Gas gangrene in animals is a phenomenon that farmers encounter everywhere. Since malignant acute edema is sporadic in nature, the economic damage from the disease is small. Cattle are susceptible to the diseaseTherefore, it is important to follow the rules of antisepsis and asepsis when providing obstetric care or performing surgical interventions.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
The disease occurs in an acute form and can affect both cattle and humans. A group of microorganisms belonging to the genus Clostridium is the causative agent of disease in animals.The environment for the existence of pathogenic microorganisms is the normal flora of the intestinal tract of cattle and the upper layers of the soil.
The main causes of infection are damage to the skin and mucous membrane during grazing on stubble, during childbirth or castration. The rapid progression of the disease is facilitated by the ingress of manure and soil into the wounds. Cases of malignant edema are often observed in cows after calving, when the placenta is retained and non-sterile instruments are used to separate it.
Diagnostic rules
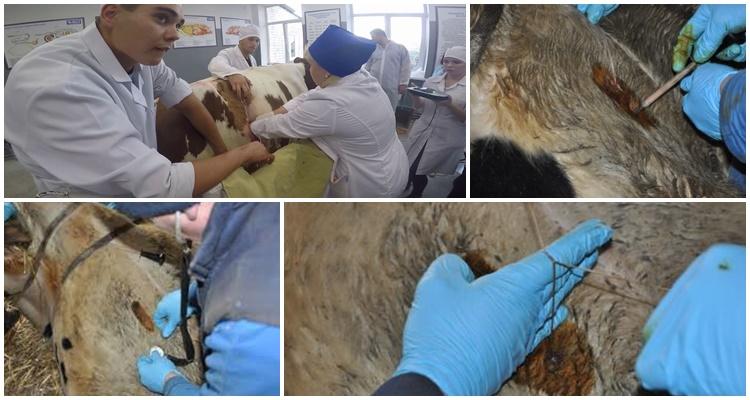
Painful swelling quickly forms at the wound site. If the wound site is opened, a foamy liquid of different shades will be released from the wound (from deep brown to red or even transparent). In the case of maternity malignant edema in a cow, the pelvic muscles, perineal area and genitals are affected. Thickening of the mucous membranes of the uterus and vagina is observed. The organs are covered with necrotic masses with an unpleasant, pungent odor.
The duration of the incubation period for malignant edema in an animal depends on a number of factors: the level of immunity of the cattle individual, the number and type of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the disease may manifest itself after several hours or days. To exclude diseases with similar symptoms (carbuncle, anthrax), it is recommended to make a final diagnosis based on bacteriological studies.
Treatment methods for malignant edema
Methods of treating animals - surgical intervention and elimination of general intoxication through medications:
- The essence of the surgical method: a wide and deep tissue dissection is made to provide air access to the affected organs or areas (oxygen prevents the proliferation of anaerobes). Necrotic tissue is removed. The treated areas are irrigated with hydrogen peroxide, a solution of potassium permanganate, and antiseptic medications;
- To combat intoxication and inflammatory processes during malignant edema in animals, antimicrobial drugs and antibiotics are used (sulfonamides, Tetracycline, Aspirin).
It should be noted that standard treatment methods are not always effective. The best treatment results are demonstrated by intravenous administration of ozonated sodium chloride.
Possible consequences
The transience of the disease depends on the location of the source of infection and the type of pathogen. In animals, tissue breakdown from the skin to the bones, pulmonary edema, degeneration of the heart muscle and liver, enlargement of the lymph nodes and hemorrhages in them often occur.
Animals that are found to have malignant edema should not be allowed to be slaughtered. Such cattle are pre-treated.
However, it is recommended to carry out a sanitary assessment of meat obtained from the slaughter of such animals. Individual organs affected by edema must be destroyed. The remaining parts of the carcass are boiled for a long time (as quickly as possible). If extensive lesions are detected, the carcass is disposed of. Sometimes it is allowed to use skins treated with disinfectants in industry.
Prevention of the problem
Animals suffering from malignant edema must be isolated. General quarantine is not introduced, but the premises where sick livestock were kept are cleaned and disinfected (with bleach, 5% formaldehyde solution, 3% sodium hydroxide solution).Infected manure is also burned.
Compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements during calving is the main measure for the prevention of malignant maternity edema. If the farm is located in an unfavorable area, cows are injected with a massive polyvalent antitoxic serum before calving.
Malignant edema is a rapidly developing disease. Therefore, a successful treatment outcome is determined by the timeliness of assistance. It is important to thoroughly clean the affected areas of the body and properly treat wounds with antiseptics. Drinking plenty of fluids and a nutritious diet will help the animals recover quickly.