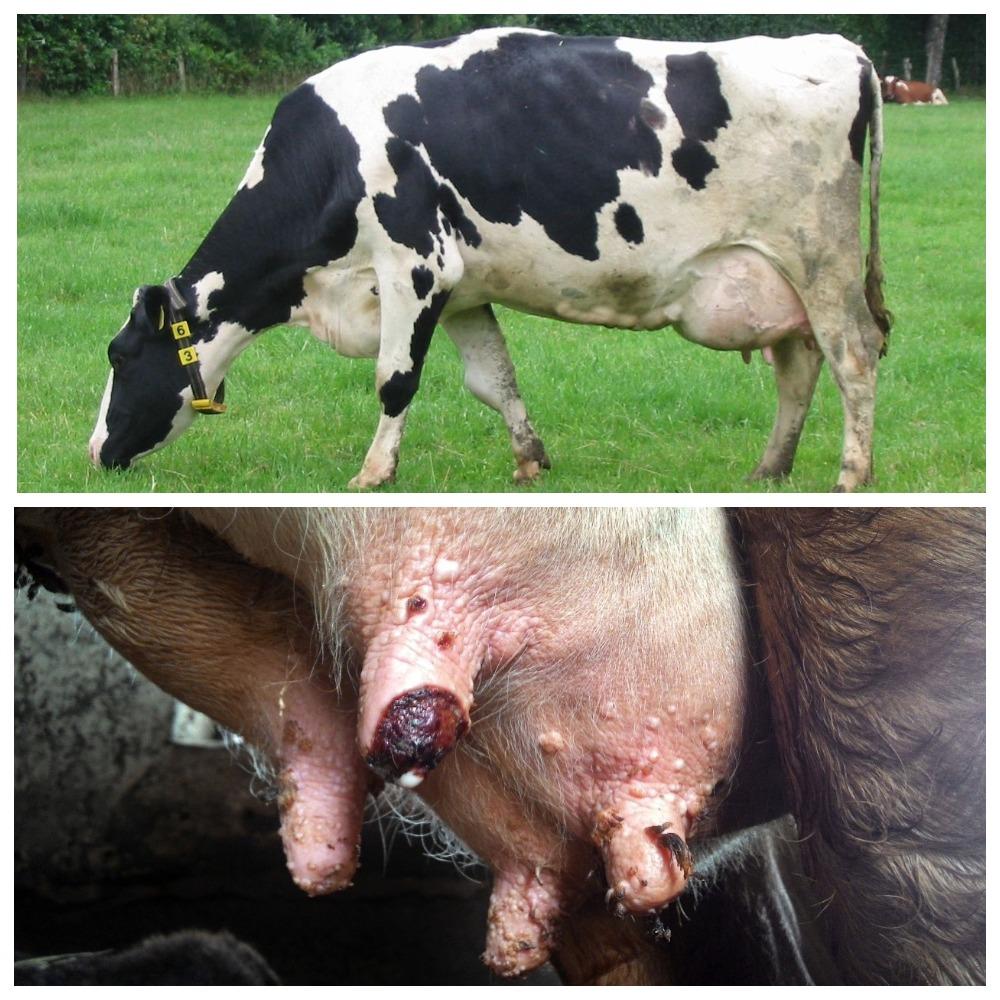
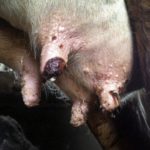
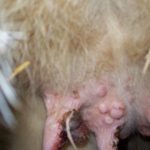
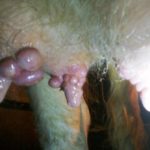
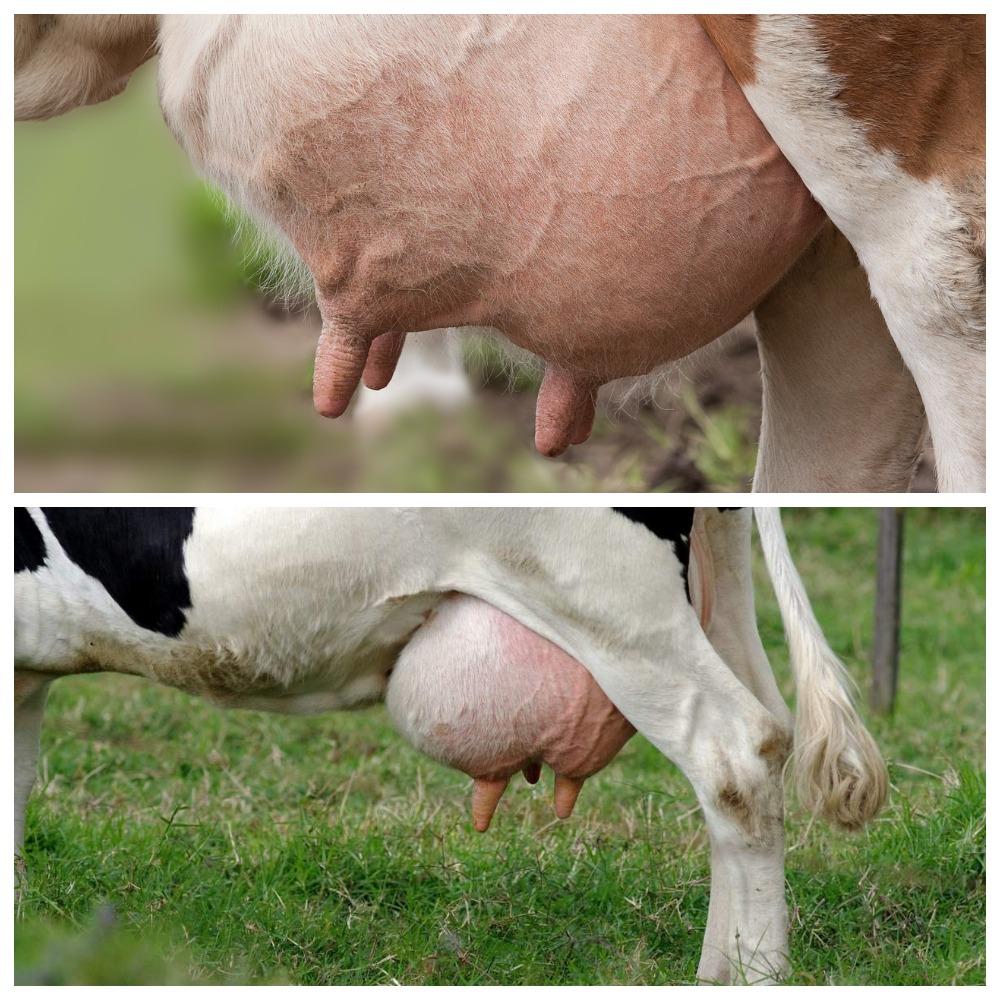
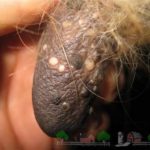
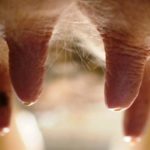
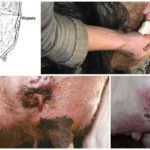
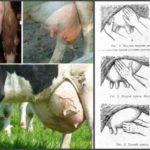
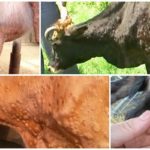
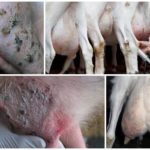
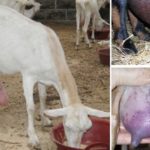
The appearance of warts in a cow on the udder is associated with the penetration of a viral agent into the epithelium, causing cell proliferation in the form of warts (papillomas). Young cows under two years of age are more often susceptible to the disease. The course of the disease can be benign or malignant. The best results are obtained with complex therapy with novocaine and vitamins. Surgical treatment is possible.
Reasons for the problem
The main reason is the penetration of the papilloma virus into small cracks and wounds of the skin. In mature cows with a high immune status, penetration of the virus rarely causes aapillomatosis. The manifestation of the disease is facilitated by factors that generally have a negative effect on the condition of animals:
- improper diet;
- poor conditions for keeping cows, dirty premises, feeders and drinking bowls, lack of ventilation;
- wounding of the skin by branches and thorns of grass while walking.
- non-compliance with hygiene measures during milking, incorrect, traumatic installation of the milking machine, dry skin of the nipples;
- infection from animal carriers who are kept nearby, and human carriers of the virus from among the service personnel.
Main symptoms
