Psoroptosis, or psorioptic mange, is an unpleasant skin disease of animals. The causative agents of ear mites in domestic rabbits are the mites Psoroptes cuniculi. These external parasites most often settle inside the animal’s ears and affect the ear canals. Outbreaks of psoroptosis can occur at any time of the year, but rabbits are most often affected in late winter or spring. Animals of all ages are susceptible to infection, but females with offspring are especially vulnerable.
Routes of infection by ear mites and their development phases
The disease is most often transmitted from a sick animal to a healthy one. Skin scales fall off the ears of sick individuals. They can get directly onto the fur of healthy rabbits. Very often, ticks land on bedding, household items, and then move on to the inhabitants of the cage. In some cases, the pathogen is transmitted from animal to animal by the person himself. A sick mother infects her rabbits.
Risk factors are:
- crowded content;
- high indoor humidity;
- frequent regrouping of animals;
- non-compliance with quarantine standards;
- poor feeding.
Mite development begins after the fertilized female lays eggs. To prevent them from rolling, she glues them with a special secret.
Further development of the rabbit ear mite includes the following phases:
- Larva. She emerges from the egg after 4 days. It feeds on secretions in the animal's ear for 5 days. After which comes molting.
- Protonymph, or nymph of the first instar. The stage lasts about 5 days.
- Deutonympha. At this stage, the genital organs are formed. Duration – 5 days.
- Imago, or adult tick. At this stage, fertilized females lay eggs and males continue fertilization.
The lifespan of ear scabies pathogens at a temperature of + 35 degrees and high humidity does not exceed 60 days.
Signs and symptoms of a parasite
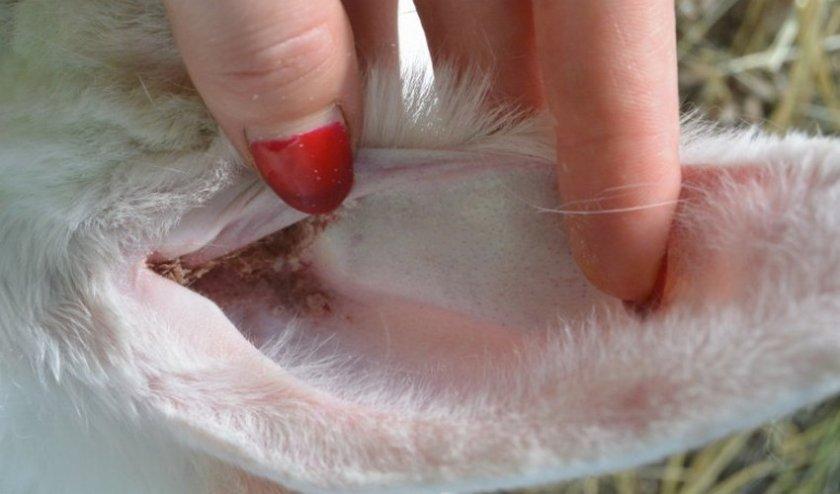
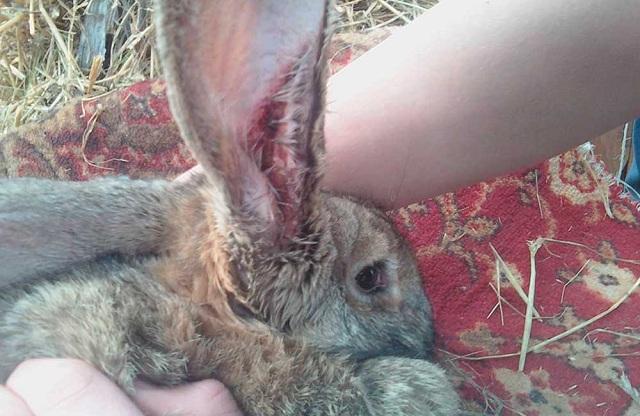
The initial stage of the disease may occur without visible symptoms. This period lasts from one and a half weeks to a month. The first signs can be identified by regularly examining the animal’s ears.The appearance of visible individual areas of skin redness and an increase in ear discharge is a cause for concern. The diagnosis can be confirmed by examining skin scrapings.
No complications
If the disease in the ears occurs without complications, then you can guess its appearance by looking at the inside of the ear. She always looks dirty and sticky.
Under the plaque, you can distinguish individual reddened areas and nodules with liquid. If measures are not taken at this stage, the disease can be complicated by various unpleasant symptoms.
With complications
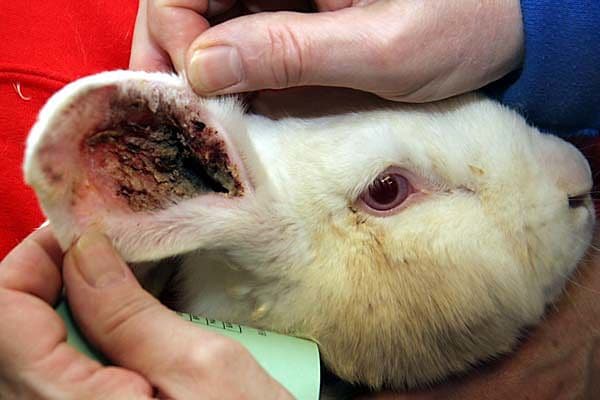
If ear scabies occurs with complications, the following symptoms appear:
- the animal is worried and scratches its ears almost non-stop, shakes its head, rubs it against the walls of the cage;
- the ears are covered with brown crusts inside and outside, the affected areas are noticeable on the neck, back, paws;
- loses appetite, sometimes does not eat at all;
- discharge from the eyes and nose is observed.
