabbit is kept in quarantine for 3 weeks.
Mistakes of inexperienced farmers
Beginning farmers make primitive mistakes in breeding rabbits, which is why their business collapses. You cannot do the following:
- forget about maintaining hygiene in the rabbitry;
- place cages in heat and draft;
- ignore vaccinations and preventive visits to the veterinarian;
- give rabbits food without checking for the presence of poisonous herbs (milkweed, bindweed, tansy, larkspur, hemlock, wild garlic, datura);
- ignore the underdevelopment of the maternal instinct in the female rabbit (females who refuse their offspring and devour them are not allowed to breed).
Also, a novice farmer must take into account the moral side of raising rabbits. Not everyone can kill animals and gut them. You can entrust this matter to another farmer, but then the cost of production will increase, which will negatively affect the profitability of the business.