Onions are grown everywhere. But if onions rot in the garden, not every gardener knows what to do. Finding out the reasons why onions are rotting and what measures are necessary to preserve the harvest will help you cope with the problem.
The main causes of rotting in garden beds and how to deal with them
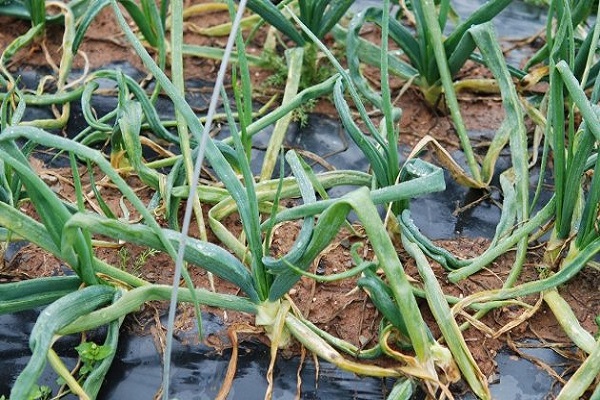
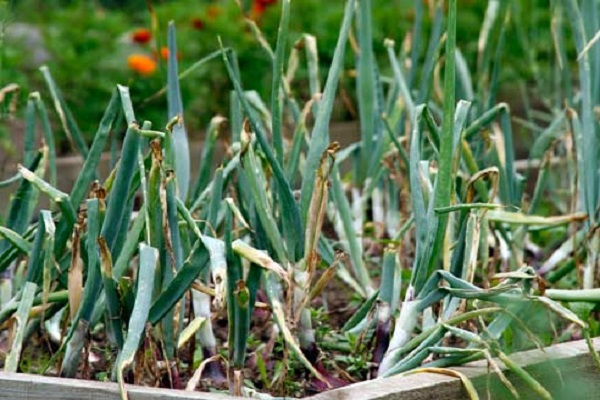
If the feathers of a vegetable turn yellow, you urgently need to make sure that the onion has not begun to rot. If it has softened, become watery and smells unpleasant, then there is a problem - the root crop is rotting. A number of actions need to be taken to save the crop.
Rotting onions causes a number of reasons, the identification of which will help solve the problem.
Excess moisture
The plant rots primarily due to improper watering. Excess moisture negatively affects crop growth. Even if there is a summer drought, you should only water the beds until mid-July.
30-45 days before the expected start of harvesting, it is necessary to sharply reduce, or better yet stop, irrigation.
Onions also rot in rainy summers if the owners have not taken care of drainage to remove excess water from the beds.
Failure to comply with crop rotation
Compliance with the rules of crop rotation is no less important than proper watering. Of great importance is the selection of crops that will be consistently grown in the same place every year.
Onions grow well after potatoes, cabbage or cucumbers. Zucchini or beets are acceptable, but not the best option. The frequency of planting in one place is every 3-5 years.
The vegetable loves the sun's rays, so the beds must be placed taking this circumstance into account. It is necessary to thoroughly loosen the soil and regularly destroy weeds at the root. Without careful weeding there is no harvest.
Excess nitrogen in the soil
One of the reasons why onions rot may be excess nitrogen in the soil. This can lead to slower growth and reduce the crop's resistance to various fungal diseases. Abundant washing of the soil and treatment with an ash solution will help restore balance.
It is worth considering that excess nitrogen can be caused by an overdose of fertilizers. Therefore, failure to comply with the norms and timing of fertilizing will lead to disastrous consequences for the crop.
Proper planting, in compliance with the necessary requirements (for example, pre-heating and disinfection), and cultivation in accordance with the rules of agricultural technology will be the key to a good harvest.
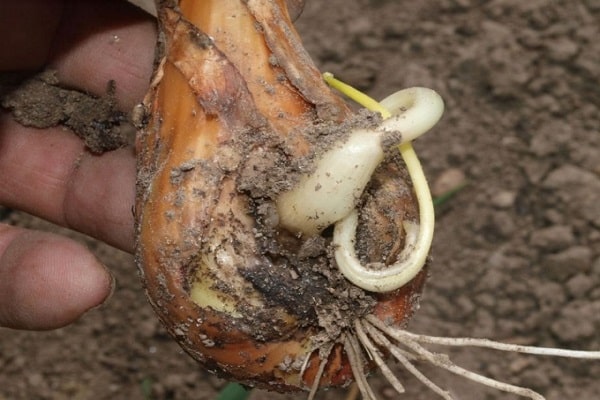
Infected planting material
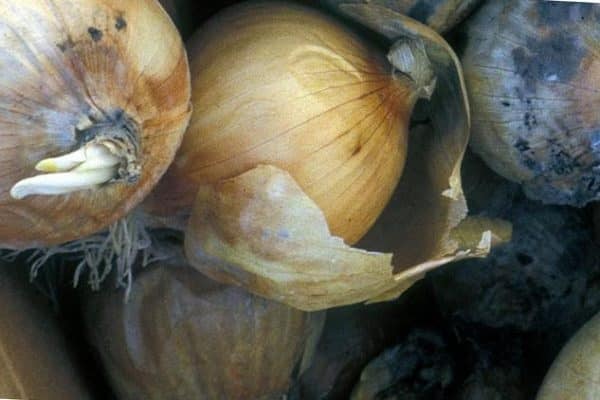
If seedlings and saplings intended for planting are infected, this will become a big problem. Seed material infected with rot, when planted in the soil, can cause the destruction of the entire crop.
