Leptospirosis infection is a natural focal disease and often affects both farm and domestic animals. At the first signs of leptospirosis in horses, it is necessary to separate healthy individuals from sick ones. Quarantine is introduced, isolated patients are treated. The release of bacteria from the body can last for years (depending on the form of the disease). Therefore, healthy horses must be vaccinated.
Description of the disease
One of the acute infectious diseases is leptospirosis (the causative agent is the Leptospira bacterium). Stagnant reservoirs, rivers, lakes, and moist soil are suitable environments for bacteria to multiply. Leptospira are not resistant to disinfectants. Recovered and sick horses act as a source of leptospirosis. Spread options - contact, through feed, water. The incubation period lasts from 2-5 to 12-20 days. Characteristics of the infection - the liver, kidneys, muscles, capillaries are affected, intoxication and fever appear.
Danger to horses
Leptospirosis affects animals in all regions. The infection progresses in a severe form, and in an advanced state there is a need for resuscitation. Consequences of the occurrence and spread of leptospirosis:
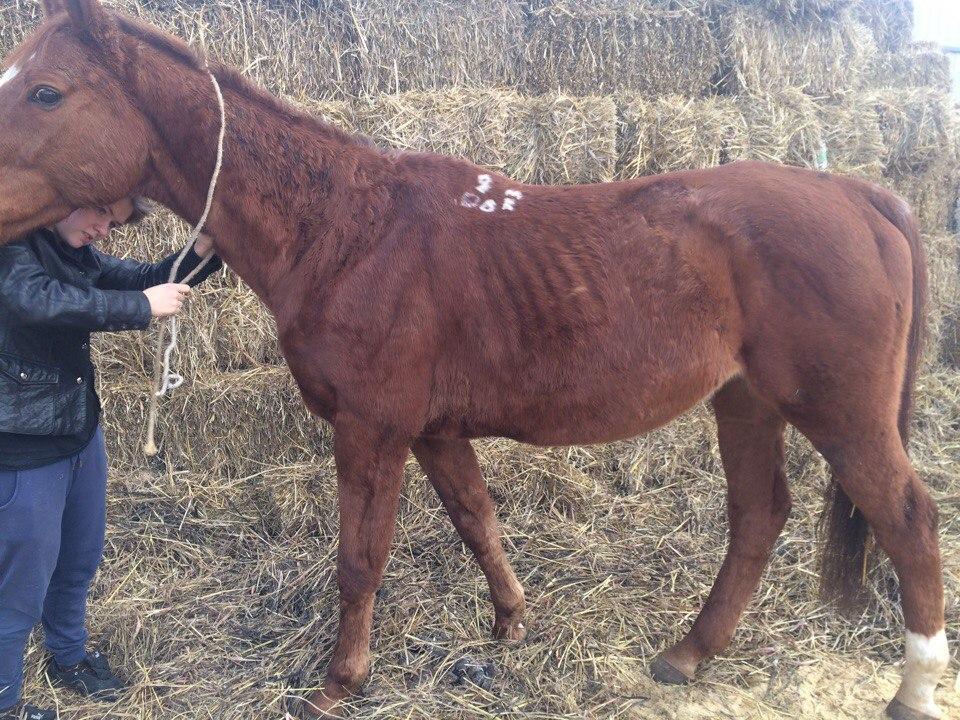
- significant weight loss in animals (17-28%);
- slower growth of foals;
- loss of horse performance.
Severe disease often leads to the death of the animal. The likelihood of abortion and loss of reproductive function also increases.
Causes and symptoms
Damage to the skin, mucous membranes of the body, contaminated feed, and bathing horses in contaminated water are the main routes for bacteria to enter the body. During the incubation period, there are no clinical signs.
In the following days, the following stages of the disease can be distinguished:
- Leptospiremia – characterized by the active proliferation of bacteria that accumulate in the adrenal glands, liver, and spleen. Symptoms: body temperature rises sharply, thirst appears, signs of anorexia, hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- toxic period - characterized by damage to blood cells and parenchymal organs caused by endotoxins (due to damage to bacteria by antibodies).External and internal bleeding in horses is accompanied by vomiting blood and prolonged bloody diarrhea.
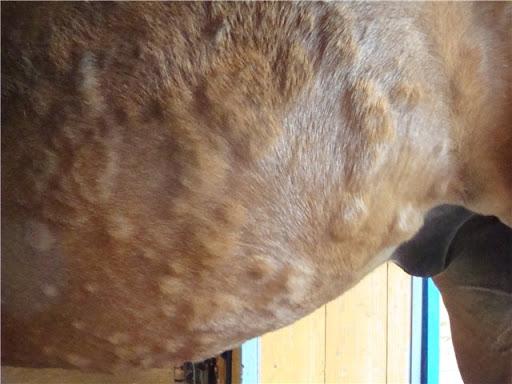
Leptospirosis is also manifested by severe dehydration of the horse's body, stomatitis (ulcerative and necrotic), and acute renal failure are observed. Sometimes the disease is subacute (the clinical manifestations appear more slowly and the symptoms are less pronounced). The main dangers of the subacute form are mortality of 30-50% and transition to a chronic disease.
