It is possible to determine in a timely manner that chickens have Marek's disease by regularly examining the birds. To do this, chickens should often go for walks, since often the first symptoms are mild. The disease can occur in stages and affect the entire chicken coop in a short time. Symptoms may vary depending on the age of the bird.
- General information about the disease
- Causes of Marek's disease
- Routes of infection
- How is the incubation period?
- Symptoms of the disease
- Acute form
- Classic shape
- Diagnosis of the problem
- Therapeutic measures
- In chickens
- In adult chickens
- In broilers
- Vaccination against disease
- Is it possible to eat meat and eggs from infected birds?
- General preventive measures
- Conclusion
General information about the disease
Infection with the disease occurs as a result of activation of the virus in the bird’s body. The virus most often affects nerve cells and internal organs of laying hens. When examining the affected areas, you can notice swelling of the soft tissues and the presence of formations.
The types of disease are distinguished:
- Neural - this type affects nerve cells. As a result, paralysis occurs in chickens.
- Ocular - the virus affects the visual organs. The bird begins to see poorly and as a result goes blind.
- Visceral - internal organs are affected. Soft tissues are destroyed, resulting in organs not performing their functions.
Often the disease appears in complex forms that lead to the death of laying hens. In order to promptly identify the type of disease, it is necessary to consult a veterinarian.
Causes of Marek's disease
The disease occurs as a result of improper care of the chicken coop and birds. The virus spreads through the air and can remain indoors. The disease can be transmitted by pests, flies, beetles or food. The cause of the disease is reduced immunity. More often, the disease affects chicks up to 2 weeks old. The reason is unsanitary conditions and a poorly treated incubator. However, infection of adults can occur.
Routes of infection
Disease carriers can be sick birds. The virus can spread through airborne droplets over long distances. The virus can also be transmitted through droppings, food and feathers.
The carrier of the disease is cleaning equipment. The virus also persists on feeders and drinkers. Once infected, the chicken does not show symptoms, so further damage to the coop occurs.
Important.After infection, the bird does not show any symptoms for 10-15 days. The virus can remain in an inactive form and progress rapidly after a decrease in immunity.
How is the incubation period?
If young individuals are infected, the virus adapts in the body within 2 weeks. After this period, the chicken can infect other chickens without noticeable symptoms of the disease. The acute period of infection occurs in the first 5 weeks after the virus enters the bird’s body.
Often the disease begins to manifest itself only in the 5th week after infection.
Adult chickens have a positive incubation period. The first signs of the disease are noticeable only after 6-7 weeks. The acute form of the virus affects the entire chicken coop within 2 days.
Symptoms of the disease
Marek's disease can have symptoms depending on the developmental stage and age of the bird. You can notice the first signs of the disease during daily walks or after carefully monitoring the laying hens.
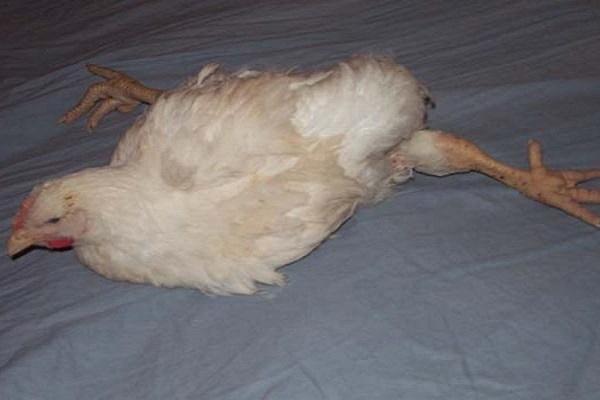
Acute form
This type of viral infection may resemble other types of diseases. Has the following symptoms:
- chickens’ limbs do not move or are subject to paralysis;
- the chicken moves poorly, coordination of movements is often impaired;
- wheezing and difficulty breathing;
- lack of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting;
- the wings are spread out and not symmetrically positioned;
- loss of vision.
This type may present with additional symptoms that appear in each case of infection.
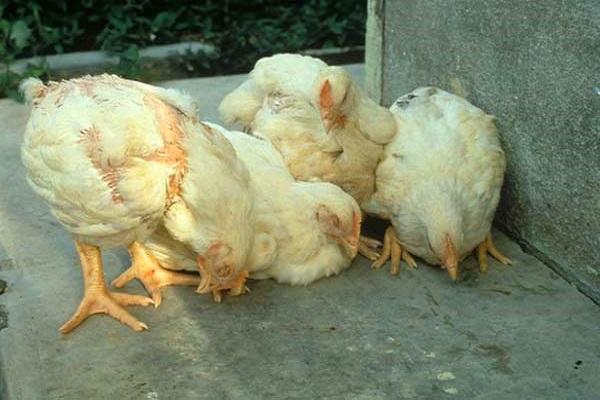
Classic shape
This species is often ignored by poultry farmers. The disease manifests itself with mild symptoms and is often confused with other types of infection. Symptoms of classic Marek's pathology are as follows:
- the chicken is weak and lies down most of the day;
- poorly coordinated in movement;
- limbs are paralyzed;
- wings droop.
