Lactation in cattle lasts about a year; for regular production of dairy products, annual fertilization of animals is required. How much milk a cow produces per day and per year on average depends on breed characteristics, age, body condition, quality of maintenance and feeding, and climatic conditions. There are record-breaking breeds that are characterized by consistently high productivity, but even the most productive cow needs proper care.
Average milk yield
Lactation in a cow, like a woman, begins during pregnancy. Young individuals are ready to conceive from the age of 2. A newborn calf feeds on colostrum, a fatty, dense, yellowish substance. After a certain time, the strong cub is removed from the mother, but milk continues to be synthesized and must be milked. Regular milking stimulates lactation.
Milking continues until the next conception. 2 months before birth, milk synthesis stops and resumes after the birth of the calf. It happens that milk yield before calving does not decrease, the cow cannot rest before the next lactation period. In this situation, the portion of succulent food in the diet is reduced. The animal enters the dry phase when the daily milk yield decreases to 500 ml.
Average daily norm
On average, during an annual pregnancy, the daily amount of product is 18-20 liters. But highly productive dairy cows can give 70-80 liters per day.
Differences in daily milk production and milk fat content between common cattle breeds are shown in the table.
| Breed | Milk yield, liters per day | Fat content, % |
| Holstein | 40 | 3 |
| Yaroslavl | 16-18 | 5 |
| steppe red | 10-15 | 4 |
| black-and-white | 16-18 | 4 |
| Jersey | 10-15 | 6 |
Monthly
To get the average monthly milk yield, the average daily volume of milk should be multiplied by the number of days in the month. From one cow they get from 300 to 1800 liters of product per month. When calculating, the conditions of keeping cattle and climatic conditions are taken into account.
The highest monthly milk yield is observed in Israel, which is due to the favorable climate and optimal conditions on the farms there.
After calving, the amount of milk gradually increases, reaching a peak value by the 2nd month of milking. The peak lasts for 2 months, and from the fourth month a slow decline in milk production begins. By the tenth month, milk yield becomes minimal, followed by a dry period. A clear example of changes in the amount of milk per day by month is shown in the table.
| Month | Average daily milk yield, l | In just 30 days, l |
| 1 | 28-30 | 870 |
| 2 | 30-32 | 930 |
| 3 | 29-31 | 900 |
| 4 | 28-30 | 870 |
| 5 | 26-28 | 810 |
| 6 | 25-27 | 780 |
| 7 | 23-25 | 720 |
| 8 | 20-22 | 630 |
| 9 | 16-18 | 510 |
| 10 | 13-15 | 420 |
Average annual
The highest annual milk yield is demonstrated by farms in the USA, Great Britain, and Israel. In these countries, cows produce 10-15 thousand liters of milk per individual during the year. Breeding highly productive breeds and normal maintenance contribute to this.
How common cattle breeds differ in annual productivity is shown in the table.
| Breed | Annual milk yield, tons |
| Holstein | 8-9 |
| Yaroslavl | 4-6 |
| black-and-white | 5,5-8,5 |
| steppe red | 3-4 |
| Ayrshire | 5-8 |
| Kholmogory | 4-5 |
Factors influencing milk yield
The milk yield of cattle changes not only with age, but also depending on housing conditions, quality of care and feeding, seasonal and climatic characteristics, and breed characteristics.
Age and weight of the animal
The first calving occurs when the cow reaches 2 years of age, weighing approximately 300 kg at this age. For good milk production after the second calving, a dairy animal must weigh at least 500 kg, and the height at the withers must be from 1.2 m.
From first calving cows waiting for a lot of milk not worth it. A young individual rarely produces more than 10 liters per day. Daily milk yield gradually increases with each new pregnancy.The most productive cow is milked after 5-6 pregnancy. An old individual, calved 10-12 times, produces significantly less milk.
Season
The amount of milk changes seasonally, which is associated with changes in diet. In the summer months, cows eat food rich in proteins and vitamins, so milk yield is significantly higher than in winter. If in winter an individual produces 10-12 liters of milk, then in summer the daily volume increases to 18-25 liters. If calving occurs in the fall, then the cow will have more milk than usual during the winter months. To make winter milking more productive, the hay in the diet is supplemented with juicy root vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins:
- carrots;
- pumpkin;
- potatoes;
- fodder beet.
Best dairy breeds
A cow's belonging to a highly productive dairy breed has a great influence on milk productivity.
It is not difficult to identify a productive individual; it has:
- small skull;
- strong and muscular hind legs;
- large udder;
- moderately rounded belly;
- back without strong hunchback.
