Rabbit farming as a farming industry originated in the 19th century. Burrowing animals were raised in conditions close to natural. Farmers kept them in special holes dug in the ground. The Eared Ears multiplied and took care of their offspring, but did not obtain food. With the development of the industry, the acceleration method and cage keeping of rabbits began to be used, but pit breeding remains an alternative and economical method.
Pros and cons of raising rabbits in a pit
The enclosure and pit methods differ in financial costs, living conditions, hygiene and the rate of reproduction of animals. Raising rabbits in a pit is profitable due to the savings:
- finances and time for arranging the place of detention - the construction of a rabbitry includes drawing up a project, erecting or re-equipping the premises, installing heating, electricity and plumbing. To dig a hole, you do not need to have special knowledge, buy building materials and hire workers;
- time for cleaning - in rabbitries built according to Mikhailov’s scheme, a system for removing litter has been thought out, freeing farmers from daily cleaning of cages. But you will have to change the litter and clean the drain over time. You can clean the pit much less often;
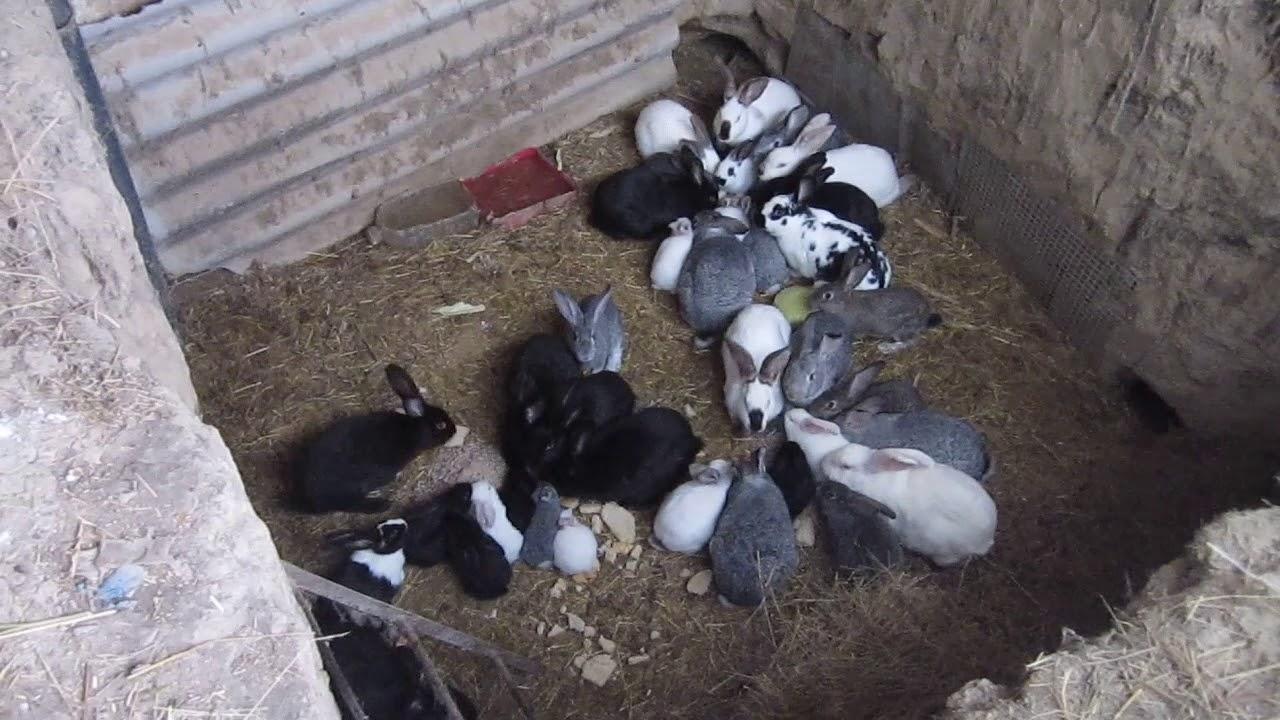
- space - to accommodate 200 individuals in cages you will need a separate area. With the pit method of breeding, for such a number of rabbits, a standard hole of 2 meters in length, width and depth is dug.
