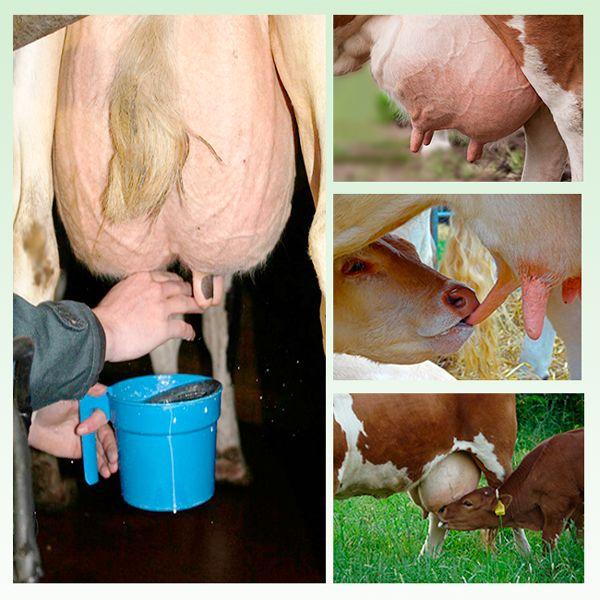
Calving a cow is a responsible event even for an experienced farmer; for novice owners, everything connected with it causes understandable anxiety. A cow has calved, but there is no milk, what can be done - people who do not have many years of experience with Burenki often try to get an answer to this question. Let's figure out the reasons for low milk yields together and correct the situation.
Reasons for being dairy-free
There are a huge number of reasons for a significant decrease in milk yield or a complete cessation of milk production, each of which should be dealt with in detail in order to understand how to solve the problem.
Breeds
There are several varieties of cattle breeds: meat, meat and dairy, dairy type. The most milk-producing breeds are dairy breeds, meat and dairy breeds give less milk, and meat breeds only have enough milk to feed calves. The meat and dairy industry is the most developed in Russia, since animals are universal, more adaptive to our harsh climate.
Meat and dairy cows produce less milk than their dairy friends. To get a lot of high-quality product from an animal, you need to carefully choose a pet when purchasing or take care of it from calf age. This requires additional costs, because the first heifer produces less milk than other animals, and she must be properly milked in order to get a productive cow.
Food quality
Particularly affects milk yield. If the animal does not receive enough food, it is of poor quality, and there will be little milk. Productivity will be low if Burenka’s drinking regime is disrupted (she drinks little, has no access to water) or if she receives a lot of dry food. In summer, a cow definitely needs pasture; grass provides it with the necessary substances, increasing productivity.
The winter diet should include:
- hay;
- silage;
- roots;
- vitamins and mineral supplements (containers with salt and chalk are left in the barn);
- a small share of feed.
Cake, fish oil, meat and bone meal, and brewer's yeast must be added to the feed. These components help replenish the animal's need for vitamins and minerals. A cow drinks at least 70 liters of water per day, the consumption rate is 110-150 liters for each animal.If there is crowding in the barn, weaker animals do not receive enough water, then the cow does not give milk, there is simply nothing for it to be produced from, because the product is 88% water.
Quality of content
Another important aspect affecting milk yield. If animals are poorly cared for, dirty, kept in a damp, not cleaned and not ventilated barn, where there is almost no light and little space, you should not expect productivity from them. The room for pets should be dry and warm; each animal needs 6 square meters of space. Feeders and drinkers are washed and doused with a hot 2% baking soda solution for disinfection. Pets are placed on a thick straw bedding.
Pregnant cows, sick animals, and bulls are kept separately from the main livestock. Conduct routine vaccinations of animals and regular preventive veterinary examinations. If the cow begins to produce less milk under the usual conditions of housing and nutrition, you should call a veterinarian.
Incorrect milking
A common cause of decreased productivity. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the udder and treat cuts and scratches. Before milking, the udder is washed with warm water, wiped dry and lubricated with cream. The heifer is milked dry so that the remaining milk does not stagnate in the udder. Sometimes a cow will pinch her milk if she senses a calf nearby.