Representatives of the following breeds produce more milk:
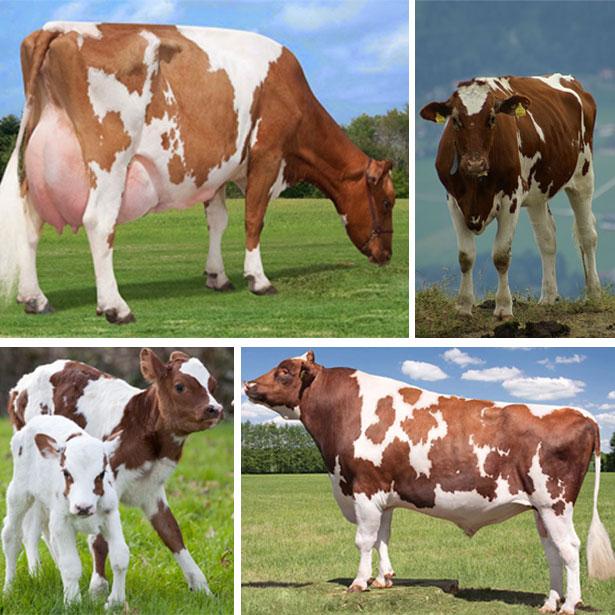
- The Holstein is the most popular breed developed in the Netherlands. The representatives are constant record holders for annual milk volume. An adult cow weighs 700 kg, she has a large udder with a beautiful round shape.
- Kholmogory is a breed with a strong skeleton and developed muscle mass. The weight of an adult is 500 kg, the skull is narrow, the color is red with black spots.
- Black-and-White is a Soviet breed with a strong skeleton. The cow weighs 400 kg and is adapted to the climatic conditions of Russia.
- The Steppe Red is a common breed in Ukraine and is distinguished by its unpretentiousness and ease of care. The animal weighs 400 kg, the skeleton is light, the physique is lean.
- Yaroslavl is a popular cow in Russia, undemanding in nutrition. An adult weighs 500 kg and is predominantly black in color.
- The Ayrshire is a red-and-white Scottish breed. The weight of an adult is 450 kg, the skeleton is light.
Competent care
The main conditions for good cattle yield are proper feeding and regular grazing. In summer the cows are out on pasture. During the winter months, hay becomes the basis of the diet; animals must have constant access to it. To obtain high-quality milk with good taste and high fat content, the diet is enriched with grain, mixed feed, and juicy foods. Food and water should always be fresh. On hot days, cows drink more than 100 liters of water per day. Animals are periodically given food supplements and vitamin complexes.
An important factor in milk yield is the farmer’s attitude towards his livestock. Cows produce more milk when their owner treats them kindly.
The conditions under which cattle are kept have a strong influence on milk yield. Cows should be in a warm, clean, dry, well-lit barn. The owner must regularly clean and ventilate the room, collect manure, and prevent drafts. It is advisable to equip the barn with lighting sources to maintain acceptable daylight hours. In good weather, the cattle are taken out into the pen. Staying in the fresh air has a positive effect on milk production. Animals are regularly cleaned, the udder and genital area are washed, and the hooves are cleaned.
Milk production records
Every country has record-breaking cows that produce large volumes of milk. But the record holder, which no one has yet managed to overtake, is the Cuban cow Ubre Blanca, obtained by crossing a Holstein breed and a zebu. Fidel Castro was personally proud of her, and for good reason: in 1981, more than 41 thousand liters of milk were received from her.
There are also many record holders among Russian breeds. In 3rd place in the world ranking is Yaroslavl cow Vienna, which in 1940 produced 31 thousand liters. In 5th place is a black-and-white cow, which in 1972 produced 19.5 thousand liters.
How long can a cow produce milk?
Cow's mammary glands produce product throughout life from the first calving. There are 3 periods in the life of an animal with different productivity:
- Maturation is the stage from birth to first calving.
- Mature age is the productive period of time from the first pregnancy to 14-16 years.
- Old age is the stage of decline in milk production.
The milking period, when the hormone prolactin is actively produced, lasts from 10 to 50 days. It is important to milk the cow regularly during this period to stimulate lactation. During milking, 2 times a day, the calf should be brought into the mother for a few minutes so that by sucking the udder it will promote milking.
The milking period lasts about 10 months, ending 2 months before insemination. If pregnancy does not occur, the cow is called barren and does not produce milk. Representatives of some dairy breeds maintain productivity for 2 years, but in the second year the milk yield becomes low.