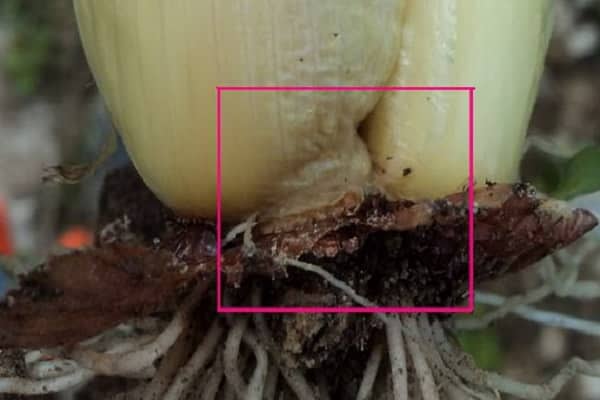
The disease damages the plant completely - from root to leaves. Damage to the onion head leads to the need to completely dispose of root vegetables, since eating them is dangerous to health.
Problems can be avoided with the help of preventive measures. It is recommended to preheat the seed material to +45 °C and disinfect it before planting.
It takes about 12 hours to warm up the planting material intended for sowing. For disinfection, a solution of potassium permanganate is suitable, in which the bulbs need to be soaked overnight.
Planting material should be purchased from sellers with a proven and reliable reputation.
Onion diseases
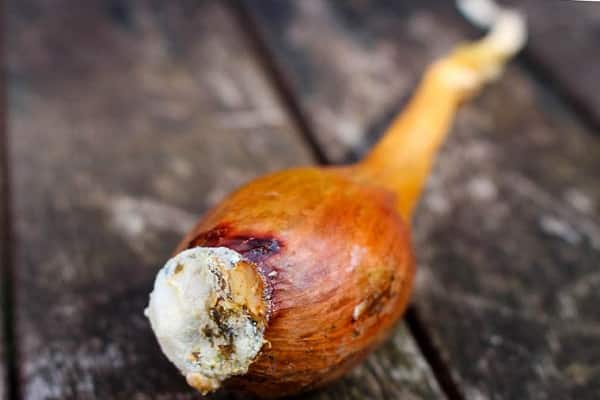
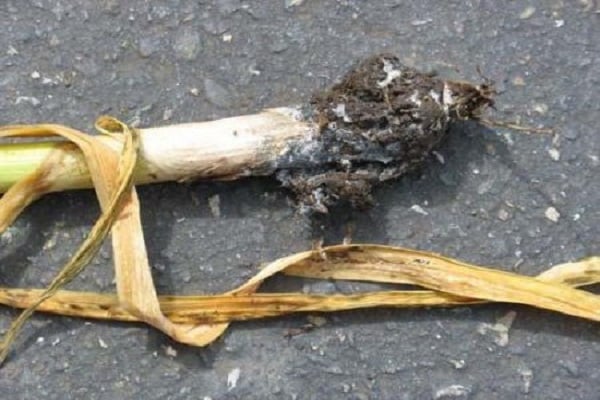
The appearance of diseases is associated with fungal or bacterial infection, as well as damp weather. High humidity can also cause onion disease. Fusarium rot is a disease that is fungal in nature.
It all starts with feathers. Then the roots become damaged and begin to rot. In the end, the bulb is affected. Cervical rot spreads in wet, stormy weather. Rains before harvesting root crops from the garden also cause rotting.
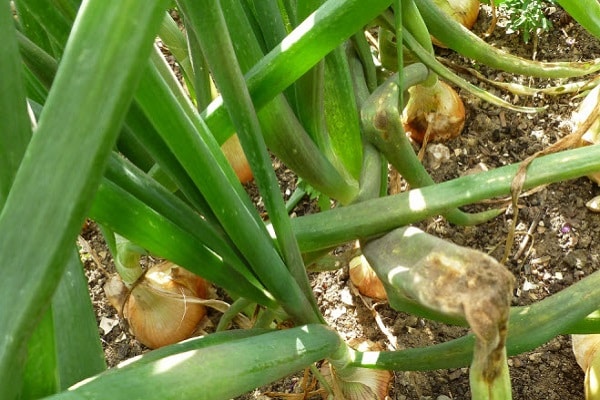
Diseases associated with bacteria often appear during the rainy season. Vegetable contamination cannot always be detected during cultivation.If during storage the bulbs turn black and begin to rot, it means that diseased root crops were collected together with healthy ones. This could destroy all supplies.