Symptoms and manifestations can be benign or malignant. With a benign course, leathery growths or crusty growths - warts - appear on the skin of the udder, nipples, muzzle or abdomen. The inner part of the growths consists of dead epithelial cells and waste products of the virus. The shape of warts can be raised or pedunculated, in size from a pea to a medium-sized plum, single or multiple.
If at this stage you take measures to improve the care of animals and increase immunity, then after 2-4 months the papillomas will dry out and disappear without a trace.
In the case of a malignant course of the disease, over a short period (up to 6 months) there is a significant growth of warts, their fusion, they cause discomfort to the cow and calf, and subsequently can tear off from the base, bleed and suppurate. The blood vessels are compressed, and the viral infection spreads through the bloodstream to all tissues and organs. Other variants of malignant course:
- the growth of warts inside the mammary gland canal, its compression, the appearance of mastitis and inflammation of the ducts;
- the appearance of papillomas in internal organs, disruption of their functioning, even death.
Diagnostic measures
On large farms where many cattle are kept at the same time, diagnosis of the papillomatosis virus is carried out without waiting for signs of warts to appear on the skin - as planned. A blood test helps identify the DNA of the virus and antibodies to it. In small farms, blood tests are done on cows when it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
Rules for the treatment of warts in cows on the udder
When the first signs of wart growth are detected, cows are isolated from the main herd, vitamin therapy and balanced feed are prescribed. Constant monitoring of the development of the disease is necessary.
