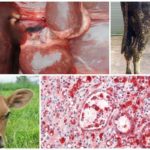
Coccidiosis in domestic chickens is a contagious disease caused by protozoan single-celled parasites. Chickens have their own types of coccidia. Due to the developing inflammatory process, their digestive function is disrupted and nutrients are not absorbed. As a result, the bird dies from exhaustion and associated bacterial and viral infections. The danger of infection is the same for chickens of any age, but is fatal for chickens.
- What is coccidiosis
- Causes of disease in chickens
- Main symptoms of the disease
- Diagnosis of the disease
- How to deal with disease in birds
- Coccidiostatics
- Antibiotics
- Probiotics in complex treatment
- Folk remedies
- Consequences
- What to do to prevent the spread of infection in the chicken coop
- Preventive actions
- Is it possible to eat meat from chickens with coccidiosis?
What is coccidiosis
Chicken coccidia are eimeria or parasites that require a host and an external environment for their full biological development.
Infection occurs through ingestion of coccidia eggs (oocysts). Depending on the type of pathogen, chickens are affected in the large or small intestine. In a favorable environment, the oocyst shell is destroyed, and sporozoites (motile single-celled forms) invade the intestinal epithelium.
Further transformation of the parasite includes several stages:
- Schizogony:
- transformation into a multinucleated trophozoite cell;
- the first division (schizont) into mononuclear merozoite cells, with the destruction of the host cell;
- release of merozoites into the intestinal lumen;
- re-penetration into the epithelial layer;
- second schizont;
- repetition of the cycle;
- end of asexual reproduction.
- Gametogony:
- on the 3rd, 4th schizont, germ cells are formed (female - macrogametocide and male - microgametocide);
- as a result of their fusion, a zygote develops;
- after the formation of the shell is completed, it turns into an oocyst and is released with feces into the external environment.
- Sporogony:
- under favorable conditions of humidity and temperature, the oocysts “mature” and divide into sporoblasts;
- sporoblasts become covered with a membrane;
- become spores that can infect birds.
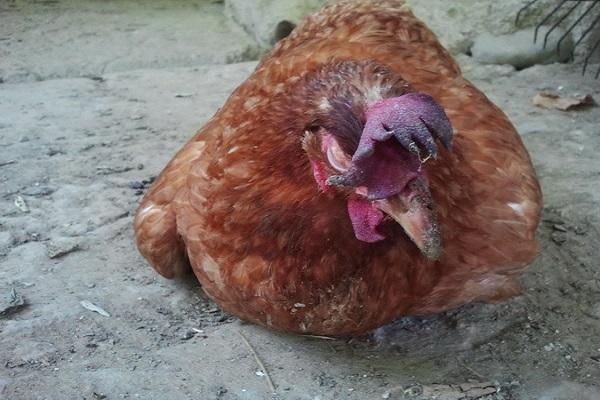
In adult birds, coccidiosis occurs in a mild form, but can become chronic. High mortality is observed in sick chickens under 8 weeks of age: 80-100%. This is explained by the weakness of the immune system of young animals.
Causes of disease in chickens
Coccidia eggs retain their invasive properties for 12 months. The source of infection can be:
- Carriers of infection:
- birds sick in the chronic stage;
- recently ill chickens.
- Failure to comply with sanitary standards for keeping young animals:
- litter, feeders, drinking bowls contaminated with feces;
- inventory;
- workwear;
- increased temperature and humidity.
- Food, water, and soil contaminated with oocysts for free range.
The likelihood of infection is highest when sick chickens are carriers of the infection.
Main symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of the pathological process depend on the stage of development of coccidia and the age of the bird.
Pre-latent period. It goes unnoticed. Oocysts turn into eimeria. The first signs of coccidiosis appear at 6-21 days.
Initial phase (introduction and reproduction of unicellular forms). The chickens' health deteriorates sharply due to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. The duration of the first schizont is 5 days. In chickens older than 2 months or with good immunity, the disease occurs in a mild form or becomes chronic.