The advantage of keeping them in a pit is also that the rabbits move more, are not limited in communicating with each other, and therefore reproduce faster.
Negative aspects of breeding in a pit:
- rapid spread of diseases - the first sick rabbit will infect the rest. Viral diseases cannot be treated, and in community settings there is a high risk of reinfection of recovered individuals. Therefore, it will most likely not be possible to save the herd;
- specific problems with cleaning - when cleaning cages, rabbits are placed one at a time in a separate box. It is difficult to catch nimble animals in a pit, so the procedure for replacing the bedding must be thought out in advance;
- breed restrictions - pits are suitable for meat rabbits;
- incest - rabbits in the pit multiply quickly, but uncontrollably.Gradually, most individuals in the population become close relatives. Their offspring are weakening. Rabbits are more likely to develop genetic defects.
With proper arrangement, pit housing for rabbits provides more benefits. In winter and summer, the earth maintains the same temperature due to the natural release of heat by animals. The special microclimate has a beneficial effect on the health and reproduction of rabbits.
What breeds are suitable for the method?
Meat breeds raised in pits and enclosures have the same high quality meat. But the skin looks better on rabbits living in separate cages.
Meat breeds that can be kept in a pit:
- rex - distinguished by small paws and large ears. The average weight of an adult rabbit is 4.5 kilograms. Most of the mass is meat. Rexes tolerate frost well -30 degrees and are unpretentious in food, but cannot stand heat, are shy and can bite. There are 4-5 rabbits in the litter;
- Flanders - Belgian giants, kind in nature, reach a weight of 12 kilograms. 14 cubs are born in one litter. Giant rabbits are sensitive to drafts and often catch colds due to sudden temperature changes;
- gray giant - large-sized rabbits weigh 6-7 kilograms. Giants need a lot of space, so they will be more comfortable in a hole than in cages;
- black-brown - an easy-to-care rabbit weighing 5 kilograms quickly adapts to the changeable weather in winter.
The cultivation technology depends on the breed. The pit for purebred and large rabbits is well insulated and no more than 20 individuals are allowed in. Small breeds are more mobile and tend to dig holes. To do this, leave an area free of insulation on one of the walls.
Selection of a place for a pit
The main requirements for a place to keep rabbits are warmth and dryness. Therefore, the pit is prepared on a slightly shaded hill with deep groundwater. The parameters are selected according to the number and size of animals. The length, width and height of a standard recess are 2 meters. If the hole is not deep enough, rabbits can dig their way up and get out.
A layer of sand 20 centimeters thick is placed on the bottom to absorb odor. A metal grid or wooden slats impregnated with an antibacterial compound are placed on top. The floor is concreted and made sloping so that waste flows to one wall and is convenient to clean up.
The walls are reinforced with brick or slate and insulated with straw. A straw bedding is placed at the bottom of the pit. One wall below is left earthen so that the rabbits can build a hole. The pit is protected from the sun and precipitation by a canopy. Nearby they set up a fenced green lawn like an enclosure and build a passage for rabbits to it. A metal mesh with small cells is used as a fence. A pit with access to an enclosure allows animals to move more, eat lush grass and bask in the sun. The passage must be equipped with a door that will protect the rabbits from wild animals at night.
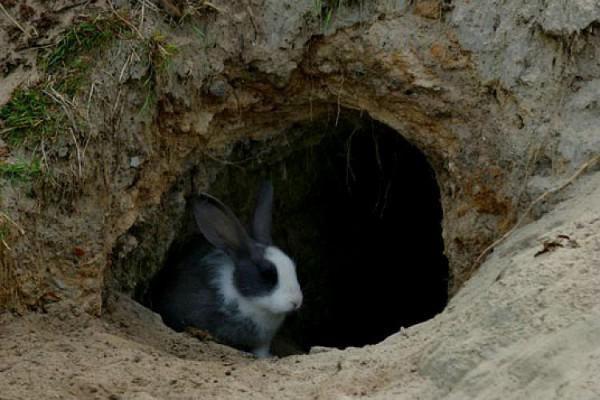
Burrow dimensions
The instincts of young rabbits from nurseries are dulled, and they do not dig holes. In this case, you need to make a home for the animals yourself. The hole is placed at a height of 12 centimeters from the floor. If the hole is flooded, water will not penetrate there. The depth of a rabbit hole in nature is 15-20 meters. In the pit it is enough to set the beginning of the move so that there is enough space for the rabbits and baby rabbits. Over time, their instincts will awaken, and the animals will dig a hole deeper.
