Horse breeders need to know how much a horse actually weighs to compare with standard values. Weight deviations can mean either deficiencies in care, or a disproportion of physical effort to the nutrition received, or health problems. Each age and breed of horse has its own weight gradation. To determine the body weight of animals, grooms use special techniques.
- What does a horse's weight depend on?
- Main categories
- Poor nutritional status
- Sports
- Working
- Factory
- Exhibition
- Weight fluctuations depending on horse breed
- Brabançons
- Shires
- Heavy trucks
- Budyonnovsky
- Trotters
- Pony
- How to calculate the mass of an animal
- Taking measurements
- Formulas used for calculations
- Calculating a horse's weight through its height
- Dursta
- Matorina
- Platonov and Dzeverina
- World records
- The largest horse
- The smallest horse
What does a horse's weight depend on?
The weight of a horse is determined based on the breed standard and the degree of fatness. The height and weight of animals are closely related and affect the body type. The development of bones and muscle tissue is judged by fatness.
Draft horses are the tallest and heaviest horses in the world. The traction force directly depends on the height and weight of the animals. Riding and light draft breeds have a more graceful skeletal structure. Their muscle corset should be developed harmoniously. Excess weight load will require additional effort when moving the animal. Lack of weight will affect the endurance of horses.
Horse nutrition is the most important aspect of keeping and care. The volume and calorie content are determined based on the economic purpose of the animals. On average, the total weight of daily feeds including all supplements should be between 1.8% and 2% of the horse's weight.
The weight of animals is observed over time to monitor how the physical development of horses occurs throughout their lives.
Main categories
In horse breeding, a weight classification has been adopted that is directly related to the characteristics of the breeds.
There are 3 groups in total:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
The first includes horses weighing up to 400, the second - from 401 to 600, the third - over 601 kilograms. The gradation applies to sexually mature mares and stallions. Monitoring the weight over time allows you to adjust the load and type of activity of the horse. In adult individuals, it should not change when riding and draft breeds reach 5 years of age, and in heavy draft animals - 7 years of age.
The fatness of any breed is judged using the Henneke scale:
- Exhausted.
- Very thin.
- Skinny.
- Moderately thin.
- Moderate.
- Moderately well-fed.
- Well-fed.
- Fat.
- Very thick.
The condition is determined visually and by palpation.
Poor nutritional status
According to the description of categories 1-2-3 of the Henneke scale, this is an “emaciated”, “very thin”, “thin” horse. In the first two categories, there is no adipose tissue at all, the bones are covered with skin and a small muscle layer. In a “thin” person, the fat layer appears on the neck, withers and shoulders.
If for some reason a horse has lost 50% of its weight, then it will no longer be able to regain it and must be culled. With a loss of 30% of weight, the animal can be rehabilitated, but this will require significant time and effort from the horse breeder. For young horses, there are age weight guidelines that breeders adhere to so that young horses develop correctly.
Sports
For performance horses, the ideal body condition ratings are “moderately lean” and “well-fed.” “Moderately thin” means that the spine and outline of the ribs are visible. The withers, shoulders and neck do not appear thin.
“Moderate” fatness is when the spine and ribs are not visible, but the ribs are felt when stroking. The withers, shoulders, and neck are rounded or smooth.
Working
The working group includes animals with a well-developed muscle corset, with fatty layers on the withers, neck, and between the ribs. According to the Henneke grading scale, body condition is rated as “moderate”.
Factory
To reproduce the breed, animals with an ideal exterior and high sexual activity are selected. The best reproductive performance is achieved by stallions with body condition indicators of “moderate” and “moderately well-fed”. Horses of this category can be transferred to the working group, as they maintain excellent physical condition.
Exhibition
To demonstrate the breed, the best representatives with beautiful and proportional bones are selected. Horses are fattened so that the muscle relief has a smoother shape due to subcutaneous fat, and the wool has a bright shade.
The evaluation category is “well-fed”. Exhibition animals are not suitable for competitions due to insufficient muscle mass.
Weight fluctuations depending on horse breed
The breed of a horse determines its purpose. Heavyweights will lose in speed to lighter horses, but will have an advantage in endurance and carrying capacity.
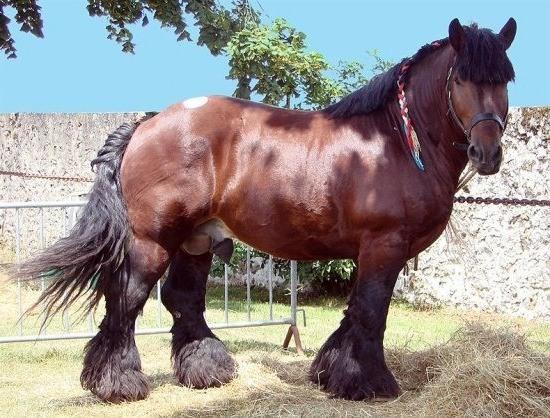
Brabançons
Belgian heavy truck. The breed was finally formed at the end of the 19th century. The average height at the withers is 170 centimeters, the average weight is 900 kilograms. Massive, muscular horses are capable of moving loads that are 3-4 times their own weight.