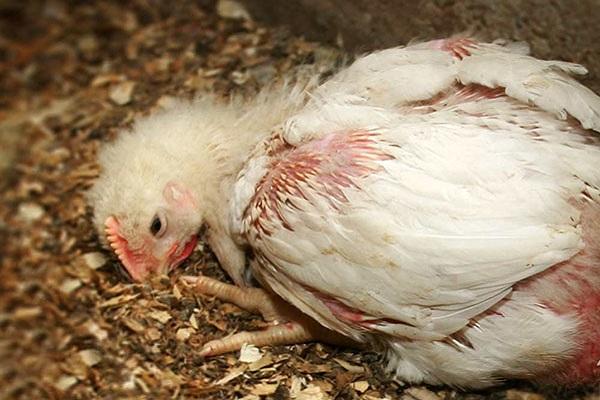
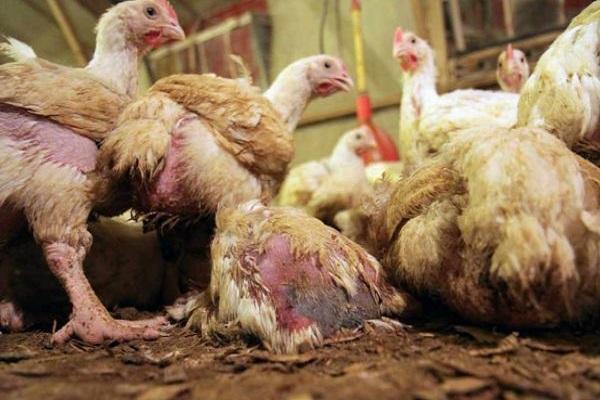
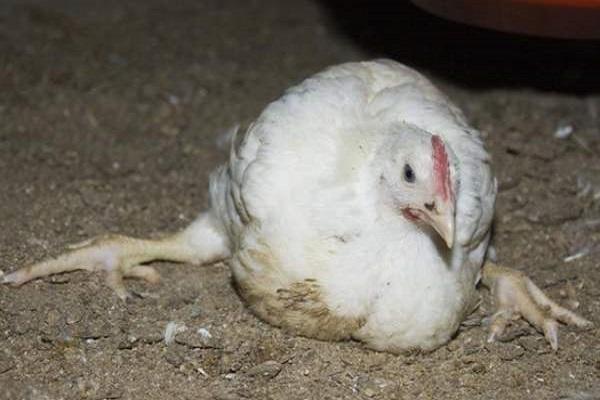
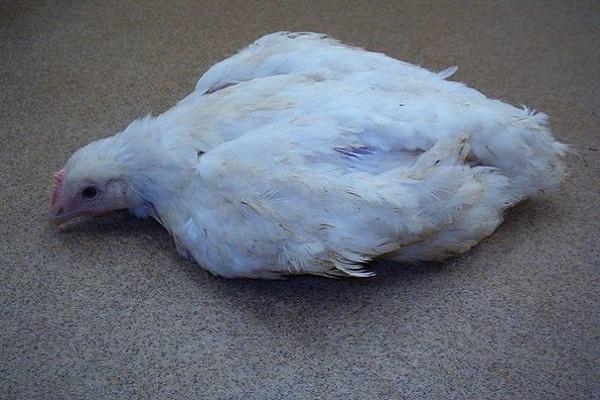
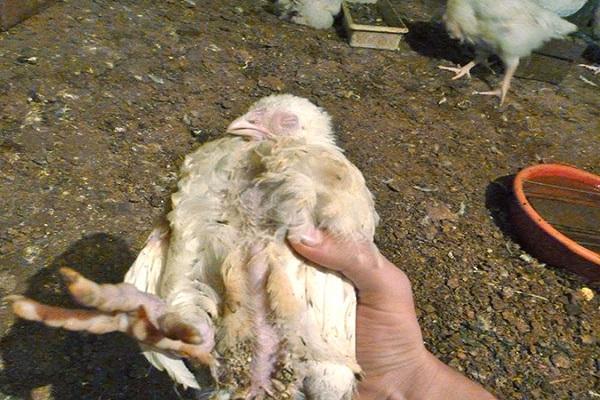
In chickens and weakened young chickens, the symptoms of coccidiosis become more pronounced. The intestines stop working. Blood appears in the stool. The bird loses weight, becomes lethargic, and mostly sits. The second clinical period lasts 7 days.
Against the background of a sharp loss of strength and decreased immunity, staphylococcal and streptococcal infections and E. coli begin to develop. Sick chickens show signs of anemia: the earrings and comb become pale pink. The nervous system begins to suffer, which is expressed in lameness and paresis of the wings. The feathers are ruffled, the crop droops. Frequent stools turn into diarrhea with green, red-brown stool.At this stage, the death of chickens and young chickens may occur.
If the body's immune forces and medications have stopped asexual reproduction, then a slow recovery begins. The stool is normalized, blood in the stool disappears, and hematopoiesis is restored. The death of a bird at this stage can be caused by dystrophic changes. Coccidia spores are present in the stool.
Recovery ends with the restoration of all body functions. For 1-4 weeks, recovered chickens are a source of Eimeria eggs.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of coccidiosis is made based on a comparison of 4 factors:
- sanitary conditions for keeping poultry;
- symptoms of the disease;
- results of pathological examination of the intestine;
- data from laboratory tests of stool for the presence of oocysts.
Based on the information obtained, the type of protozoa and the degree of infection are identified.
How to deal with disease in birds
Treatment for coccidiosis involves blocking the development of parasites or killing them.
Coccidiostatics
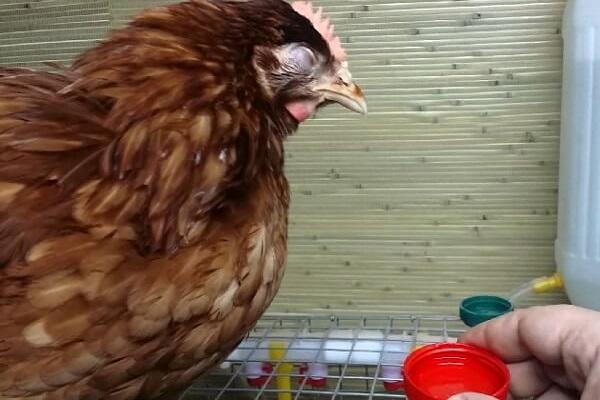
Coccidiostatic drugs affect the formation in the intestine of enzymes and vitamins necessary for the formation of trophozoites and schizonts. A sick chicken is treated by introducing coccidiostats into food or drink.