Be sure to test for mastitis and massage the organ to avoid stagnation of milk and inflammation. Cows are milked 2-3 times a day, depending on the productivity of the animal. Milking should be done at the same time every day.
Age
The cow is first covered at 15-18 months. If you do this earlier, the animal will not have time to grow and develop, and the milk yield from the cow will be low.Then the amount of milk gradually increases until 4-5 years, and then begins to decrease. A 10-12 year old cow is considered old and usually no longer produces much milk, although some individuals do not reduce their milk yield at 12-15 years of age. It all depends on the characteristics of the animal.
Seasonality
The productivity of the animal depends on the season. Animals that calve in late autumn and winter produce 10% more milk than those that calve in summer. This happens because the peak of productivity occurs 2-3 months after calving, and when the animals move to pasture, milk yield further increases. This does not happen in cows that calve in the spring or summer.
Stress
Milk yield is greatly reduced when animals are stressed. It is caused by a change of owners or familiar premises, a change in diet, changes in temperature and humidity in the barn, noise or sharp sounds. Heat stress occurs in cattle at temperatures above +26 °C; the animal tries to move less and breathe more often. When a cow is stressed, her udder is empty, she may moo, struggle, and refuse to eat or drink.
Diagnostics
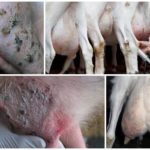
The udder should be examined before milking. It should be symmetrical, with elastic skin, without bumps or compactions. Redness, severe swelling of the udder or nipples, or impaired milk flow is a reason to consult a veterinarian.
Each lobe needs to be examined. The udder is palpated before milking the animal and after milking. It is better to entrust this to a doctor or person with experience in animal husbandry.
What to do if a cow loses milk
If Burenka’s milk yield decreases, a set of measures should be taken to restore lactation:
- Call a veterinarian to examine the animal.Mastitis, foot and mouth disease, and udder or teat injuries should be excluded. If necessary, carry out treatment.
- Monitor your diet and drinking regime. Introduce a vitamin complex into your diet after consultation with your doctor.
- Provide the cow with the opportunity to move, organize a walk.
- If lactation is disrupted due to stress, try to eliminate negative factors. Treat the animal with care and affection, give it a few days to calm down.
There are folk remedies for increasing lactation: you can give the cow nettles (fresh or dry), and do not forget to massage her udder.
Important: experienced owners advise removing the calf from the cow immediately after she has licked it, and milking the colostrum with your hands and giving it to the baby from a bottle or bucket so that the cow does not squeeze the milk, leaving it for the calf.
If immediately after calving the cow does not fully produce milk, an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection of oxytocin is given. The dosage is determined by the veterinarian, taking into account the weight and condition of the animal.
If the decrease in milk yield is not caused by illness or age of the cow, lactation can be restored. But it is better to prevent a decrease in productivity by resorting to preventive measures.
Preventive actions
To ensure that a cow always gives a lot of milk, several rules must be followed. Milk yield will always be high if:
- When purchasing, a highly productive animal was selected.
- The correct conditions for keeping and feeding the livestock are observed.
- The cow is treated kindly, and before milking she is treated to something tasty.
- Keep the animal clean, milk it correctly, wash the udder and lubricate it with cream before milking.
- They treat, deworm and vaccinate the livestock in a timely manner. Conduct preventive examinations.
Only a set of measures and knowledge will help the owner not to make mistakes at the initial stage. You should not save money by refusing the services of a veterinarian. Disinfection should be prepared in advance for calvingmedicinal products, medicines, organize separate places for the cow and calf.
Veterinarian advice
It is necessary to examine the animal after calving to prevent inflammation of the genital organs. There are several types of mastitis. This disease is the main factor in reducing milk production after calving. Express milk tests and laboratory diagnostics make it possible to detect the disease at an early stage. Before each milking, you should carefully inspect the udder and teats.
If you treat the cow responsibly and carefully, milk yield will always be high, because Burenka will definitely respond to love and sincere care. You can learn the intricacies of animal husbandry and expand your own knowledge by consulting a veterinarian or communicating with more experienced neighbors.