Let's consider gardeners' recommendations on how to deal with this in order to prevent infection of the entire crop and the rapid spread of diseases:
- Even before planting, you need to carefully select onions. At the slightest suspicion of damage, immediately throw away such a specimen.
- To destroy the bacteria present in the soil, you should pour ordinary boiling water over the beds a couple of days before planting. According to reviews, this is a good way to disinfect soil.
- Onions should only be grown in places well lit by the sun.
- In case of Fusarium infection, the soil must be treated with fungicides or copper sulfate solution.
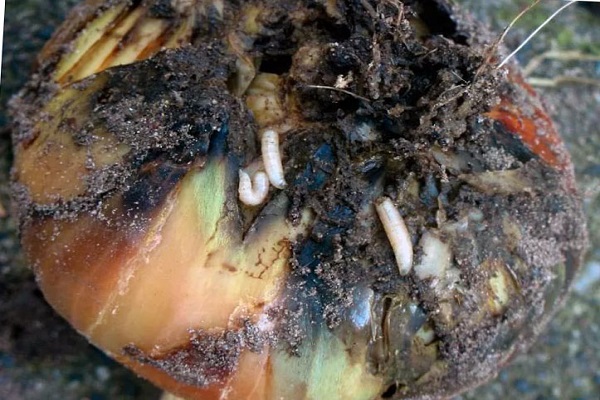
Onion pests
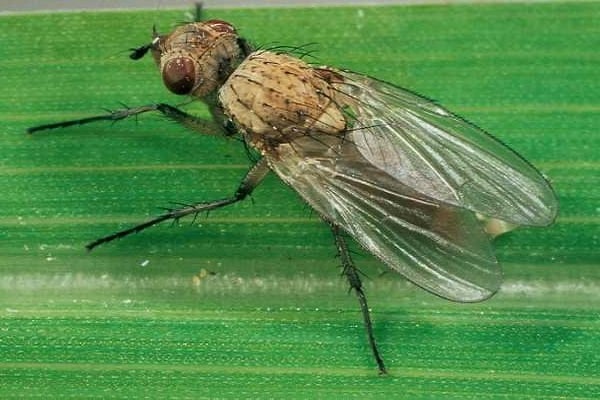
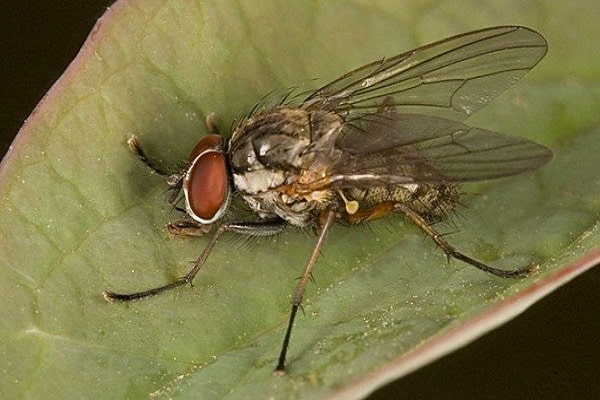
The onion fly is one of the most formidable pests. Starting from the second half of spring, it can cause significant damage to the future harvest. The fly leaves behind larvae that eat both the feather and the root crop. Small white worms destroy the pulp, and this leads to rotting of the entire onion.
The larvae can overwinter in the ground, hence the recommendation not to plant onions in one place every year. This may be the reason why onions rot. The earth, like humans, needs rest and variety, so the next planting should be done no earlier than in 3-5 years.
All means, including preventative ones, are suitable for combating onion flies. You cannot do without pre-planting seed treatment with various protective compounds and insecticides.
Gardeners advise growing onions together with carrots, which the onion fly is afraid of. You can place beds of celery or parsley nearby.
Treatment with tobacco ash or dust also effectively repels the pest.
Preventive measures in garden beds
In order to prevent onions from rotting, it is important to carry out preventive measures at all stages of crop cultivation, and infected onions must be detected and destroyed in time.
Having found out the cause of rotting, they begin to fight the disease. Violation of the rules of crop rotation and care significantly increases the risk of infection and, as a result, can lead to loss of onion yield.
Causes of rotting during storage at home
Harvesting is only half the battle. Keeping it safe and sound for a long time is the task of any gardener.
The causes of rotting during storage may be hidden in improper harvesting. The bulbs are removed carefully so as not to damage them. Wipe off any stuck soil from each root crop.
The slightest suspicion of damage or disease serves as grounds for destroying the bulb. Placing it together with healthy specimens can ruin the entire harvest.
After harvesting, it is advisable to dry the onions or even warm them. You need to sort through root vegetables regularly. If the vegetable is properly processed for storage, there will be no rot. In favorable conditions, onions will last as long as possible.