Burrow preparation scheme:
- dig a passage in the wall with a diameter of 20 centimeters and a length of 1.5-2 meters;
- as you move, make a downward slope at an angle of 20 degrees so that the rabbits do not dig a path to the surface of the earth outside the hole;
- expand the entrance to 40 centimeters in diameter and give the hole a cone shape;
- coat the walls with clay.
For breeding rabbits at home, a cellar is sometimes used. In a ready-made underground shelter with reinforced walls, animals will not be able to dig passages. It is better to place cages in the cellar and put straw bedding inside. Breeds of sedentary giants are bred in this way. The pit is populated with young animals 6 months old for 3-4 years. Then the first settlers are let in for meat. Burrows are dug by female rabbits for their offspring. At an older age, their reproductive capacity decreases and their instinct to dig weakens. Representatives of the older generation occupy the holes dug by the younger generation. To avoid conflicts in the herd, it is necessary to remove 4-year-old individuals from the pit or remove young animals.
Content Rules
The pit is populated in stages: for 2 days the rabbits are transferred from the cages, then they are returned back and after 2 days they are put back into the pit. After 5 approaches, the animals are left in a new place.
Settlers are selected by gender: 6 females and 1 male. It is better to start breeding with a small number of 14 individuals.
Diet
The menu for pit husbandry is the same as for breeding on a mini-farm:
- green food - fresh grass, hay, silage, branches of fruit trees, beet tops;
- vegetables - raw and boiled potatoes, beets, turnips, beans, carrots, cabbage leaves;
- roughage - cereals, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, flax seeds.
Animals are fed 2 times a day. Dishes with food and water are placed above the floor to prevent waste from getting there.When breeding rabbits in the basement, feeders and drinkers can be hung inside the cages.
Reproduction
The rabbit population in the pit increases naturally. Female rabbits take care of their own and other people's rabbits. There should always be water in the drinking bowls, otherwise they will lose milk due to dehydration. If it is impossible to feed the offspring, the rabbit destroys it. When breeding animals in a pit, the following rules are adhered to:
- change males every six months to prevent degeneration;
- transplant the young animals into another pit;
- remove aggressive and weak individuals from the herd.
Males injure each other in fights, so conflicting rabbits need to be separated. If breeding females do not receive enough food and water in the herd, it is better to keep them in cages.
How to get a rabbit out of a hole
The animals live separately most of the time, wean themselves off humans and hide in holes when they appear. It is impossible to get rabbits out of a deep hole using any available means. They are attracted only by the food they receive from their owner.
To make it easier to catch animals in the pit, farmers use the following trick:
- when constructing an artificial hole, a damper is hung at the entrance;
- from the moment of settlement, feeding is accompanied by a signal - a whistle, call or clapping;
- minks dug by animals are also equipped with shutters.
The inhabitants of the pit will develop a reflex - the signal means food. They will come running when you whistle or call. It takes two people to catch a rabbit. One person calls the herd, and the other closes the holes with flaps. The animals will have nowhere to hide. The intended rabbit is caught with a net.
What problems might there be and methods for solving them
Difficulties that await rabbits in an insufficiently comfortable pit:
- the appearance of rats and insects;
- attacks by wild predators;
- blindness from poor lighting during the day;
- diseases.
Rats and insects are carriers of viruses and bacteria. To prevent the animals from becoming infected, they are vaccinated before moving in. If pests have entered the pit, the herd must be removed and disinfected or immediately transplanted into a new pit. Rabbits will hide from predators in deep holes. If the young animals do not know how to dig them, an experienced rabbit raised in a hole is added to the herd. The problem of lack of sunlight will be solved by providing an exit to the enclosure.