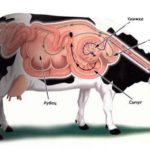
Tympany is a serious disease of the gastrointestinal tract of cows, which occurs due to increased accumulation of gases in the stomach or disruption of their discharge. Gases in the stomach cause discomfort to animals and can even lead to death. Let's consider the causes, symptoms and stages of rumen tympany in cows, how the disease can be diagnosed, methods of therapy and prevention at home.
Causes of tympania
Rumen bloating in ruminants occurs if they eat a lot of easily fermented feed. This could be clover, legumes, cereals, corn leaves, beet tops, cabbage.Grass wet from rain or dew is especially dangerous.
If a cow is hungry, she can overeat any feed, and this will also make her bloated. Breaks in feeding, prolonged eating of the same food, and lack of roughage in the diet are dangerous. The cows are blowing and because they move little, they rarely take walks or only for short periods of time and do not graze in the pasture.
Chronic tympany in cattle develops as a complication that occurs after blockage of the esophagus or esophagus foreign objects, hypotension of the proventriculus, food poisoning and substance poisoning, traumatic reticuloperitonitis.
Symptoms and types
Tympania can be acute or chronic; each stage is characterized by symptoms. In case of acute disease, the cow or calf requires immediate assistance.
Acute
At this stage of tympania, swelling develops quickly; 1 hour may be enough. If a cow is bloated, her belly swells, this becomes noticeable as it becomes rounder and increases in size. The animal behaves restlessly, excitedly, gets up and lies down alternately, wags its tail, hums and moans. These are signs that he has a stomach ache.
When inflammation occurs, the cow stops chewing cud, has no appetite, and salivation increases. First there is a belching, then it disappears.
A characteristic sign of acute tympany is that the animal’s left side is swollen; if you put your hand on the stomach, you can feel that its walls are tense; when you tap, a characteristic sound is heard. The body temperature is initially normal, then rises to subfebrile.If the cow is not helped, the bloating will continue, and within 2-3 hours symptoms such as heart failure, shortness of breath, and cyanosis of the mucous membranes may develop. This condition often ends in the death of the animal.
Chronic
Periodic tympany begins due to feeding disturbances. The symptoms of chronic bloating are the same, but less pronounced. Animals do not refuse food, but their chewing gum is weakened, peristalsis is sluggish, feces are dry and dense, and constipation is noted. If a cow is bloated, she loses weight, temporarily loses productivity, and her breeding and economic value decreases.
Abdominal bloating in a calf is observed in weak individuals during the transition from milk to plant foods. Often in those who have previously suffered a serious illness or who eat low-quality hay, food poor in mineral elements and vitamins. With severe bloating, the animal does not stand up and does not eat.
Diagnostics
Tympany is diagnosed based on what the animal ate before the bloat began (usually food that can easily ferment) and characteristic signs. Symptoms of foamy tympany, which develops after excessive consumption of raw grass, develop more slowly than with gas tympany.
Therefore, when switching from stall housing to pasture housing, when distributing fresh, not withered grass, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the animals.
Treatment methods
They depend on the rate of development of gas formation, the duration of the process and the condition of the animal. In some cases, tympany can be treated with medication, while in others, surgical intervention is required (much less often).
Ambulance
In case of acute tympany in a cow, it is necessary to carry out treatment without delay; if you delay, the animal’s condition will sharply worsen. Then the therapy will be longer, the cattle will recover longer. You can stop the formation of gases by using special drugs, for example, Timpanol. They need to be given as soon as possible, they act quickly. Plant and synthetic components prevent further formation of gases, destroy already formed bubbles and remove them from the body. The drugs have a ruminator and antiseptic effect, increase secretion in the gastrointestinal tract and peristalsis, and relax the sphincters of the proventriculus. For dairy calves, the volume of milk is reduced by half; instead of water, a 0.9% solution of table salt is used.