You can also often notice a lack of appetite and the appearance of fleas. Such additional symptoms appear as a result of weakened immunity.
Diagnosis of the problem
In order to identify the stage of the disease, you need to contact a veterinarian who will conduct a diagnosis. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- external examination of the bird during a walk;
- inspection of poultry under quarantine conditions;
- analysis of feathers of sick birds;
- bacteriological culture study;
- detection of the virus by sampling.
Healthy and sick laying hens are examined. If the hen dies, it is necessary to do an examination of the internal organs.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment methods depend on the age of the bird. Sick birds in acute form are not treated, since the virus has already spread throughout the body and affected all internal organs.
In chickens
If the disease develops in chickens before the 2nd week, it is not advisable to carry out treatment. Most often, such chicks do not have immunity. In rare cases, a special vaccine may be used.
In adult chickens
Treatment in adults should be carried out at the first stages of the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. For treatment, special antiviral drugs are used, for example Acyclovir. The action of the drug is aimed at suppressing the virus and blocking its further spread throughout the bird’s body. In order for the bird to survive the negative effects of the drug, it is necessary to use additional probiotics. The action of probiotics is aimed at protecting the stomach lining from destruction. The duration of treatment is at least 5 days.
Important. When the first symptoms of paralysis appear, treatment is not carried out. The bird dies.
In broilers
Broilers are a meat breed of chicken. The use of special drugs does not give the desired result. Since birds raised in artificial conditions, as a rule, do not have immunity to diseases and viruses. Therefore, on the third day after hatching, broilers are recommended to undergo a special vaccination, which will reduce the risk of the disease.
Once infected, the birds die and can infect healthy individuals within a week. After each batch of chicks, the incubator and surrounding areas must be thoroughly disinfected.
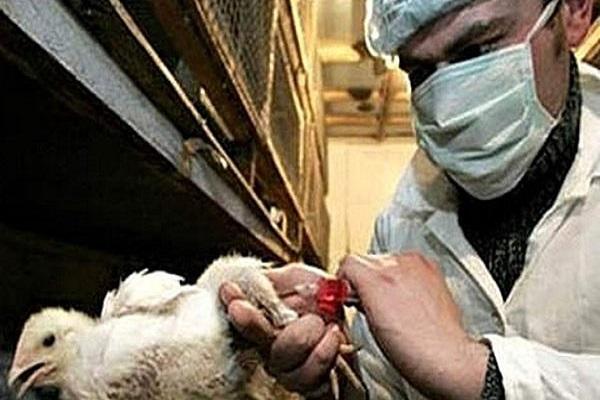
Vaccination against disease
The use of a special vaccine does not give a 100% result, but the risk of the virus is reduced. A live virus is used for vaccination, which promotes the development of immunity. Once administered, the vaccine begins to produce antibodies that suppress the virus after infection. The following form can be used:
- M 22/72;
- "Interve".
The vaccine is purchased at a veterinary pharmacy. The drug is stored in a cool place. Before use, it is necessary to check the expiration date and carry out a test injection into the chicken.
Is it possible to eat meat and eggs from infected birds?
Marek's virus is not dangerous to human health. It should also be noted that in adults, symptoms appear late. Therefore, people often eat eggs laid by affected hens, but veterinarians do not recommend eating contaminated meat and eggs. Since pathology often provokes the appearance of other infectious diseases that can negatively affect human health.
It is prohibited to use meat products that have a yellow tint or signs of muscle fiber damage.
General preventive measures
The virus is difficult to treat, so veterinarians recommend taking preventative measures that will keep birds healthy. Among the preventive measures it is necessary to highlight:
- When purchasing young animals, carefully inspect the chicks. Do not buy chicks from unverified organizations.
- Use a veterinary first aid kit that contains medications to prevent the occurrence of viral diseases from the first days of life in chicks.
- Vaccinate chickens.
- Eliminate sick chickens in a timely manner.
- Clean the chicken coop and drinking bowls regularly.
- Promptly remove droppings that can act as a carrier of diseases.
- The chicken coop should have a flat floor without cracks or holes. This prevents pests and insects from entering.
- After death, the affected chicken must be removed from the chicken coop within 24 hours and the premises must be treated.
- Strengthen the immunity of birds with the help of vitamins and minerals that are added to food.
- Treat equipment used during the cleaning process with antiseptics.
- Walk chickens regularly to identify infected individuals.
If an individual appears that has suspicious symptoms, it is necessary to separate the chicken from the livestock. Observe under quarantine conditions until the type of infection is fully identified.
Conclusion
Marek's virus can lead to the death of birds in a chicken coop in a short period of time. Both adult and young chickens can be infected; the virus also often affects ducks and geese. When the first symptoms of the virus are detected, the bird must be isolated and treatment measures taken. Birds that were treated in the early stages of the virus are cured, but such individuals lose immunity and are susceptible to other types of infection. Therefore, veterinarians recommend taking timely preventive measures against the disease.