Reproduction is an integral stage in the animal husbandry process, including when breeding cows. Without mating, not a single calf will be born, and there will be no procreation. In order to properly prepare for mating cows, you need to be able to determine the period of heat in females, choose males and females that are suitable for each other, control the mating process, and also know what problems you may encounter.
- Natural instinct
- Readiness of a bull and cow for mating
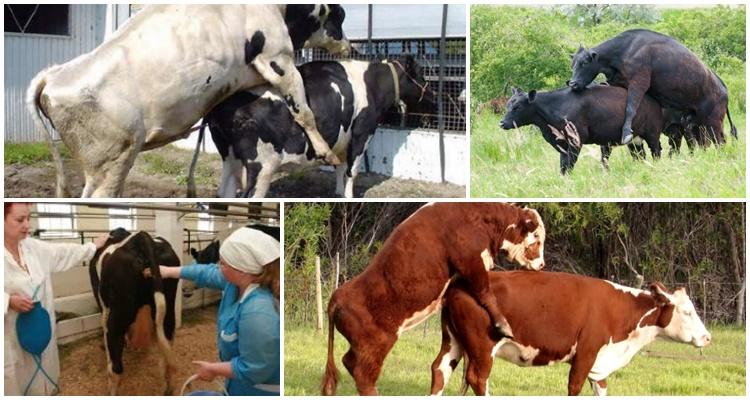
- Mating cows in nature
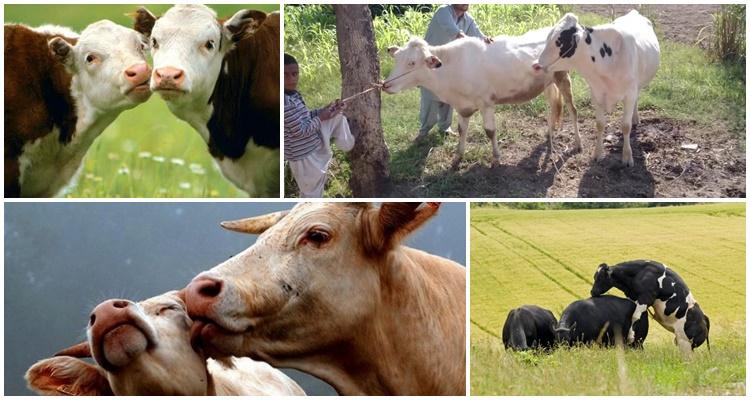
- Signs of the hunt
- Methods for determining heat in cows
- Body temperature measurement
- Probe Bulls
- Instrumental method
- Pedometry
- Heat detector
- How to prepare a female for mating
- How to choose a bull for mating
- Mating process
- Possible problems
Natural instinct
Sexual arousal and mating in cows are regulated by instinct. If the animal is healthy, it comes into a state of hunting at certain intervals.
Readiness of a bull and cow for mating
Heifers can be conceived at 1.5 years of age, although physiological development allows them to become pregnant from about 7-8 months. However, at this age, young females still continue to grow rapidly, so pregnancy is undesirable. Carrying a calf will not benefit either the heifer or the offspring; it will slow down the development of the mother’s body, the calf will be weak, small, and susceptible to disease.
Mating cows in nature
If cows are constantly together in the same herd, then mating occurs under the influence of instinct. The bull has the ability to control the condition of each female and inseminates when they come into heat.
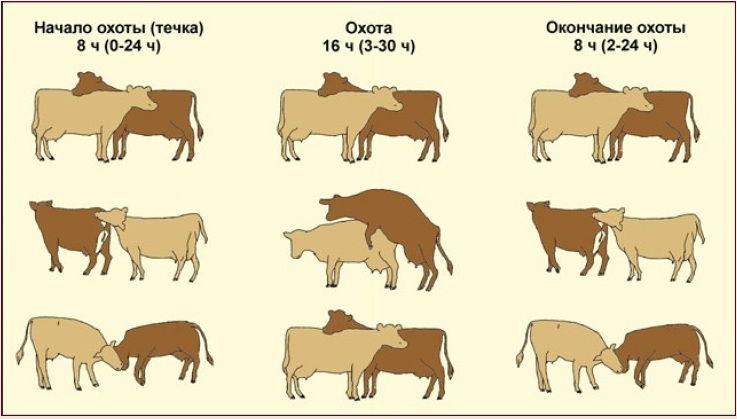
Signs of the hunt
Mating in livestock is carried out at the moment when the female body is ready to conceive. The state of sexual activity can be determined by the behavior of cows, which become restless, eat little, moo, motor activity increases, and milk yield decreases. Hunting begins in heifers at the age of 7-8 months, lasts 0.5-1.5 days, and is repeated every 18-25 days. If mating takes place during the heat period, the likelihood of fertilization will be maximum.