Medicines used for coccidiosis:
- Decox;
- Coccidin;
- Amprolium;
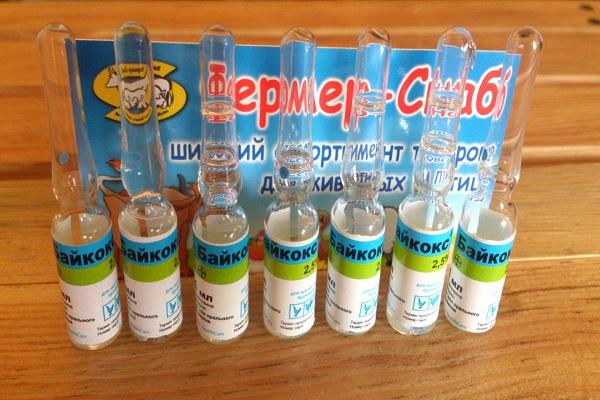
- Baycox;
- Sacox.
The doses used and duration of treatment are indicated in the instructions for use. For example, Amprolium is mixed with feed in a ratio of 2.5 grams per 10 kilograms and given to chickens for a week. Baycox is added to drinking water as a 2.5% solution: 10 milliliters per 10 liters. Treatment lasts 2 days. In case of severe symptoms of coccidiosis, the procedure is repeated after 5 days.
Antibiotics
To destroy parasites, bacteriostatic antimicrobial agents are used. The mechanism of influence is to replace the amino acids necessary for the development of coccidia with chemical analogues. As a result, the formation of nucleic acids is disrupted, and the pathogen cell cannot function and reproduce.
Antibacterial agents used to treat coccidiosis in chickens and young chickens: nitrofurans, sulfalazoles. Features of antibiotic treatment: increase in vitamin B1 and A in the feed; To avoid the emergence of resistant strains of coccidia, one medicine should not be used for more than a year.
Some chicken breeders consider “human” antibiotics to be more effective against coccidiosis than veterinary drugs. The five-day course includes taking Levomycetin, Erythromycin, Metronidazole in combination with the Trivit vitamin complex. In a liter of water, mix 1 tablet of antibiotic and ½ tablet of Trivita. On days 4 and 5, mix 2 tablets of antibiotics (Levomycetin + Erythromycin; Erythromycin + Metronidazole) and ½ tablet of Trivita.
Probiotics in complex treatment
Probiotics are preparations containing live bacteria that restore intestinal microflora after treatment with antibiotics. They are useful for poultry at any age, as they strengthen the immune system, promote growth, weight gain, and egg production.
For chickens, laying hens, and boilers, veterinarians recommend adding OLIN, Bioximin Chicken, and Chiktonik food to the drink.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicinal methods against coccidiosis are ineffective. Only modern medications can help against the pathogen, without which the mortality rate of young animals will be 100%.
Consequences
Untimely veterinary care for coccidiosis will lead to the death of chicks and young chickens.
In adult birds, the disease occurs in the form of poisoning, with minor disturbances in appetite and bowel movements. The pathogen dies under the influence of the body's immune forces. But such individuals remain carriers of oocysts released into the external environment for 2 months.
Recovery of young animals after an acute form of coccidiosis occurs slowly. In advanced forms of the disease, the likelihood of complete recovery is very low. In such cases, breeders prefer to destroy sick chickens.
What to do to prevent the spread of infection in the chicken coop
It is completely impossible to get rid of oocysts due to resistance to disinfectants based on phenol, manganese, and ammonia. Keeping chickens in cages for up to 8-9 weeks protects them from infection by spores, which can occur when kept outdoors. Periodic burning of cells helps achieve sterility.
The birds in the chicken coop should have enough space to roam, plenty of light and air. When kept in an enclosure, the area must be cleaned of feces weekly. Feeders are emptied after each meal.
Preventive actions
A preventive measure against an outbreak of coccidiosis is vaccination of livestock, including eggs. If 1-2 sick birds are detected, veterinary drugs are introduced into the food and drink in prophylactic doses.
Popular vaccines against coccidiosis:
- Cocciprodine (except for laying hens);
- Baycox;
- Avikoks (chickens up to 9 days of age).
Cocciprodine, Baycox is added to water (10 milliliters per 10 liters) for 2 days. Avicox is given once in food or drink.
Is it possible to eat meat from chickens with coccidiosis?
Oocysts may persist after the chicken has recovered. Avian Eimeria do not pose a threat to humans. But broilers are slaughtered 7 days after cessation of treatment. Heat treatment and freezing kill viable spores. During early slaughter, carcasses are sent for processing into meat and bone meal.
When coccidiosis is treated with antibiotics, chicken meat and eggs are not suitable for food for 14 days after treatment.