Shires
The breed was bred in England at the end of the 18th century for military purposes. Subsequently, muscular and very strong horses began to be used as the main labor force in agriculture and industry. The height at the withers is, on average, 170 centimeters (from 165 to 176). Weight can reach 1200 kilograms.
Heavy trucks
Brabançons and Shires were among the ancestors of other heavyweight breeds:
- Scottish;
- Irish;
- Vladimir;
- Bolognese;
- Australian.
French Percherons have an admixture of Arabian horse blood. The origins of the English Suffolk are unknown. All heavy draft horses are strong, massive, strong horses with a minimum weight of 700 kilograms.
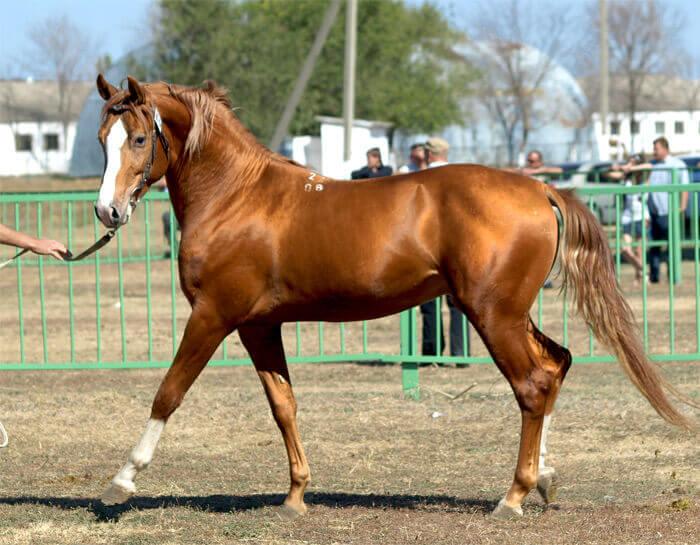
Budyonnovsky
A universal sports breed of horse.
Characteristic features of the Budennovsky horse:
- average height at withers – up to 165 centimeters;
- powerful croup;
- Long neck;
- well developed, muscular legs.
The weight of an adult horse is from 400 to 600 kilograms.
Trotters
Light-duty breeds are designed for long runs. Trotters are large horses. At the withers they can reach 170 centimeters, length – 160 centimeters, chest circumference – 180 centimeters. The horse's weight is from 500 to 550 kilograms.
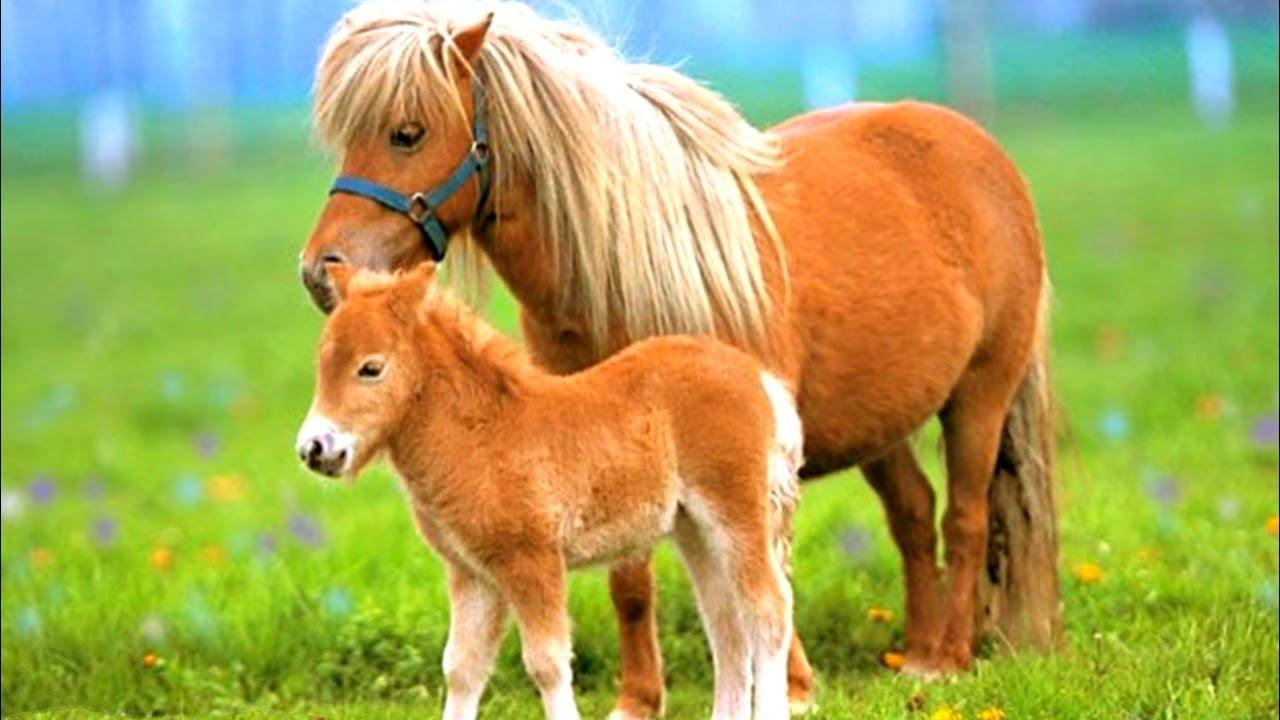
Pony
Pony is a special type of horse, which includes 2 subspecies. The first one was formed under natural conditions with a lack of food supply and harsh climatic conditions. These animals are 1.5-2 times lower and lighter than ordinary horses. In terms of physique, such ponies resemble a smaller copy of heavy trucks. Horses are used in tourism and entertainment. The tallest are Scottish ponies. At the withers they reach 107 centimeters and weigh 200 kilograms.
The second subspecies is dwarf horses, bred by humans for decorative purposes. The smallest breed is the Falabella. A reduced copy of the horse does not exceed 75 centimeters (minimum 40 centimeters) and weighs from 20 to 60 kilograms. Smart and easy to train animals are used as companions, in particular, guides for the blind.
How to calculate the mass of an animal
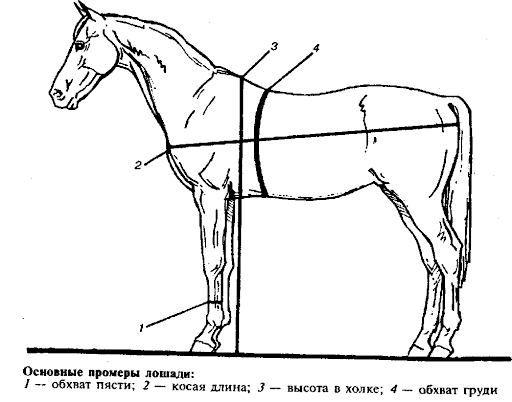
To determine the live body weight of a horse, body measurements in centimeters and calculation formulas are used, since the use of scales requires significant material costs.