Very often, dangerous complications such as the abandonment of offspring by nursing rabbits and the development of tumors are observed.
At an advanced stage, numerous pathogens can be detected on particles of the epidermis using a magnifying glass or microscope.
Treatment rules
Proper treatment begins with a diagnosis. To do this, all suspicious animals must be examined by a veterinarian. He will also take scrapings for laboratory testing. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the specialist will select medications for sick animals. Self-treatment can only be started if it is impossible to seek veterinary help.
Use of drugs
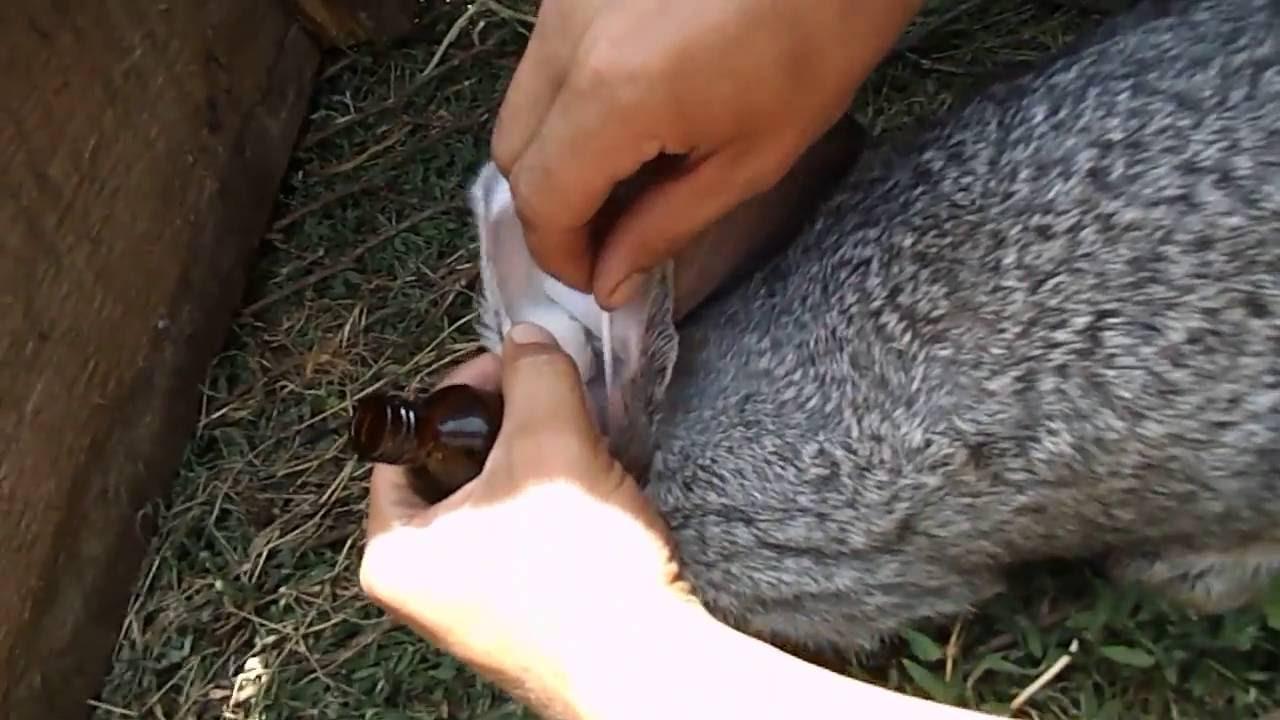
Ear mites can be effectively treated with medications.A specialist or animal owner selects external agents aimed at destroying scabies pathogens.
Effective against it:
- "Acaromectin" is a spray based on ivermectin. Causes paralysis and death of ticks. Quite popular among amateur rabbit breeders.
- Aversectil ointment - a product based on aversectin-s, an ointment developed specifically for rabbits.
- "Neostomazan" is an effective drug against many types of ticks.
- “Butox” is available in the form of a broad-spectrum concentrate. It is used for spraying animals after diluting 50 ml in a liter of water. It is highly toxic.
All drugs require compliance with the instructions for use and safety rules.
Folk remedies and recipes
At home, in addition to pharmaceutical drugs, you can use folk remedies. If it is not possible to buy a ready-made drug against ear mites, then you can combine kerosene with vegetable oil in equal quantities and every other day lubricate the affected areas with this composition.
A mixture of an alcohol solution of iodine with oil or glycerin has a similar effect. It helps to instill camphor oil into the ears using a syringe without a needle.
Prevention measures
It is easier to prevent a disease than to spend money and effort on its treatment. The main preventive measures are to maintain good sanitary conditions on the farm. It is advisable to disinfect cages and enclosures where animals are kept at least once a season in disease-prone regions. If no cases of disease are observed, then the frequency of treatments can be reduced to one every six months. The procedure is also carried out before calving. For these purposes, metal cages should be burned with a blowtorch.
Wooden structures should be whitened with slaked lime with the addition of “Whiteness” or ammonia. Feeders, scrapers and other equipment are also washed with a bleach solution. Newly acquired animals must undergo mandatory quarantine. If a newcomer appears on the farm, for preventive purposes he must be kept separately for 14 days.