Methods for determining heat in cows
The efficiency of cattle breeding depends on the rate of reproduction of the cow population and is associated with the effectiveness of fertilization, which, in turn, affects the productivity of livestock and the number of calves produced.Achieving excellent performance in this direction is possible only if the rules of control and mating are observed. In addition to external signs, such as changed behavior and secretion of mucus from the genitals, the onset of heat can be determined using several methods.
Body temperature measurement
When cows are in heat, their temperature increases. In cattle, it is measured using a thermometer inserted into the rectum or vagina. The disadvantage of this method is that an increase in temperature may not be the result of sexual arousal, but of inflammatory processes.
Probe Bulls
The readiness of females to reproduce is determined with the help of castrated bulls, which are released into the general herd with cows. Those individuals that allow them to approach them and allow them to jump on them are most likely to be in the hunt.
Instrumental method
It is based on the fact that when in a state of heat, cows allow other individuals, both bulls and cows, to jump on them. For heifers and adult females, bright paint of different colors is applied to the root of the tail, which wears off when the animals come into contact. This way you can find out whether an individual exhibits sexual behavior. This method is not considered reliable, so you should not rely on it alone.
The degree of follicle maturation is determined by rectal or vaginal examination. During the examination, you can notice obvious signs of heat - swelling and redness of the genital tract, changes in the ovaries and uterus.
Pedometry
A walking cow exhibits increased motor activity, so electronic pedometers are placed on the animals’ legs. The devices record measurements 2 times a day and process data for the last 3-5 days. Some pedometer models indicate increased activity with a red glow.
Heat detector
Pressure-sensitive devices are attached to the animal's back, between the pelvic bones. The device records the moment when a cow is mounted and changes color from white to red.
How to prepare a female for mating
One-and-a-half-year-old heifers are allowed to mate for the first time when they reach a body weight of 70% of what they will have as adults. Cows that have already given birth occur in the first 1-3 heats following the next calving.
Only females in heat are allowed to mate, as they can excite the male, after intercourse with whom fertilization occurs with maximum probability. Mating is carried out in the middle of the hunting period, approximately 9 hours after it begins.
It is recommended that heifers be mated before cows are inseminated, as they can carry calves to term. This period is 2-3 weeks.
How to choose a bull for mating
The bull is selected taking into account the breed, its meat or milk characteristics, the weight of the animal, fertility and the ability to transmit desirable traits to offspring. With manual insemination, the moment of mating can be recorded in order to calculate the calving date. For better results, 2 matings are carried out with an interval of 12 hours (the bull covers the cow in the morning and evening).
In case of natural mating of cattle, before the start of the breeding period, it is necessary to conduct an examination of the genital organs of the sire and its limbs. Often, problems with fertilization can arise due to poor sperm condition or a lack of desire to mate due to pain in the legs.
At the end of the breeding period, the efficiency of covering cows with a healthy bull should be 85-90%. At the same time, the bull himself loses a lot of energy and live weight.During the mating period, it is fed with grain mixtures and vitamin and mineral premixes.
Mating process
In households, they inseminate cattle using natural and artificial mating. In natural breeding, the bull and the cows assigned to it are left on the pasture, where the male himself determines the time when and with whom to mate. This method has disadvantages - not all females can become pregnant, it is difficult to determine the exact date of mating, and therefore the birth. During manual mating, the bull covers the cow when he is brought to her. The effectiveness of this method is higher; it is possible to record matings and calculate the calving date.
To cover a cow, it is not necessary to keep a bull on the farm. Artificial mating has been used on farms and in private households for a long time. In this case, the bull does not inseminate the cow directly; she is injected with his sperm. The advantages of this method: you can get offspring from purebred animals that will have improved characteristics, you can get more calves from one dose of sperm from one bull than usual, it is easier to control the insemination process, the effectiveness of the method is higher than with natural mating.
Possible problems
Intensive use of cows often has a negative effect on their reproductive function. Some have to be inseminated during not one, but several heats. Cows that cannot conceive after 3 subsequent matings are considered problem cows. Moreover, their sexual cycle proceeds normally, heat occurs at the right time, but the animal is not fertilized.
The reasons for this condition of females may lie in hormonal abnormalities (problem individuals have a higher level of progesterone than usual), in a change in the uterine environment, which rejects the embryo. The cause may be embryonic mortality.
Poor living conditions, insufficient nutrition or, conversely, excessive feeding when animals become fat - all this also leads to disturbances in the reproductive sphere of cattle.
Mating of cows should be carried out at a certain time, when the animal’s body is maximally prepared for fertilization. To determine the date of mating, you need to monitor the manifestations of the reproductive cycle of cows and conduct mating during the hunting period. At home, natural and artificial insemination methods can be used to successfully breed cows. Which one to choose depends on whether there is a bull on the farm and on the number of livestock.