Taking measurements
Parameters required for calculations:
- height at withers;
- chest girth;
- horse length.
To obtain accurate results, the horse is placed on a firm and level platform. Before starting measurements, the animal must be calmed by affectionately stroking the rump. Measuring bars and tapes are used as measuring tools.
When determining the height at the withers, the lower end of the stick is placed opposite the left front hoof at the outer heel. The transverse bar is lowered to the highest point of the withers. When measuring chest circumference, the tape is pulled tightly along the path of the girth, touching the corners of the shoulder blade. The oblique length of the body is measured by two people using a measuring stick: from the glenohumeral joint to the ischium. For self-control, measurements are taken twice.
Formulas used for calculations
The advantage of calculated indicators is their accessibility and simplicity. The disadvantage is the approximate result: they are less accurate than weighing a horse on scales.
Calculating a horse's weight through its height
The height at the withers is multiplied by the coefficient:
- 2.58 – for working horses in the “fat” category;
- 2.33 – for working horses with a “moderate”/“moderately well-fed” rating;
- 2.1 – for “thin” working horses;
- 3.39 – for “fat” heavy trucks;
- 3.1 – for “thin” heavy trucks.
The difficulty of the calculation lies in the correct choice of coefficient.
Dursta
The calculation uses chest circumference and coefficients, the product of which gives the approximate weight of the horse. Coefficients: 3.5 – for a heavy breed; 3.1 – average; 2.7 – light.
Matorina
Formula for calculating a horse's weight: increase the chest volume by 6 times and subtract the numerical value of 620.
Platonov and Dzeverina
The mass of a horse is determined as the product of height and chest girth.
World records
By weight and height of all breeds horses stand out for draft horses and ponies.
The largest horse
The maximum weight and height were recorded at the end of the 19th century for Shire Samson: 1574 kilograms and 219 centimeters, respectively. The modern record holder is inferior to him by more than 100 kilograms.
The smallest horse
Argentine falabellas do not exceed 36 centimeters in height and weigh up to 9 kilograms.