Diagnosis and treatment of leptospirosis
Upon visual examination of a sick individual, the following symptoms are observed: icteric color of the mucous membranes, mild colic, rapid pulse and heartbeat. The urine becomes dark yellow or brown, and a complete blood count shows a low red blood cell count and decreased hemoglobin levels.
Streptomycin and hyperimmune serum are mainly used to treat leptospirosis in horses. Specific antibodies to Leptospira are the basis of the serum.
Important! When using serum, it is necessary to take into account that recovered animals may remain carriers of the infection.
Vaccine use
Horse breeders and farmers should pay great attention to preventive measures. The main emphasis is on vaccinating healthy animals.
Composition, release form and principle of action
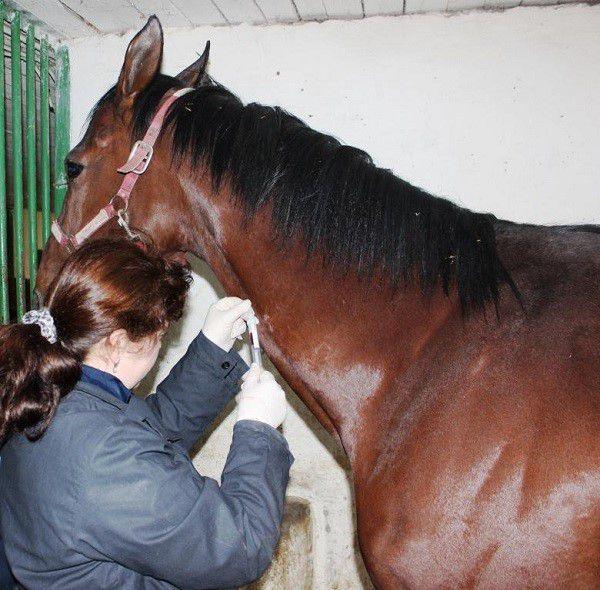
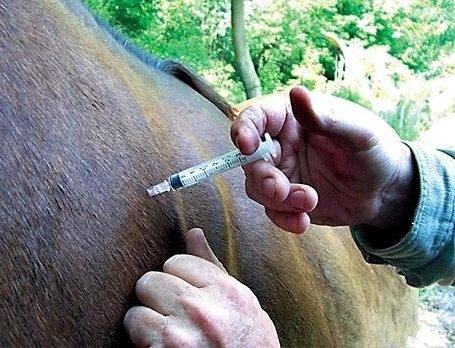
The vaccine is produced in the form of a clear, colorless liquid (contains an inactivated strain of Leptospira). A single dose is 1-2 ml, contained in a hermetically sealed bottle. When administered intramuscularly, horses develop stable immunity to leptospirosis.
Indications for use
It is recommended to vaccinate animals that are raised in unsafe farms (relative to the likelihood of an outbreak of the disease), when grazing horses in areas of possible infection.The main purpose of vaccination is preventative. Using a vaccine, it is possible to prevent the occurrence and spread of infection and reduce the likelihood of abortion.
Instructions for use
When administered intramuscularly, the vaccine is injected into the neck (upper third area). When using the product, take into account the age of the animal. The first vaccination for foals up to 6 weeks of age is given in a volume of 1 ml, the next one is given six months later in the same volume. Older foals (age 6-12 months) are injected with 1 ml of serum, a second injection is given after 6 months. For adult horses, the dose is increased to 2 ml, the subsequent vaccination is given a year later.
When starting the vaccination process, you need to take into account that immunity to leptospirosis in animals appears 2-3 weeks after administration of the drug. Resistance to infection remains in foals for 6-8 months, and in adults for 12-15 months.
Important! The drug should not be mixed with other medications in one syringe.
Contraindications and side effects
When using a vaccine, it must be taken into account that the drug is harmless and does not have medicinal qualities. Sick or weakened horses should absolutely not be vaccinated. Animals that have taken anti-helminth medications are also not vaccinated for a week. Mares are not vaccinated in the last four weeks of pregnancy and the first 7 days after birth.
Sometimes swelling may appear at the injection site, which will resolve naturally over time. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions. To quickly stop the development of allergies, it is recommended to always have calcium chloride or diphenhydramine on hand during the period of animal vaccination.
Precautionary measures
To store the drug, provide appropriate conditions: temperature - 2-15 ° C, container protected from sunlight. When vaccinating animals, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment (gloves, gown). Certain requirements are also met:
- hands are thoroughly washed with soap after completing the drug administration procedure;
- if the vaccine gets on a person’s skin or mucous membranes, the liquid is wiped off with a swab moistened with alcohol, and parts of the body are washed with water;
- used syringes and vials are disposed of.
Do not use medications that have been frozen or if the expiration date is not marked on the bottles. Vaccines that have expired or are stored in containers with poor sealing or integrity must be disposed of.
The drug that remains unused within 25-30 minutes after opening is also destroyed (the vaccine is boiled for 15-20 minutes and disposed of). Disease prevention is given great attention when keeping any animals. It is important not only to provide the correct conditions for keeping and feeding horses and foals. It is necessary to vaccinate all healthy individuals in a timely manner.