Surgery
It is advisable to remove warts if they are single, located in inconvenient places where they are forced into contact with milking equipment or other parts of the body, or interfere with the calf’s ability to suck milk. In all other cases, treatment begins with drug therapy and, if it does not bring results, resort to a scalpel.
In the initial phases of mild disease, papilloma constriction using cow or horse hair is effective. After some time, the growth dries out and falls off.
In populated areas with developed veterinary care, warts can be removed in a veterinary clinic using liquid nitrogen.
Medications
Treatment with drugs boils down to the following use:
- subcutaneous or intradermal;
- intramuscular;
- intravenous;
- with drinking water or food;
- externally, in the form of ointments and applications.
Papillomatosis is easier to cure if medications are used in combination.To treat warts, magnesium is used orally in a dosage of 30 grams, the duration of treatment is 10 days. Good results are shown by intravenous infusions with novocaine, 80 milliliters of a 1% solution four times. The drug "ASD" mixed with "Tetravit" is injected subcutaneously. A 2% solution of novocaine can be injected into the base of the papilloma.
For external use use: “Papillomacid” (solution), sulfur-salicylic, interferon, oxolinic ointments - apply individually or in combination to the affected areas 4-5 times a day. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
Vitamin complexes
Increasing the body's immunity helps to resist the penetration and development of viruses. Vitamin complexes normalize metabolism and energy metabolism in cells, saturate them with oxygen, and improve the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system.
Preparations with interferon are effective. This is a substance that inactivates a pathogenic agent in the body. With the rapid development of the disease, your own interferon does not have time to be produced, so the introduction of ready-made interferon significantly helps to cope. In cases where the skin under the warts dries, cracks, and then suppuration and bacterial infection appear, complex injections with antibiotics are effective.
Use of folk remedies
Applications of natural components in some cases can be effective for the treatment of warts.
Onion and wax mixture
Onions contain a complex of phytoncides, and wax dries out growths.This mixture helps remove warts and can be used in combination with drug treatment.
The onion is pre-fried in vegetable oil until golden brown. Let it sit for a while so that it releases the valuable substances more fully. Then the onion is removed, the oil begins to be heated again, 25 g of wax are added while stirring, the mixture is brought to a boil, and cooled. Apply by lubricating the affected areas of the skin 1-2 times a day. The course of treatment is 12-14 days.
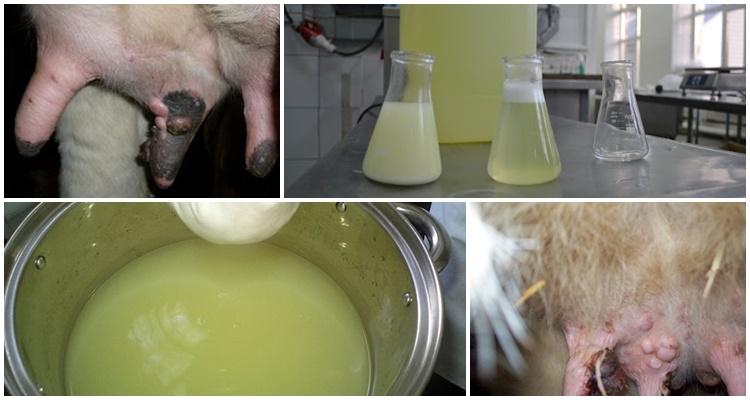
Curd whey
The biologically active substances of curd whey make it possible to treat papillomatosis in a few weeks. The serum is sterilized, the udder and nipples are washed with it 2-4 times a day.
Potato decoction
Potato peels and sprouts contain a complex of physiologically active substances, vitamins, and minerals. Potato decoction helps remove papillomas on the udder of cows. The potatoes are washed, peeled, the peelings along with the sprouts are poured with water and put on fire, brought to a boil and boiled for 10-15 minutes. The broth should become dark. The liquid is cooled and used to wash the udder of cows 3-4 times a day.
Garlic mixture
The active substances of garlic are effective when mixed with animal fats. To prepare it, lard is first melted. A few cloves of garlic are finely crushed and mixed evenly with lard. The mixture is applied to warts on the udder 1-2 times a day. Leave for 30-40 minutes, then rinse with warm water and wipe dry with a clean towel.
Prevention
Prevention of papillomatosis is to increase immunity in cows. Stalls and milking equipment must be kept clean, and bedding must be changed daily. If there are many animals on the farm, it is important to comply with the standards for the area of their keeping and avoid overcrowding.In the summer, animals should stay in the sun for several hours a day.
Treating udder warts in cows requires patience. If there is no lasting effect from one combination of agents, they switch to others. In young cows after calving, spontaneous healing is possible.