Some infectious diseases in cows can be transmitted to humans. The danger of cowpox is that the disease harms cows, reduces productivity and makes production less profitable. Let's consider the causes of the disease, characteristic symptoms, features of cowpox treatment and preventive measures that should prevent the occurrence of infection on the farm.
- What kind of disease is this
- Causes of occurrence in cattle
- Symptoms of cowpox
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Features of treatment of the disease
- Medicinal methods of control
- Folk remedies and recipes
- Epidemic prevention
- Is it possible to drink milk from sick animals?
- Smallpox vaccination
- Other preventive measures
What kind of disease is this
Cowpox is a viral disease caused by a virus from the Orthopoxvirus genus. The pathogen can be transmitted from animals to humans. In cows, manifestations of smallpox are observed only on the udder. The disease appears during the stall period or in the spring, often in young dairy cows and in recently calved cows.
Smallpox in cows occurs acutely, subacutely and chronically. The acute form lasts 3 weeks and occurs with obvious symptoms. Subacute lasts from 21 to 25 days, characteristic symptoms such as rash may not be observed. Recovery may occur without treatment after 3 weeks if the infection is mild.
Calves are most seriously affected by smallpox, since their immune system is still imperfect and cannot resist infection. If calves are left untreated, pathogens enter the respiratory and digestive systems, causing gastroenteritis and bronchopneumonia. In severe cases, the death of young animals may occur. Therefore, if suspicious symptoms appear, animals should be examined by a veterinarian.
Causes of occurrence in cattle
The main carriers of the pathogen are sick animals. Viruses are transmitted through secretions from the nose and mouth that land on the skin. A weakened immune system due to a lack of vitamins in winter contributes to the development of the disease. The virus can be carried by blood-sucking insects and rodents. The virus especially often enters the cow’s body through microdamages in the skin.
Smallpox spreads massively in the herd due to unfavorable conditions - cold or heat, high indoor humidity, dirt, lack of fresh air.Unbalanced feeding and lack of exercise also contribute to decreased immunity in cows. These factors, together or separately, lead to a weakening of the protective functions of the animal’s body.
Symptoms of cowpox
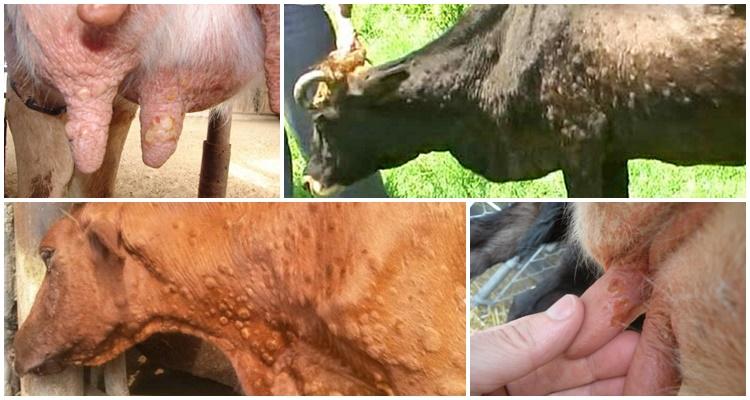
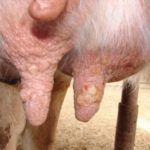
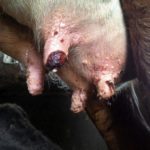
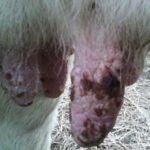
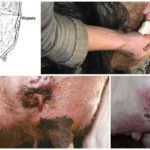
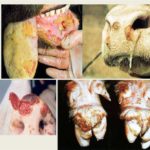
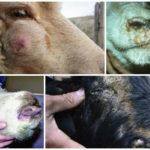
The incubation period for cowpox lasts 3-9 days, after which time symptoms characteristic of the infection begin to appear. On the first day, small reddened spots appear on the udder, in the mouth and on the nasal mucosa. Over the next 2-3 days, compacted nodules form in place of the roseola.
Over another 3-4 days, the nodules turn into fluid-filled blisters. On days 10-12 they turn into purulent vesicles. After 2 weeks of symptoms developing, they become covered with dark crusts that become cracked and bleed. In appearance, the rash on the udder of cattle is round or slightly elongated, with a pronounced center and clearly defined.