To stimulate the rumen, massage the abdomen, pour cold water over it, and put a rope dipped in turpentine over the mouth to induce belching. The cow is not fed until it is cured, after which it is given hay and water. It is necessary to completely exclude those products from which the animal suffered.
Probing
To release gases from the rumen, cows are probed. A large-diameter probe is inserted into the esophagus, then the scar is massaged. Gases exit through the probe (for this, the front of the animal must be raised higher than the back).
With foamy tympania in animals, gases may not come out, so you need to pour in antifoaming agents through the probe - alcohol solutions based on menthol or thymol (2 g per 0.4-0.5 l of alcohol). Or special drugs with a similar effect. For bloating in a bull or heifer, you can use the following products: creolin, ichthyol or iodine (15-20 g per 1 liter of water), turpentine (10-15 ml per 0.3-0.4 liter of alcohol).After the gases are released, the rumen is washed with water - 5-10 liters of water are introduced through the probe, gradually, in small portions.
Surgical intervention
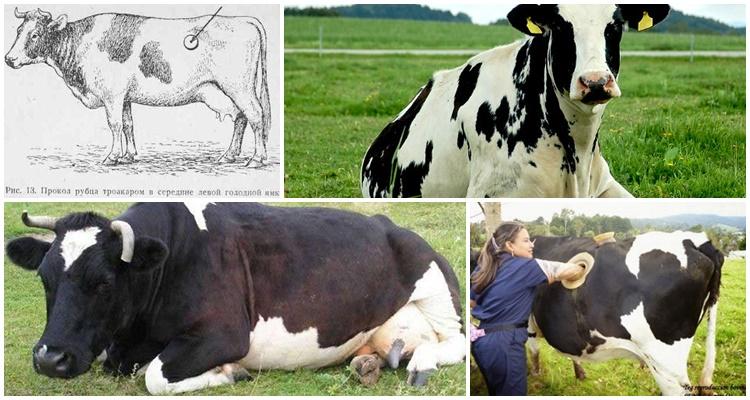
When other methods do not help, the cow still becomes bloated, the only thing left is to resort to surgery. You need to treat like this: fix the sick animal in a standing position. To pierce the scar, a tool called a trocar is used. They are punctured in a special place - on the left side, in the center of the hungry fossa. During the development of the disease, when the abdomen is swollen, it is difficult to determine the exact location, so the hole is made on a line that runs from the lower edge of the macular to the last rib. In its middle there will be a hungry hole.
Before piercing, the wool is cut off at the selected location and treated with alcohol. The tool is applied to the skin, the end should be directed towards the elbow joint of the opposite leg. The peritoneum and scar are pierced with a sharp movement. The stylet is removed, the sleeve remains in the hole, and gases escape through it. From time to time the hole needs to be closed and then opened again.
Through the trocar, you can administer Timpanol, lactic acid and other drugs aimed at restoring the functioning of the scar. After this, the trocar is removed, the wound is treated with iodine and a bandage is applied.
Traditional methods
At home, if there are no drugs, you can help the cow by giving her 0.4 liters of vodka diluted in the same volume with water (additionally 100 ml of turpentine). Give hellebore tincture (20 ml). Infusions of valerian, caraway, dill, chamomile, and ammonia solution have a mild effect. You can pour cold water on the cow and be sure to force her to walk, so that the stomachs are massaged in this way.
Prevention from tympany
You should not graze cattle on wet or frozen grass, or give water immediately after eating green food, especially one that can easily ferment. You should not overfeed animals with any food, even dry food. To prevent them from eating it greedily, you need to feed them in accordance with the regime and give them a sufficient amount of food.
Do not use rotten root crops, moldy grain, old hay and straw for feeding. Walk cows every day so they can move, thereby stimulating normal digestive processes.
Rumen tympany is a serious digestive disorder in cattle. Often occurs due to errors in feeding livestock. A common cause is eating damp or wet grass. Due to fermentation, gases accumulate in the rumen, which must be eliminated using drugs or special methods. Without treatment, the animal will experience severe suffering and may die.