Other symptoms of infection with the virus: loss of appetite, depression, increased temperature, fever, aggressiveness, decreased milk yield. In animals, the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose are swollen, the lymph nodes are inflamed. Since touching the inflamed areas of the udder causes pain to the cow, during milking she tries to keep people away from her. The gait may change as the animal spreads its legs to avoid touching the udder.
Diagnosis of the disease
The rash on the udder due to smallpox has a characteristic appearance, so if you have some experience, it is not difficult to identify it. However, to exclude the possibility of other infections, the symptoms of which are also rashes, tests are necessary.
To do this, take a blood sample from a sick animal, the contents of the vesicles, and smears from the inflamed areas.
The material is examined in a laboratory, where the presence of the virus will be confirmed or refuted.If the diagnosis of smallpox is confirmed, the degree of development of the disease is also determined. After confirmation of the disease, sick individuals are immediately separated from healthy ones.
Features of treatment of the disease
There are no special drugs that would destroy the smallpox virus in cows. Treatment is limited to maintenance therapy.
Medicinal methods of control
Animals are given antibiotics if there are secondary infections. They cannot destroy the virus. So that the cow’s body can fight the virus, they are given lactic acid and the drug Vetom 11. The dosage and treatment regimen are prescribed by a veterinarian and based on the severity of the disease.
Ulcers on the udder are treated with a 3% solution of Chloramine, potassium iodide and borax. The use of the products stops the further spread of the rash on the udder. Inflamed areas are lubricated with Vaseline, zinc or ichthyol ointment. The products dry out the rash and speed up regenerative processes. Ointments based on glycerin and vegetable oils soften the crusts to prevent them from cracking and bleeding. The nasopharynx of cows is washed with a 3% solution of boric acid. During the treatment period, cows are fed with liquid mixtures, then given wet mash. Drink plenty of water. Saturating the body with fluid promotes a speedy recovery.
Folk remedies and recipes
In addition to the main therapy, folk remedies are also used comprehensively. These include feeding blackberry leaves, elderberry leaf, tops and garlic cloves to cows. The udder and other areas affected by pockmarks are treated 2 times a day with a herbal decoction of elderberry and sorrel.
Folk remedies are too weak against the smallpox virus, so you should not rely only on their effect.Medicines should be the main method of treatment.
Epidemic prevention
When an infection occurs on a farm, it is necessary to separate sick animals from healthy ones and conduct a thorough examination of the entire livestock. Also disinfect the barn, stalls, and equipment with formaldehyde (2%), caustic soda (4%), and calcium oxide (20%). Feeders and milking equipment - sodium hypochlorite (1 to 100).
The place where the manure is stored must be disinfected with chlorine, and the litter must be burned. Animals can be returned from quarantine only 3 weeks after recovery.
Is it possible to drink milk from sick animals?
Fresh, unprocessed milk from sick cows cannot be drunk. But it is believed that it can be consumed after pasteurization or boiling. Milk should be milked as usual so that there is no stagnation and mastitis does not develop. If it is difficult to do this manually, you need to use a catheter. Milked milk can be given to calves, but only after preliminary boiling.
Smallpox vaccination
Cows are given two types of vaccinations - against a strain of smallpox and against a mixed type of smallpox. In the first case, vaccination allows the animal to acquire lifelong immunity against infection, in the second, it does not last forever, only for a few months, then re-vaccination is required.
Other preventive measures
When purchasing new animals, they are first quarantined for a month. If no symptoms appear during this time, the cows can be transferred to the general herd. It is necessary to regularly disinfect stalls and equipment and do daily cleaning.
In spring and autumn, whitewash the walls of the room with lime and treat them against insects and rodents.Keep drinking bowls clean and avoid stagnation of water, in which the smallpox virus multiplies favorably. The barn and stalls should be dry, warm, spacious; any discomfort that poor living conditions cause in the animal increases the risk of disease. Feed animals with complete food to avoid hypovitaminosis.
If detected early, smallpox in cows can be cured, and the animals will be healthy again and return to the productive process. Treatment must be prescribed by a veterinarian and carried out under his supervision. The use of medications is mandatory; folk remedies do not have any noticeable effect. Recovered cows acquire lifelong immunity.